Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chapter 2 Reliability
Загружено:
zazu zuzu0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
18 просмотров9 страницОригинальное название
chapter 2 reliability
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
18 просмотров9 страницChapter 2 Reliability
Загружено:
zazu zuzuАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 9
Ch.
6: Reliability and Validity
in Measurement and Research
Rosnow, Beginning Behavioral Research, 5/e. Copyright 2005 by Prentice Hall
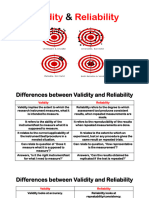
Validity and Reliability
Validity: How well does the measure or
design do what it purports to do?
Reliability: How consistent or stable is
the instrument?
Is the instrument dependable?
Rosnow, Beginning Behavioral Research, 5/e. Copyright 2005 by Prentice Hall
Random and Systematic Error
Random Error: Chance fluctuations
Tend to cancel out over repeated
measurements.
Systematic Error: Fluctuations that are
slanted in a particular direction.
Also known as “bias”
Rosnow, Beginning Behavioral Research, 5/e. Copyright 2005 by Prentice Hall
Types of Reliability
Test-Retest Reliability: Degree of temporal
stability of the instrument.
Assessed by having instrument completed by
same people during two different time periods.
Alternate-Forms Reliability: Degree of
relatedness of different forms of test.
Used to minimize inflated reliability correlations
due to familiarity with test items.
Rosnow, Beginning Behavioral Research, 5/e. Copyright 2005 by Prentice Hall
Types of Reliability (cont.)
Internal-Consistency Reliability: Overall
degree of relatedness of all test items
or raters.
Also called reliability of components.
Item-to-Item Reliability: The reliability
of any single item on average.
Judge-to-Judge Reliability: The reliability of
any single judge on average.
Rosnow, Beginning Behavioral Research, 5/e. Copyright 2005 by Prentice Hall
Reliability, Replication, and
External Validity
External Validity: The generalizability of
an inferred causal relationship.
The dependability of causal
generalizations is based on replicable
findings.
But how know if have replicated a finding?
Role of the effect size.
Rosnow, Beginning Behavioral Research, 5/e. Copyright 2005 by Prentice Hall
Validity in Test and Instrument
Construction
Content Validity: Is the relevant
material adequately sampled?
Criterion Validity: How well does the
test correlated with outcome criteria?
Concurrent Validity
Predictive Validity
Rosnow, Beginning Behavioral Research, 5/e. Copyright 2005 by Prentice Hall
Construct Validity in Test
Development
Construct Validity: What does the test
really assess?
Does the test have the “ability to
discriminate”?
Establishing construct validity
Convergent validity
Discriminant validity
Rosnow, Beginning Behavioral Research, 5/e. Copyright 2005 by Prentice Hall
Validity and Causal Inference
in Experimental Design
External Validity
Construct Validity: The validity of the
hypothetical idea linking the IV and DV.
Statistical Conclusion Validity: Are the
statistical conclusions well-grounded?
Internal Validity: Ability to rule out
plausible rival hypotheses.
