Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Mechanism of Heat Transfer
Загружено:
Shiela Dianne Caliwanagan0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
50 просмотров25 страницone of the topic in general physics 2
Оригинальное название
Mechanism of heat Transfer
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документone of the topic in general physics 2
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
50 просмотров25 страницMechanism of Heat Transfer
Загружено:
Shiela Dianne Caliwanaganone of the topic in general physics 2
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 25
HYSICS 1
Prepared by:
Shiela Dianne C. Caliwanagan
Solve multi-concept, rich
context problems using
concepts from rotational
motion, fluids, oscillations,
gravity, and thermodynamics.
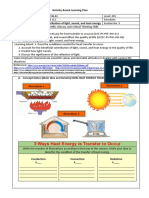
1. Describe the mechanism of Thermal
Conduction
Solve numerical problems
2. involving composite
conductors
Explain the process of convection as a
3. sequence of a change of density; and
use this concept to explain ocean
currents and winds
Introduction/ Review Overview of the objectives and key terms for the
quarter
Motivation Defining mechanism of heat transfer
Instruction/ Delivery Key points, Illustration of heat transfer
Practice Problem solving
Enrichment Discuss the Stefan- Boltzmann law
Evaluation Explains how the types of heat transfer works
Resources
• http://teachtogether.chedk12.com/teaching_guides/view/143?fbclid=IwAR32uS
bIEFwbOpso4zTEd94f_FXspzkmzpLstKEiGIGg6DXrzHxIqYfXJnc#section4
• https://www.google.com/search?q=analyzing+the+hr+diagram&source=lnms
&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjk2vWH2unlAhWbMt4KHXg9DY8Q_AUIEigB&
biw=1366&bih=657
• https://www.google.com/search?source=hp&ei=yc7PXcvlH_SdmgeP1L_IDg&q
=mechanism+of+heat+transfer&oq=mechanism+of+h&gs_l=psy-
ab.3.0.0l10.804.6540..7843...2.0..0.232.1648.11j4j1......0....1..gws-
wiz.......0i131j0i10.A2pBuicKLeY
1.The following activity can be performed in
groups.
2.a. Pour cold water into a large beaker.
Prepare a flask of hot water (about 50°C) and
color it with food dye. Close it with a stopper
with two holes.
b. Lower and immerse the flask into the beaker
of cold water (see figure below). If the hot
water does not flow, you may need to prod one
of the holes with a stirrer to start it.
3. Review previous discussions:
a. Temperature and thermal expansion
b. Heat capacities
4. Review conventions and definitions:
a. Heat moves from object of higher
temperature to one of lower
temperature
b. Heat is not stored energy; the form
that energy takes as it is transferred
from one object to another object
How will I know if the water is
hot or not without touching
the water itself and without
using a thermometer?
• The answer to the question
is related to the fact that the
skin is a “thermal sensor”:
Get a balloon filled with air
then try to tap it on the
candle with light. What do
you think will happen to the
balloon? What do you think
will happen to the candle?
• Heat is a transfer of energy from one
object to another due to a difference in
temperature
• Temperature is a measure of the
molecular energy in an object
• Heat always flows from an object of
higher temp (TH) to one of lower temp
(TL)
• We are often interested in the rate at
which this heat transfer takes place
• Molecules are in constant motion, their
speed is proportionate to the temperature
of the object
• When two objects come in contact, their
surface molecules will transfer momentum
• An aluminum pot will conduct heat from a
glass stove-top
• For two objects at TH and the other at TL,
connected by a rod of uniform material
P = kA(TH – TL)/L
Where k is the thermal conductivity of the
rod, A is the cross-sectional area, and L is
the length of the rod
• Home owners are concerned with the “R-
value” of their insulation
R = L/k
• A fluid’s density will change when its
temperature changes (through conduction)
• This density change can create movement
within the fluid
• Warmer fluid is usually less dense, and will
rise
• Cooler fluid will rush in to take the place of
the rising, warmer fluid
• This mixing is called convection
• Mixing of the atmosphere within the
troposphere is mostly convection
– Sea breeze: land warms faster, air over
land rises, air from over the sea comes in
• Mechanism for energy transfer between
atmospheric layers is not well understood
– If all of the atmosphere were mixing in a
convective fashion, there wouldn’t be
layers.
