Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
What Is NOUN
Загружено:
Han You0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
227 просмотров24 страницыОригинальное название
What is NOUN
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
227 просмотров24 страницыWhat Is NOUN
Загружено:
Han YouАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 24
What is NOUN
A noun is a part of speech that denotes a person, animal, place,
thing, or idea. The English word noun has its roots in the Latin word
nomen, which means “name.” Every language has words that are
nouns.
Person – A term for a person, whether proper name, gender, title,
or class, is a noun.
Animal – A term for an animal, whether proper name, species,
gender, or class is a noun.
Place – A term for a place, whether proper name, physical location,
or general locale is a noun.
Thing – A term for a thing, whether it exists now, will exist, or
existed in the past is a noun.
Idea – A term for an idea, be it a real, workable idea or a fantasy
that might never come to fruition is a noun.
Person – He is the person to see.
Person – John started to run.
Person – Plato was an influential Greek philosopher.
Person – Sharon admires her grandfather.
Person – My mother looks a lot like
my grandmother, and I look very much like them.
Animal – The dog barked at the cat.
Animal – Elephants never forget.
Animal – Sophie is my favorite horse.
Place – The restaurant is open.
Place – Let’s go to the beach.
Place – Look over there.
Place – Come here.
Place – Harvard and Yale are two famous universities.
Place – Look! There’s the Eiffel Tower.
Thing – Throw the ball.
Thing – Please close the door and lock it.
Thing – Use words properly to be understood.
Thing – The lamp sits on a table next to the sofa.
Thing – Money doesn’t grow on trees.
Idea – Follow the rules.
Idea – The theory of relativity is an important concept.
Idea – Love is a wonderful emotion.
Types of noun
There are several different types of noun, as follows:
Common noun
A common noun is a noun that refers to people or things in
general, e.g. boy, country, bridge, city, birth, day, happiness.
Proper noun
A proper noun is a name that identifies a particular person,
place, or thing, e.g. Steven, Africa, London, Monday. In written
English, proper nouns begin with capital letters.
Concrete noun
A concrete noun is a noun which refers to people and to things
that exist physically and can be seen, touched, smelled, heard, or
tasted. Examples include dog, building, coffee, tree, rain, beach,
tune.
Abstract noun
An abstract noun is a noun which refers to ideas,
qualities, and conditions - things that cannot be seen or
touched and things which have no physical reality,
e.g. truth, danger, happiness, time, friendship, humour.
Collective nouns
Collective nouns refer to groups of people or things,
e.g. audience, family, government, team, jury. In
American English, most collective nouns are treated as
singular, with a singular verb:
The whole family was at the table.
In British English, the preceding sentence would be
correct, but it would also be correct to treat the collective
noun as a plural, with a plural verb:
The whole family were at the table.
A noun may belong to more than one category. For
example, happiness is both a common noun and an
abstract noun, while Mount Everest is both a concrete
noun and a proper noun.
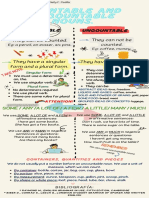
Count and mass nouns
Nouns can be
either countable or uncountable. Countable
nouns (or count nouns) are those that refer to
something that can be counted. Uncountable
nouns (or mass nouns) do not typically refer to things
that can be counted and so they do not regularly have a
plural form.
1. Proper Nouns.
Proper Nouns are used to refer to specific person, place or
thing.
A proper noun always starts with a capital letter. These nouns
also refer to the names of the days of week and months, and
also various names of organization, institution, religious, etc.
Which are proper and specific.
Ali
Pakistan
Hazara Town
2. Common Nouns
Proper nouns refer to general, unspecific person, place or thing.
Boys
Girls
Students
3. Compound Nouns
A compound noun is a noun which contains two or more
words which join together to make a single noun is called
compound noun.
A compound noun can be written together, Such as “
Football” can be hyphenated such as “ six-pack, Mother-in-
law”or separate words such as “ Post office”.
Classroom
Paper-clip
Police station
4. Collective Nouns
A Collective noun is a noun which refers to a group of people
or group of something in a specific manner or unit.
Family
Audience
People
5. Concrete Nouns
A concrete noun is a noun which can be touched, smelled, seen, felt
or tasted.
Concrete nouns can be countable or uncountable, common noun,
proper noun or collective nouns can be concrete noun.
Plate
Chair
Water
6. Abstract Noun
Abstract nouns are the names of things that you can perceive or
recognize with your five senses.
Freedom
Love
Happiness
7. Material Nouns
Material nouns refer to material or substance out of which things are
made.