Rosnow, Beginning Behavioral Research, 5/e. Copyright 2005 by Prentice Hall
Вам также может понравиться
- Ch. 6: Reliability and Validity in Measurement and ResearchДокумент10 страницCh. 6: Reliability and Validity in Measurement and ResearchDisha MathurОценок пока нет
- Ensuring Validity and Reliability in ResearchДокумент15 страницEnsuring Validity and Reliability in ResearchMelii SafiraОценок пока нет
- Validity and ReliabilityДокумент62 страницыValidity and ReliabilityAhmad MakhloufОценок пока нет
- ValidityДокумент26 страницValidityRathiОценок пока нет
- Translet No 5Документ1 страницаTranslet No 5Indah SiswantiОценок пока нет
- Reliability by Vartika VermaДокумент17 страницReliability by Vartika VermaVartika VermaОценок пока нет
- Thursday Validity, Reliability and GeneralizabilityДокумент16 страницThursday Validity, Reliability and GeneralizabilityThomas Adam Johnson100% (1)
- Introduction to Validity, Reliability and Their EstimationДокумент6 страницIntroduction to Validity, Reliability and Their EstimationWinifridaОценок пока нет
- 2 - Validitas Dalam Penelitian EksperimenДокумент44 страницы2 - Validitas Dalam Penelitian Eksperimensilmi sofyanОценок пока нет
- Intro to Psychological Testing ExplainedДокумент5 страницIntro to Psychological Testing Explainedabdu raufОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Part 1 Validity Reliability 1Документ29 страницChapter 3 Part 1 Validity Reliability 1anjeesahiri91589Оценок пока нет
- Validity and ReliabilityДокумент5 страницValidity and Reliabilityrawan.taha2000.rtmОценок пока нет
- Validty and Reliability HandoutДокумент39 страницValidty and Reliability HandoutNERISSA ROQUEОценок пока нет
- Reliability vs Validity - Key DifferencesДокумент6 страницReliability vs Validity - Key DifferencesAnjaliОценок пока нет
- SS2712 - Lect 2 - MethodДокумент37 страницSS2712 - Lect 2 - MethodNelson LamОценок пока нет
- 4 ValidityДокумент55 страниц4 ValidityVivian Gladys MendozaОценок пока нет
- Characteristics of Research ToolsДокумент3 страницыCharacteristics of Research ToolsLalrinchhani SailoОценок пока нет
- Types of validity and reliability in researchДокумент4 страницыTypes of validity and reliability in researchminnalecvaОценок пока нет
- What Is Construct Validity? What Is Construct Validity?: Questions and Answers About Language Testing StatisticsДокумент5 страницWhat Is Construct Validity? What Is Construct Validity?: Questions and Answers About Language Testing StatisticsJosé Ángel Zapata HernándezОценок пока нет
- QuestionnairesДокумент6 страницQuestionnairesfasilistheoОценок пока нет
- Research Instrument Validity and ReliabilityДокумент16 страницResearch Instrument Validity and ReliabilityRENIER ACE ABORDO100% (1)
- Internal Consistency: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент18 страницInternal Consistency: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaaichoo8100% (2)
- Validity and ReliabilityДокумент6 страницValidity and ReliabilityfarlynzОценок пока нет
- Validity and ReliabilityДокумент6 страницValidity and ReliabilityAngelica QuiñonesОценок пока нет
- Validity N Reliability PDFДокумент19 страницValidity N Reliability PDFGurpreet Singh Walia100% (1)
- 2014S Psychometric Analysis of Childhood Vocab TestsДокумент15 страниц2014S Psychometric Analysis of Childhood Vocab Testsismail39 orthoОценок пока нет
- Is The Research Investigation Providing Answers To The Research Questions For Which It Was Undertaken?Документ16 страницIs The Research Investigation Providing Answers To The Research Questions For Which It Was Undertaken?Praveen Kumar MОценок пока нет
- Reliability in Language Assessment: English Publications EnglishДокумент8 страницReliability in Language Assessment: English Publications EnglishPolina SushinaОценок пока нет
- Validity & Reliability: Md. Musfiq-Al-Mahadi B.SC - Ag (Hons.) Ms in AgextДокумент12 страницValidity & Reliability: Md. Musfiq-Al-Mahadi B.SC - Ag (Hons.) Ms in AgextRhea CaasiОценок пока нет
- Reliability Validity Measures InstrumentsДокумент20 страницReliability Validity Measures InstrumentsPiyulОценок пока нет