• Objects tends to absorb electromagnetic
waves from their surroundings
• An ideal absorber is called a blackbody, an
ideal reflector is called a white body
• Objects tend to radiate electromagnetic
waves as efficiently as they absorb them
• The transfer of energy through the
emission of EM waves is called radiation
• The rate of energy radiation is related to
an object’s surface area A and the nature
of the surface, called emissivity, e
• The Stefan-Boltzmann Law for heat
transfer is P = AeσT4
– Don’t forget that heat transfer = energy
per unit time = power
• σ is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant, which
is equal to 5.67 x 10-8 W/(m2K4)
(a)Calculate the rate of heat conduction through
house walls that are 13.0 cm thick and have an
average thermal conductivity twice that of glass
wool. Assume there are no windows or doors.
The walls’ surface area is 120m2120m2 and their
inside surface is at 18.0°C18.0°C, while their
outside surface is at 5.00°C5.00°C. (b) How
many 1-kW room heaters would be needed to
balance the heat transfer due to conduction?
(a)An infrared heater for a sauna has a surface area
of 0.050m20.050m2 and an emissivity of 0.84.
What temperature must it run at if the required
power is 360 W? Neglect the temperature of the
environment.
Discuss how the Stefan–Boltzmann
radiation law is used to determine the size
of stars
iv. Some mathematical examples
are presented in the references.
v. The Stefan–Boltzmann radiation law can
be rewritten as: , which is “luminosity”
and used to determine the size of stars as
well as classify them through the
Hertzsprung–Russell diagram.
The Stefan-Baltzmann law is the For stars of the given
key to understanding the H-R temperature, the larger the
diagram: radius, the larger the luminosity
Therefore, As the On the other hand,
one moves up the for a given
H-R diagram, a luminosity, the
star’s radius must larger the radius,
become bigger the smaller the
temperature
The net effect of this is that the
Therefore, as one moves right on smallest stars most be in the
the H-R diagram, a star’s radius lower left corner of the diagram
must increase. and the largest stars in the upper
right
Is the
picture
below
accurate?
Explain
your
answer.
http://teachtogether.chedk12.com/teaching_guides/view/143?fbcli
d=IwAR32uSbIEFwbOpso4zTEd94f_FXspzkmzpLstKEiGIGg6DXrzHxIq
YfXJnc#section4
https://www.google.com/search?q=analyzing+the+hr+diagram&sou
rce=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjk2vWH2unlAhWbMt4KH
Xg9DY8Q_AUIEigB&biw=1366&bih=657
https://www.google.com/search?source=hp&ei=yc7PXcvlH_SdmgeP1L_IDg&q
=mechanism+of+heat+transfer&oq=mechanism+of+h&gs_l=psy-
ab.3.0.0l10.804.6540..7843...2.0..0.232.1648.11j4j1......0....1..gws-
wiz.......0i131j0i10.A2pBuicKLeY
Вам также может понравиться
- HMT Unit 1Документ17 страницHMT Unit 1Thulasi RamОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1 Methods of Heat TransferДокумент6 страницLesson 1 Methods of Heat TransferKoshu TakatsujiОценок пока нет
- Heat and Mass Transfer Course OutlineДокумент61 страницаHeat and Mass Transfer Course OutlineMohammad Raza100% (3)
- 7.3.1 - Thermal PhysicsДокумент27 страниц7.3.1 - Thermal Physicsmaha mohОценок пока нет
- Heat Equation CourseworkДокумент6 страницHeat Equation Courseworkafjwftijfbwmen100% (2)