8. Countable nouns
Countable nouns are the nouns which can be counted.
These nouns can be used in both the singular and plural
forms, When used as plural forms they can be counted.
Friends
Chairs
She had a pet dog. –Dog is also a countable noun as its
plural is dogs.
9.Uncountable Nouns
Uncountable nouns are the nouns which cannot be
counted and have only singular form.
These nouns are exact opposite of countable nouns.
Water
Rice
Sugar
VERB
What is Verb
• A verb is a "doing" word. A verb can express:
• A physical action (e.g., to swim, to write, to
climb).
• A mental action (e.g., to think, to guess, to
consider).
• A state of being (e.g., to be, to exist, to
appear).
Verbs Can Express Physical Actions
Here are some sentences with verbs that express
physical actions. (In each example, the verb is
highlighted.)
1. She sells pegs and lucky heather.
(In this example, the word sells is a verb. It expresses
the physical activity to sell.)
2. The doctor wrote the prescription.
(In this example, the word wrote is a verb. It expresses
the physical activity to write.)
3. Alison bought a ticket.
(The word bought is a verb. It expresses the physical
activity to buy.)
Verbs Can Express Mental Actions
While many verbs express physical actions (e.g., to
jump, to dance, to sing), verbs can also express
mental actions. For example:
She considers the job done.
(The word considers is a verb. It expresses the mental
activity to consider.)
Peter guessed the right number.
(The word guessed is a verb. It expresses the mental
activity to guess.
I thought the same thing.
(The word thought is a verb. It expresses the mental
activity to think.)
Verbs Can Express a State of Being
A small but extremely important group of verbs do not
express any activity at all. The most important verb in
this group (arguably of all) is the verb to be.
Here is the verb to be in the different tenses:
Here are some real examples with the verb to
be:Edwina is the largest elephant in this area.
(The word is is a verb from the verb to be.)It was a joke.
(The word was is a verb from the verb to be.)I am.
(The word am is a verb from the verb to be.)
(Point of interest: I am is the shortest sentence in
English.)
The Types of Verbs
As we've covered, a verb can be categorized as a physical verb (e.g.,
to run), a mental verb (e.g., to think), or a state-of-being verb (e.g.,
to be). However, a verb will often be further categorized as one of
the following:
Action Verb
An action verb expresses an activity that a person or thing can do.
For example:Lee eats cake.
(Eating is something Lee can do.)
The bear chased the salmon in the shallow rapids.
(Chasing is something the bear can do.)
Compare those verbs with these
:Lee likes cake.
(To like is not an activity. It's a state.)
The bear is hungry.
(To be is not an activity. It's a state.)
Stative Verb
A stative verb expresses a state rather than an action. A
stative verb typically relates to a state of being, a thought, or
an emotion. For example:
I am at home.
She believes in fairies.
He feels elated.
Transitive Verb
A transitive verb is one that acts on something (i.e., it
has a direct object). For example:
I saw the dog.
(Here, the direct object is the dog.)
Lee ate the pie.
(Here, the direct object is the pie.)
The postman will give Sarah the letter.
(Here, the direct object is the letter.)
Note: The direct object of a transitive verb can be found
by finding the verb and asking "what?" For example,
"saw what?" (answer: the dog); "ate what?" (answer:
the pie); "will give what?" (answer: the letter).
Intransitive Verb
An intransitive verb is one that does not act on something (i.e.,
there is no direct object). For example:
The rain fell.
My throat hurts.
The cat sneezed.
Auxiliary Verb
An auxiliary verb (or helping verb) accompanies a main verb to help
express tense, voice or mood. The most common auxiliary verbs
are be, do, and have (in their various forms). Here are some
examples of auxiliary verbs:Lee has eaten all the pies.
(Here, the auxiliary verb has helps to express tense.)
The table has been prepared.
(Here, the auxiliary verbs has been help to express voice (in this
case, the passive voice).)
If he were to arrive in the next 10 minutes, we would be on
schedule.
Phrasal Verb
A phrasal verb is a verb made up of more than one word
(usually two words). A phrasal verb has a main verb and
another word (either a preposition or a particle). The
phrasal verb usually has a meaning different to the main
verb. For example:
• A burglar will often break a window to break in.
(Here, the phrasal verb break in means to enter illegally,
which is different to break.
• If you drop the baton the team will drop back to last
place.
(Here, the phrasal verb drop back means to fall behind,
which is different to drop.)