- Face Validity PDFДокумент2 страницыFace Validity PDFJessicaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 15 - Reliability and Validity - Evaluating The Value of Tests and MeasureДокумент4 страницыChapter 15 - Reliability and Validity - Evaluating The Value of Tests and MeasureantoinnevongenesisОценок пока нет
- Qualities of a Good TestДокумент18 страницQualities of a Good TestFazal HayatОценок пока нет
- Quantitative SherlockДокумент13 страницQuantitative SherlockCARL JUSTINE LADRAОценок пока нет
- Reliability and ValidityДокумент8 страницReliability and ValidityMaggie Rose100% (1)
- The Concept of IntelligenceДокумент6 страницThe Concept of Intelligencecampus.headОценок пока нет
- Reliability Vs ValidityДокумент27 страницReliability Vs ValidityRedgie G. GabaneОценок пока нет
- Reliability and Validity of Research Instruments: Correspondence ToДокумент19 страницReliability and Validity of Research Instruments: Correspondence TonurwadiaОценок пока нет
- Research Method Validity and ReliabilityДокумент5 страницResearch Method Validity and ReliabilityMuhammad Adnan KhurshidОценок пока нет
- Reliability and Validity - A Research Paper in Professional CounselingДокумент5 страницReliability and Validity - A Research Paper in Professional CounselingMaggie RoseОценок пока нет
- 8602 Assignment No 2Документ24 страницы8602 Assignment No 2Fatima YousafОценок пока нет
- Ensuring Validity and Reliability in Qualitative Research InstrumentsДокумент2 страницыEnsuring Validity and Reliability in Qualitative Research InstrumentsMKWD NRWMОценок пока нет
- Validity and Reliability: Inter-Rater Test-Retest Parallel-Forms Internal ConsistencyДокумент1 страницаValidity and Reliability: Inter-Rater Test-Retest Parallel-Forms Internal ConsistencyCharyОценок пока нет
- TM 3 - Env Health Survey Instrument3 - 5Документ31 страницаTM 3 - Env Health Survey Instrument3 - 5Delfina BengaОценок пока нет
- Establishing Validity-and-Reliability-TestДокумент28 страницEstablishing Validity-and-Reliability-TestRay Lorenz OrtegaОценок пока нет
- Relationship Between VALIDITY and Reliability Types of ValidityДокумент4 страницыRelationship Between VALIDITY and Reliability Types of ValidityAngelica Rose EspornaОценок пока нет
- Dwnload Full Research Methods For The Behavioral Sciences 6th Edition Gravetter Solutions Manual PDFДокумент36 страницDwnload Full Research Methods For The Behavioral Sciences 6th Edition Gravetter Solutions Manual PDFarmorerdoleritercunxa100% (9)
- Instrument Reliability and Validity: Key Concepts ExplainedДокумент22 страницыInstrument Reliability and Validity: Key Concepts Explainedreza.ws1Оценок пока нет
- Validity and Reliability of Research Methods and Evaluating SourcesДокумент32 страницыValidity and Reliability of Research Methods and Evaluating Sourcesrory johnsonОценок пока нет
- Reliability & Validity: Dr. Nitu Singh SisodiaДокумент20 страницReliability & Validity: Dr. Nitu Singh Sisodiasajalasati98Оценок пока нет
- What Is Construct Validity? What Is Construct Validity?: Questions and Answers About Language Testing StatisticsДокумент5 страницWhat Is Construct Validity? What Is Construct Validity?: Questions and Answers About Language Testing StatisticsAlaОценок пока нет
- Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) For Testing Validity and Reliability Instrument in The Study of Education.Документ7 страницConfirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) For Testing Validity and Reliability Instrument in The Study of Education.Kwadwo Owusu MainooОценок пока нет
- Reliability Vs Validity in ResearchДокумент12 страницReliability Vs Validity in ResearchnurwadiaОценок пока нет
- Confirmatory Factor Analysis Cfafor Testing Validity and Reliability InstrumentinДокумент7 страницConfirmatory Factor Analysis Cfafor Testing Validity and Reliability InstrumentinKwadwo Owusu MainooОценок пока нет
- Diagnosis of Causation IДокумент31 страницаDiagnosis of Causation Ismart rusdanartoОценок пока нет
- Validity and ReliabilityДокумент6 страницValidity and ReliabilityMustapha Nasir MalumfashiОценок пока нет
- 5 1 1 Reliability and ValidityДокумент2 страницы5 1 1 Reliability and ValiditySonia MiminОценок пока нет
- Reliability and Validity in Business ResearchДокумент5 страницReliability and Validity in Business ResearchMohamed GHAFFARОценок пока нет