- Physics For Engineers Tah Module PDFДокумент15 страницPhysics For Engineers Tah Module PDFFRANCES VISAYAОценок пока нет
- ThermalДокумент48 страницThermalChris RosarioОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Heat Transfer PDFДокумент15 страницIntroduction To Heat Transfer PDFMohamed RadwanОценок пока нет
- University of Duhok College of Engineering Mechanical DepartmentДокумент28 страницUniversity of Duhok College of Engineering Mechanical DepartmentDanty HkmatОценок пока нет
- Students Unit 2 PHYSICS Energy and HeatДокумент74 страницыStudents Unit 2 PHYSICS Energy and HeatAnnalisa ChenОценок пока нет
- Modes of Heat Transfer: Conduction, Convection and RadiationДокумент63 страницыModes of Heat Transfer: Conduction, Convection and RadiationKelly ObrienОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Heat Transfer: Fourier Equation For Flow of HeatДокумент4 страницыChapter 1: Introduction To Heat Transfer: Fourier Equation For Flow of HeatJoyce VicenteОценок пока нет
- Very Short Answer QuestionsДокумент3 страницыVery Short Answer QuestionsgopichandallakaОценок пока нет
- The Atmosphere - Mechanisms of Heat TransferДокумент29 страницThe Atmosphere - Mechanisms of Heat Transferkaushik baruahОценок пока нет
- HT1-3 - (Heat Transfer Mechanism) Final VersionДокумент16 страницHT1-3 - (Heat Transfer Mechanism) Final VersionAlrence BajumОценок пока нет
- Convection&RadiationДокумент40 страницConvection&RadiationdesdainedmanОценок пока нет
- Exploring Thermo PhysicsДокумент31 страницаExploring Thermo PhysicsclstewartОценок пока нет
- Warming The Earth and The AtmosphereДокумент46 страницWarming The Earth and The AtmosphereSalih TrexieОценок пока нет
- Unsteady State Heat Transfer ExplainedДокумент4 страницыUnsteady State Heat Transfer ExplainedJocelle AlcantaraОценок пока нет
- Cep2 Assingment 1 Abubakr Ameer Khan SSSP19 CE 30Документ4 страницыCep2 Assingment 1 Abubakr Ameer Khan SSSP19 CE 30Abu Bakar Ameer KhanОценок пока нет
- Heat Transfer 2022octДокумент67 страницHeat Transfer 2022octGülgün YenigünОценок пока нет
- Heat TransferДокумент87 страницHeat TransferGülgün YenigünОценок пока нет
- Theory 1&3chapterДокумент8 страницTheory 1&3chapterWild BotОценок пока нет
- BTU and Ton HVAC Sizing GuideДокумент17 страницBTU and Ton HVAC Sizing GuideDanish YaseenОценок пока нет
- Heattemp 200218001059Документ36 страницHeattemp 200218001059Yanyan YamsonОценок пока нет
- Chapter TwoДокумент38 страницChapter TwoBK MKОценок пока нет
- Mechanism of Heat TransferДокумент31 страницаMechanism of Heat Transferedna padreОценок пока нет
- One-D Heat Conduction through Long CylinderДокумент27 страницOne-D Heat Conduction through Long Cylindersurya kiranОценок пока нет
- ThermodynamicsДокумент78 страницThermodynamicsHarold Jan R. TeranoОценок пока нет
- AUtomotive Heat ExchangerДокумент28 страницAUtomotive Heat ExchangersantoshkumarvenuОценок пока нет
- HT ConductionДокумент16 страницHT ConductionVenkatesh VenkatОценок пока нет
- AND Modes of Heat TransferДокумент41 страницаAND Modes of Heat TransferKushОценок пока нет
- PHYS4652 Planetary Science: Lecture 3: Solar Heating and Energy Transport LEE Man HoiДокумент50 страницPHYS4652 Planetary Science: Lecture 3: Solar Heating and Energy Transport LEE Man HoiYang Woo SeongОценок пока нет
- E105 - AgustinДокумент25 страницE105 - AgustinSeth Jarl G. AgustinОценок пока нет