Preposition
Prepositions may be defined as any word or
group of words that relates a noun or a
pronoun to another word in the sentence.
about above according to across
after against along amid
among around at before
behind below beside besides
between beyond by concerning
down during except for
from in into like
of off on over
past since through toward
underneath until up upon
with within without
Вам также может понравиться
- Objectives and Definition of Physical Education and DanceДокумент7 страницObjectives and Definition of Physical Education and DanceJERUZABEL ENTREVENCION DURANGOОценок пока нет
- IFP - Module 6 Session 2Документ2 страницыIFP - Module 6 Session 2Eloisa Marie C. InocentesОценок пока нет
- GIP Success Story and Absorbed BeneficiariesДокумент2 страницыGIP Success Story and Absorbed BeneficiariesRoka Unichu Camacho100% (1)
- Math 1F - Understanding Patterns in NatureДокумент2 страницыMath 1F - Understanding Patterns in NatureJaycel mae SoriaОценок пока нет
- La Liga Filipina and KatipunanДокумент22 страницыLa Liga Filipina and KatipunanStefennie Ann Benabente GelitoОценок пока нет
- The Political Self Explores How Contexts Affect Well-BeingДокумент36 страницThe Political Self Explores How Contexts Affect Well-BeingStephanie LeeОценок пока нет
- Ti Bajssít Ajkáyo NaljjajjegénjДокумент8 страницTi Bajssít Ajkáyo NaljjajjegénjDennis ValdezОценок пока нет
- Article 1159 Key NotesДокумент1 страницаArticle 1159 Key NotesEliza Jayne Princess VizcondeОценок пока нет
- Week 4 Ang Unang Paglalayag Paikot NG Mundo Ni Ferdinand MagellanДокумент30 страницWeek 4 Ang Unang Paglalayag Paikot NG Mundo Ni Ferdinand MagellanNicoleОценок пока нет
- Contributions of Ancient Chinese CivilizationДокумент4 страницыContributions of Ancient Chinese Civilizationberna28Оценок пока нет
- Physical Activity for Health and RhythmДокумент12 страницPhysical Activity for Health and RhythmJandayan DaveОценок пока нет
- Largest Island of the Philippines: An Overview of LuzonДокумент18 страницLargest Island of the Philippines: An Overview of LuzonCharlene Fadrigon-OtazuОценок пока нет
- M2 Learning ActivityДокумент2 страницыM2 Learning ActivityArish Manalastas100% (1)
- Children of the CityДокумент152 страницыChildren of the CityAngel100% (1)
- Module 3 - Exercise 1.1Документ1 страницаModule 3 - Exercise 1.1jbsbarretto100% (1)
- What Is The Law of Supply and DemandДокумент3 страницыWhat Is The Law of Supply and DemandJanna Marie DelimaОценок пока нет
- United Nation Inter-Agency Taskforce On Sport For Development and PeaceДокумент5 страницUnited Nation Inter-Agency Taskforce On Sport For Development and PeaceFrancis MontalesОценок пока нет
- NSTP-CWTS Civic Welfare Training ServiceДокумент21 страницаNSTP-CWTS Civic Welfare Training ServiceJohn Carlo PerezОценок пока нет
- Of Fish, Flies, Dogs, and WomenДокумент2 страницыOf Fish, Flies, Dogs, and WomenDane PeñalberОценок пока нет
- Assignment #2: Rizal Technological University Bachelor of Science in Accountancy SY 2020-2021Документ2 страницыAssignment #2: Rizal Technological University Bachelor of Science in Accountancy SY 2020-2021merryОценок пока нет
- Rights and Duties ExplainedДокумент40 страницRights and Duties ExplainedPCPT SHARON MALLILLINОценок пока нет
- Sample REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATUREДокумент2 страницыSample REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATUREexquisiteОценок пока нет
- NSTP Midterm Handouts 2018Документ3 страницыNSTP Midterm Handouts 2018Omega SpectrumОценок пока нет
- Project NOAHДокумент15 страницProject NOAHJerric CristobalОценок пока нет
- Frameworks and Principle of DispositionДокумент41 страницаFrameworks and Principle of DispositionCookie MonsterОценок пока нет
- Duty Versus InclinationДокумент2 страницыDuty Versus InclinationSarah Sanchez100% (1)
- Jose RodriguezДокумент3 страницыJose RodriguezJudel S. MaticОценок пока нет