- Applications of Hypothesis Testing for Environmental ScienceОт EverandApplications of Hypothesis Testing for Environmental ScienceОценок пока нет
- What I Have Learned: Activity 3 My Own Guide in Choosing A CareerДокумент3 страницыWhat I Have Learned: Activity 3 My Own Guide in Choosing A CareerJonrheym RemegiaОценок пока нет
- QBD EMEA PPTДокумент21 страницаQBD EMEA PPTElizabethValverde100% (1)
- Talisic - TQ-EN9-3rd QuarterДокумент4 страницыTalisic - TQ-EN9-3rd Quarterarmenta.shane14gmail.comОценок пока нет
- Feasibility Study For A Residential Construction Project: A Case StudyДокумент7 страницFeasibility Study For A Residential Construction Project: A Case Studyaashritha lОценок пока нет
- Standards of Proficiency Biomedical ScientistsДокумент20 страницStandards of Proficiency Biomedical ScientistsIlfan KazaroОценок пока нет
- Sources of Resilience in Adolescent Victims of BullyingДокумент14 страницSources of Resilience in Adolescent Victims of BullyingRah WidyaОценок пока нет
- Leadership and Job Satisfaction Among Azorean Hospital Nurses: An Application of The Situational Leadership ModelДокумент12 страницLeadership and Job Satisfaction Among Azorean Hospital Nurses: An Application of The Situational Leadership ModelReem AlsuwailemОценок пока нет
- Quiz 1 K53Документ4 страницыQuiz 1 K53HàMềmОценок пока нет
- Chem 162 Formal Lab ReportДокумент5 страницChem 162 Formal Lab ReportLiem LimantoОценок пока нет
- Importance of Statistics in Different FieldsДокумент3 страницыImportance of Statistics in Different FieldsTuppiyac NievaОценок пока нет
- M.Com 3rd Semester Assignments 2023Документ6 страницM.Com 3rd Semester Assignments 2023Akash Peter MishraОценок пока нет
- Review of Related Literature and StudiesДокумент2 страницыReview of Related Literature and StudiesLeo Anton Atejada100% (1)
- STA108 - Group Projects (Guidelines)Документ6 страницSTA108 - Group Projects (Guidelines)ayunna ayunniОценок пока нет
- Design Realization Manual Cycle1Документ12 страницDesign Realization Manual Cycle1Jeeva KeshavОценок пока нет
- Forrester - A Simple Prioritization ModelДокумент4 страницыForrester - A Simple Prioritization ModelSalvador Vazquez OlimonОценок пока нет
- Face ID Literature ReviewДокумент11 страницFace ID Literature ReviewRauan KumarbekovОценок пока нет
- Final Synopsis On Food Adultreation and ControlДокумент5 страницFinal Synopsis On Food Adultreation and ControlMohammad Bilal0% (1)
- Compressors and Turbines Reference GuideДокумент12 страницCompressors and Turbines Reference GuidesenthilОценок пока нет
- Template FMEA5Документ5 страницTemplate FMEA5Puneet SharmaОценок пока нет
- POMA - IM - Chapter 5Документ28 страницPOMA - IM - Chapter 5Pham Phu Cuong B2108182Оценок пока нет
- BriefДокумент22 страницыBriefHuế NguyễnОценок пока нет
- Module Handbook For Negotiated Learning (Work Based Learning) Academic Year 2021/22Документ9 страницModule Handbook For Negotiated Learning (Work Based Learning) Academic Year 2021/22Calum SyersОценок пока нет
- Đánh giá có hệ thống về hành vi công dân của khách hàng Làm rõ lĩnh vực và chương trình nghiên cứu trong tương laiДокумент15 страницĐánh giá có hệ thống về hành vi công dân của khách hàng Làm rõ lĩnh vực và chương trình nghiên cứu trong tương laiMinh HuyềnОценок пока нет
- Good Thesis Statement About TechnologyДокумент6 страницGood Thesis Statement About Technologybsr6hbaf100% (2)
- Kaizen and Six SigmaДокумент26 страницKaizen and Six Sigmaprofessor_cwardОценок пока нет
- Population Profile and Consumer Spending Pattern of The Market AreaДокумент1 страницаPopulation Profile and Consumer Spending Pattern of The Market AreaMarrieylle SiblosОценок пока нет
- Statistics Week 1Документ3 страницыStatistics Week 1Jean MalacasОценок пока нет
- Journal of English For Academic Purposes: Christopher Hill, Susan Khoo, Yi-Chin HsiehДокумент13 страницJournal of English For Academic Purposes: Christopher Hill, Susan Khoo, Yi-Chin Hsiehshuyu LoОценок пока нет
- Call For Papers Fuoye Journal of Management, Innovation and EnterpreneurshipДокумент1 страницаCall For Papers Fuoye Journal of Management, Innovation and Enterpreneurshipojo solomonОценок пока нет
- Behaviour Change Toolkit MailДокумент60 страницBehaviour Change Toolkit MailGail HoadОценок пока нет