- Module 1-C1 Heat TransferДокумент10 страницModule 1-C1 Heat TransferKlucifer XinОценок пока нет
- Heat Transfer Fundamentals ExplainedДокумент23 страницыHeat Transfer Fundamentals Explainedjhon gebreОценок пока нет
- Introduction and Basic Concepts: Chapter OneДокумент16 страницIntroduction and Basic Concepts: Chapter Oneabdi dejeneОценок пока нет
- Basics of Heat Transfer: Chapter OneДокумент28 страницBasics of Heat Transfer: Chapter OneAbodi AlaniОценок пока нет
- Beneficial uses of light, sound and heatДокумент9 страницBeneficial uses of light, sound and heatThrisha BagalanonОценок пока нет
- Warming The Earth and The AtmosphereДокумент46 страницWarming The Earth and The AtmosphereKylene AlimОценок пока нет
- Class 1 Basic Modes of Heat TransferДокумент15 страницClass 1 Basic Modes of Heat TransferShadmanSakiefHridoyОценок пока нет
- Unit 5 - Physics From Creation To Collapse: Thermal EnergyДокумент12 страницUnit 5 - Physics From Creation To Collapse: Thermal EnergyShivani MajithiaОценок пока нет
- I Unit MaterialДокумент38 страницI Unit Materialmanneli talpagiriОценок пока нет
- Heat Transfer NoteДокумент27 страницHeat Transfer Notedipzbarma5Оценок пока нет
- Interface Mass TraДокумент26 страницInterface Mass TraWahid AliОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1Документ17 страницAssignment 1SIVARAJ KUMARОценок пока нет
- Heat and Energy: - Summer Term 2004 - Weeks 1-6Документ48 страницHeat and Energy: - Summer Term 2004 - Weeks 1-6Abubakkar SiddiqОценок пока нет
- Mechanisms of Heat TransferДокумент30 страницMechanisms of Heat Transfervinod kumar maddineniОценок пока нет
- LO10 Session 08 ThermodynamicsДокумент44 страницыLO10 Session 08 ThermodynamicsAbo Alphotoh GamingОценок пока нет
- Heat Transfer Fundamentals and ApplicationsДокумент30 страницHeat Transfer Fundamentals and ApplicationsNarayana Swamy G100% (1)
- Heat Transfer MITДокумент460 страницHeat Transfer MITruano25Оценок пока нет
- Radiation Heat Transfer ThesisДокумент4 страницыRadiation Heat Transfer Thesismonicabogdaneverett100% (2)
- Heat Transfer - Radiation, Convection and ConductionДокумент9 страницHeat Transfer - Radiation, Convection and Conductionsubham dashОценок пока нет
- 3 Heat Flow in WeldingДокумент19 страниц3 Heat Flow in Weldingrpadhra8803Оценок пока нет
- Heat and Thermodynamics PDFДокумент325 страницHeat and Thermodynamics PDFNaMatazuОценок пока нет
- Progress in High Temperature Physics and Chemistry: Volume 1От EverandProgress in High Temperature Physics and Chemistry: Volume 1Оценок пока нет
- Theory and Calculation of Heat Transfer in FurnacesОт EverandTheory and Calculation of Heat Transfer in FurnacesРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (4)
- Photovoltaic Systems Technology SS 2003Документ155 страницPhotovoltaic Systems Technology SS 2003nawwar100% (2)
- Homework1 Answer Key PDFДокумент5 страницHomework1 Answer Key PDFLuther James Langston IIОценок пока нет
- GMA220 SUT3 30mar2021 EMR PrinciplesДокумент41 страницаGMA220 SUT3 30mar2021 EMR PrinciplesFanelo FelicityОценок пока нет
- Temperature Measurement Devices LMSДокумент13 страницTemperature Measurement Devices LMSshokishazadaОценок пока нет
- Black-Body Radiation - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент7 страницBlack-Body Radiation - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadonodoni0008Оценок пока нет