- Historical Antecedents in The Course of Science and TechnologyДокумент4 страницыHistorical Antecedents in The Course of Science and TechnologyJyasmine Aura V. AgustinОценок пока нет
- How Is Art Related To Humanities?Документ5 страницHow Is Art Related To Humanities?Winter SummerОценок пока нет
- RIZAL ReflectionДокумент2 страницыRIZAL ReflectionEvan BoaloyОценок пока нет
- Colonial Mentality Lack of Patriotism PhilippinesДокумент2 страницыColonial Mentality Lack of Patriotism PhilippinesNina Famoso33% (3)
- PI 100 Position PaperДокумент2 страницыPI 100 Position PaperAngel Rose TrocioОценок пока нет
- Week 2 Sts Activity 3 Concept Map ReazoДокумент1 страницаWeek 2 Sts Activity 3 Concept Map ReazoNonylon AlmacenОценок пока нет
- CHristian Living ReviewerДокумент7 страницCHristian Living ReviewerLyrMa NCОценок пока нет
- NSTP ReactionДокумент3 страницыNSTP Reactiongerald_ichigo40267% (3)
- God's laws of love and happinessДокумент4 страницыGod's laws of love and happinessJohn Carl AparicioОценок пока нет
- My Encounters with ArtДокумент6 страницMy Encounters with ArtLiecca StylesОценок пока нет
- 01 Anthropological - Lesson 01 - Historical DevelopmentДокумент8 страниц01 Anthropological - Lesson 01 - Historical DevelopmentRecto UllaniОценок пока нет
- Engage: DATE:03-30-21 Name:Ma - Lorena Akol Program&Section:Ba English 1EДокумент16 страницEngage: DATE:03-30-21 Name:Ma - Lorena Akol Program&Section:Ba English 1EMa. Lorena Akol100% (1)
- Lesson 3 Material SelfДокумент2 страницыLesson 3 Material SelfQueen MendozaОценок пока нет
- Rizal's Nationalism and its Relevance TodayДокумент2 страницыRizal's Nationalism and its Relevance TodayNevan NovaОценок пока нет
- ALIGUYONДокумент11 страницALIGUYONAnonymous AWa5p6Оценок пока нет
- Effectiveness of Public Spending: The Case of Rice Subsidies in The PhilippinesДокумент2 страницыEffectiveness of Public Spending: The Case of Rice Subsidies in The PhilippinesMarion San JoseОценок пока нет
- Understanding LiteratureДокумент2 страницыUnderstanding LiteratureLaiza MayОценок пока нет
- What Is The Difference Between Business English and Literary EnglishДокумент5 страницWhat Is The Difference Between Business English and Literary Englishdhyan09100% (1)
- Week1 2Документ4 страницыWeek1 2Liane Mae BonillaОценок пока нет
- The Prohibited Acts On The National Flag FinallДокумент4 страницыThe Prohibited Acts On The National Flag Finallpurple soyaОценок пока нет
- Review of Related Literature Native PigДокумент27 страницReview of Related Literature Native Pigsegsyyapril0729Оценок пока нет
- Fibonacci DolphinДокумент2 страницыFibonacci DolphinAnne Corine RamosОценок пока нет
- MIT Researchers Discover New Energy Source Called ThemopowerДокумент2 страницыMIT Researchers Discover New Energy Source Called ThemopowerAdriene Mikaela Orzal0% (1)
- Francisco FrondaДокумент2 страницыFrancisco FrondaAva BarramedaОценок пока нет
- Mst112 Final Reviewer Part 1Документ5 страницMst112 Final Reviewer Part 1John MichaelОценок пока нет
- Export Packing, Marking & LabelingДокумент7 страницExport Packing, Marking & LabelingKath De GuzmanОценок пока нет
- Who Is Hernando Ruiz OcampoДокумент1 страницаWho Is Hernando Ruiz OcampoNio GulapoОценок пока нет
- Filipino Socio-Cultural Factors Affecting Fast FoodДокумент1 страницаFilipino Socio-Cultural Factors Affecting Fast FoodKenneth Christian WilburОценок пока нет
- Marcos' SONA 2022 Reaction PaperДокумент1 страницаMarcos' SONA 2022 Reaction PaperArnelyn Decasa GamutanОценок пока нет
- Reflective AnalysisДокумент9 страницReflective AnalysisDaenielle ZabalaОценок пока нет
- The Magicians Twin Book ReviewДокумент6 страницThe Magicians Twin Book ReviewCee JhunОценок пока нет
- Everything You Need to Know About NounsДокумент5 страницEverything You Need to Know About NounsIbnu ShinaОценок пока нет