- Foc (Power Point)Документ53 страницыFoc (Power Point)Sana AminОценок пока нет
- I V Savelyev Physics General Course Vol 3Документ319 страницI V Savelyev Physics General Course Vol 3thuongtunhienОценок пока нет
- J. R. Simonson (Auth.) - Engineering Heat Transfer-Palgrave Macmillan UK (1988)Документ280 страницJ. R. Simonson (Auth.) - Engineering Heat Transfer-Palgrave Macmillan UK (1988)Glasst Innovacion 2019100% (2)
- High School Experiments in IR AstronomyДокумент124 страницыHigh School Experiments in IR AstronomyKishan KikkeriОценок пока нет
- Basic Concepts PDFДокумент21 страницаBasic Concepts PDFsafin kaosarОценок пока нет
- Department of Chemical Engineering School of Engineering and Architecture Saint Louis University Laboratory Report Evaluation SheetДокумент18 страницDepartment of Chemical Engineering School of Engineering and Architecture Saint Louis University Laboratory Report Evaluation SheetSarah SanchezОценок пока нет
- IOAAДокумент34 страницыIOAAJeyaraj SelvarajahОценок пока нет
- Radiation Heat Transfer Experiment PDFДокумент11 страницRadiation Heat Transfer Experiment PDFTuba JavedОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8 - Mechanisms of Heat TransferДокумент10 страницChapter 8 - Mechanisms of Heat TransferBảo Tín TrầnОценок пока нет
- Heat and TemperatureДокумент52 страницыHeat and TemperatureAngilyn LumabasОценок пока нет
- Ceramic Infrared Emitters Technical ManualДокумент21 страницаCeramic Infrared Emitters Technical ManualDelfi Castro HernandezОценок пока нет
- CAP High School Prize Exam: April 8th, 2014 9:00 - 12:00 Competitor's Information SheetДокумент7 страницCAP High School Prize Exam: April 8th, 2014 9:00 - 12:00 Competitor's Information Sheetelty TanОценок пока нет
- Radiation 22021Документ84 страницыRadiation 22021Manas ChuriОценок пока нет
- Experiment No.6 Stefan Boltzmann'S Apparatus: Heat Transfer Laboratory (MECH3123)Документ6 страницExperiment No.6 Stefan Boltzmann'S Apparatus: Heat Transfer Laboratory (MECH3123)Raj PratyushОценок пока нет
- Chapter.5.ENV HYDRAULICS Students HandoutДокумент53 страницыChapter.5.ENV HYDRAULICS Students HandoutTimothy KiryaОценок пока нет
- Week 09Документ111 страницWeek 09babita_gadbail21Оценок пока нет
- Solutions To Barbara Ryden Introduction To CosmologyДокумент87 страницSolutions To Barbara Ryden Introduction To CosmologyBONGA GIBSON BALENIОценок пока нет
- Lab 6 Stellar Temperatures and LuminosityДокумент9 страницLab 6 Stellar Temperatures and Luminositymei sya100% (1)
- Heat Transfer Lab: Inverse Square & Stefan-Boltzmann LawsДокумент4 страницыHeat Transfer Lab: Inverse Square & Stefan-Boltzmann LawsMustafa Can GüçlüОценок пока нет
- Heat Transfer Chapter One and Two-171102112832Документ74 страницыHeat Transfer Chapter One and Two-171102112832shouxun JiОценок пока нет
- Environmental Physics CourseДокумент63 страницыEnvironmental Physics CourseEkta PatilОценок пока нет
- Stefan-Boltzmann Law in A Light BulbДокумент6 страницStefan-Boltzmann Law in A Light BulbWWE SuperstarsОценок пока нет
- Irrigation Drainage Engineering Crop Water RequirementsДокумент53 страницыIrrigation Drainage Engineering Crop Water Requirementsnaeem ullahОценок пока нет
- Ans HW2Документ8 страницAns HW2Sai Swetha KVОценок пока нет