- Lec 1 Parts of SpeechДокумент90 страницLec 1 Parts of SpeechUsmanChaudhryОценок пока нет
- Marketing Management (BBA) P 2Документ107 страницMarketing Management (BBA) P 2220479Оценок пока нет
- The Importance of Communication in BusinessДокумент4 страницыThe Importance of Communication in BusinessHan YouОценок пока нет
- Direct and Indirect NarrationДокумент9 страницDirect and Indirect NarrationHan YouОценок пока нет
- Business Economics BBA 1Документ32 страницыBusiness Economics BBA 1Han YouОценок пока нет
- ADVERBДокумент20 страницADVERBHan YouОценок пока нет
- ABS1 S1L9 022812 Hindipod101Документ8 страницABS1 S1L9 022812 Hindipod101NiviNarayananОценок пока нет
- Materi Bimtek Bahasa InggrisДокумент5 страницMateri Bimtek Bahasa InggrisMonikaОценок пока нет
- Subject-Verb Agreement, Using Expressions of Quantity, by Dr. ShadiaДокумент9 страницSubject-Verb Agreement, Using Expressions of Quantity, by Dr. ShadiaDr. Shadia100% (1)
- Acp English Class 2Документ60 страницAcp English Class 2Chinmayee MishraОценок пока нет
- Countable and UncountableДокумент1 страницаCountable and UncountableMaria paula GuiñazuОценок пока нет
- شرح منهج top score فى اللغة الانجليزية (المستوى الرفيع) للصف الثانى الاعدادى اللغات الترم الاول PDFДокумент52 страницыشرح منهج top score فى اللغة الانجليزية (المستوى الرفيع) للصف الثانى الاعدادى اللغات الترم الاول PDFchristina amroОценок пока нет
- My English BookДокумент75 страницMy English Booksyahrir100% (1)
- SC PPT - The Best Resource For GMAT SC From Ivy-GMAT (Sandeep Gupta)Документ244 страницыSC PPT - The Best Resource For GMAT SC From Ivy-GMAT (Sandeep Gupta)umellamp33% (3)
- MD Romanian Language LessonsДокумент18 страницMD Romanian Language Lessonsnotebooktargus100% (2)
- Identifying Sentence ErrorsDownload NowДокумент20 страницIdentifying Sentence ErrorsDownload NowIsh TaylorОценок пока нет
- Sir Shujat Online Classes PDF Complete CourseДокумент33 страницыSir Shujat Online Classes PDF Complete CourseTanveer HussainОценок пока нет
- Learning UnitsДокумент169 страницLearning Unitshebakol275Оценок пока нет
- Top 20 Countries, Words and Body PartsДокумент52 страницыTop 20 Countries, Words and Body PartsRobertCrnkovićОценок пока нет
- AdjectiveДокумент4 страницыAdjectiveAlice Del Rosario CabanaОценок пока нет
- What If There Is A Vowel Before The in That Case, Add - : Y? S To Form The PluralДокумент10 страницWhat If There Is A Vowel Before The in That Case, Add - : Y? S To Form The Pluralkanishka saxenaОценок пока нет
- Spanish by Choice SpanishPod LessonsДокумент235 страницSpanish by Choice SpanishPod LessonsDeepthi MallikarachchiОценок пока нет
- CasesДокумент19 страницCasesromance.man333Оценок пока нет
- 6th Grade Spelling Power WorkbookДокумент88 страниц6th Grade Spelling Power Workbookdeathpum64% (33)
- Rules On Subject & Verb AgreementДокумент18 страницRules On Subject & Verb AgreementPhuong Dao100% (1)
- Amharic Units 1 To 8Документ67 страницAmharic Units 1 To 8Anonymous Wmfwbfh7p86% (7)
- Celebrating KindnessДокумент50 страницCelebrating KindnessClarissa Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- Grammar Error IdentificationДокумент29 страницGrammar Error IdentificationJoanne JoanneОценок пока нет
- Verse (50:1) - Word by Word: Quranic Arabic CorpusДокумент50 страницVerse (50:1) - Word by Word: Quranic Arabic CorpusaminchatОценок пока нет
- Module 1 NounДокумент16 страницModule 1 NounChristian O. CanonoОценок пока нет
- Psycholinguistics E416Документ103 страницыPsycholinguistics E416Amr Ali GalalОценок пока нет
- Materi Bhs IngДокумент6 страницMateri Bhs IngEllyaFitrianiОценок пока нет
- Presentasi Bahasa InggrisДокумент18 страницPresentasi Bahasa InggrisIndraPrawiroAdiredjoОценок пока нет
- Turk 2Документ204 страницыTurk 2Nguyen LanОценок пока нет
- Skeleton GrammarДокумент19 страницSkeleton GrammardiemnganОценок пока нет
- Arabic ExervviseДокумент2 страницыArabic Exervviseainabalqis roslyОценок пока нет