Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Human Culture Variation
Загружено:
Fernando Labucay Fariñas Jr0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
32 просмотров28 страницHuman cultures vary in their social behaviors and differences. Key aspects of cultural variation include religion, ethnicity, nationality, gender, socioeconomic status, and exceptionality. Religions differ in their systems of beliefs and practices. Ethnicity is expressed through cultural ideas of distinct groups. Nationality legally binds people to countries. Gender is socially constructed as masculine or feminine. Socioeconomic status separates people by class. Exceptionality refers to giftedness or disabilities. Subcultures and countercultures also lead to variation within cultures.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
HUMAN CULTURE VARIATION.pptx
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документHuman cultures vary in their social behaviors and differences. Key aspects of cultural variation include religion, ethnicity, nationality, gender, socioeconomic status, and exceptionality. Religions differ in their systems of beliefs and practices. Ethnicity is expressed through cultural ideas of distinct groups. Nationality legally binds people to countries. Gender is socially constructed as masculine or feminine. Socioeconomic status separates people by class. Exceptionality refers to giftedness or disabilities. Subcultures and countercultures also lead to variation within cultures.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
32 просмотров28 страницHuman Culture Variation
Загружено:
Fernando Labucay Fariñas JrHuman cultures vary in their social behaviors and differences. Key aspects of cultural variation include religion, ethnicity, nationality, gender, socioeconomic status, and exceptionality. Religions differ in their systems of beliefs and practices. Ethnicity is expressed through cultural ideas of distinct groups. Nationality legally binds people to countries. Gender is socially constructed as masculine or feminine. Socioeconomic status separates people by class. Exceptionality refers to giftedness or disabilities. Subcultures and countercultures also lead to variation within cultures.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 28
HUMAN CULTURE
VARIATION/SOCIAL DIFFRENCES
Mr. Fernando L. Fariñas Jr
Senior High School (SHS) Teacher
Human Culture Variation: A Definition
• It refers to the difference in social behaviors
that different cultures exhibit around the
world. What may be considered good
etiquette in one culture nay be considered bad
etiquette in another.
(globalsociology.pbworks.com)
Social Difference: A Definition
• The differences among the individuals on the
basis of social characteristics and qualities.
(definition.blurtit.com)
CULTURE VARIATION
• Religion
• Ethnicity
• Nationality
RELIGION
• ‘religare’ a Latin word – ‘to bind together’
• Is a system of beliefs and practices as well as
systems of actions directed toward entities
which are above men
• Is an organized system of ideas about the
spiritual sphere or the supernatural
RELIGION
CULTURE VARIATION
• RELIGION
• ETHNICITY
• NATIONALITY
ETHNICITY
• It is the expression of the set of cultural ideas
held by a distinct of ethics or indigenous
people
NATIONALITY
• It is the legal
relationships that
binds a person and
a country.
• It allows to protect
a have jurisdiction
over a person.
SOCIAL DIFFRENCES
• Gender
• Socio-economic status
• Exceptionality
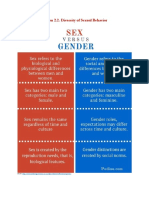
Gender
• It is socially-constructed characteristics of
being male or female.
• Serve us guide on how males and females
think and act about themselves.
• Gender vs Sex
• LGBTQi ( Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender
Queer/ Questioning, Intersex)
Gender vs Sex
• One’s sense of self as • It refers to a person
masculine or based on their
feminine regardless anatomy
of external genitalia. • Bodies
• Socially constructed
characteristics
• Personality
characteristics
• It is biological
LGBTQi
• lesbian - A women who is emotionally,
romantically, or sexually attracted to other
women
• Gay – Men attracted emotionally, romantically,
or sexually attracted to other men
• Bisexual – A person who is attracted to two
sexes pr two gender, but not necessarily
simultaneously or equally.
LGBTQi
• Transgender – Transgender (sometimes shortened to
trans or TG) people are those whose psychological
self ( “gender identity”) differs from the social
expectations for the physical sex they were born
with.
• Queer/Questioning - a person who is attracted to
multiple genders
• Intersex – Intersexuality is a set of medical conditions
that feature congenital anomaly of the reproductive
and sexual system.
SOCIAL DIFFERENCES
• Gender
• Socio-economic status
• Exceptionality
Socio-economic status
• It refers to category of person who have more
or less who have less the same socio-
economic privileges
• Upper class
• Middle class
• Lower class
Socio-economic status
SOCIAL DIFFERENCES
• Gender
• Socio-economic status
• Exceptionality
Exceptionality
• It refers to the state of being intellectually
gifted and/or having physically or mentally
challenged conditions
Exceptionality
• Personality behaviors
• Communication (learning disability, speech,
impairment, and hearing problems)
• Intellect (mind intellectual & mental
development disabilities)
• Physical appearance (blind-low vision)
• Or combination of more than one specific
exceptionality/disability.
Cultural Variation Between Cultures
• If human culture modify the natural
environment, it is also true the natural
environment initially shaped, and still shapes
to some extent, the culture of society.
•
Variation Between Cultures
• The Japanese diet consist largely fish, seafood
and vegetables because Japan is an
archipelago and the sea provided consistent
source of food and, with one twentieth of the
surface of the United State, there is no room
for grazing land for raising beef cattle.
Similarly, climate, soil, and geography affect
cultural aspects.
VARIATION WITHIN CULTURE
Subculture
• A segment of society which shares a
distinctive pattern of mores, folkways, and
values which differ from the pattern of largely
society. It is culture within a culture.
• These groups that have specific cultural traits
that set them apart from the dominant
culture.
Example of Subculture
Counter Culture
• Is group whose values and norms place it at odds
with mainstream society or a group that actively
rejects dominant cultural values norms. In most
western countries, the 1960s saw the rise of
different counter culture groups and social
movements that sought to dismantle the different
inequalities that were then part of the dominant
culture, such as racism (civil rights movement),
sexism, (modern Feminist movement) and
homophobia ( Gay rights movements).
Counter Culture
• More recently paramilitary groups, militias and survivalist
groups constitute countercultures as they reject the social
changes that came out of the 1960s and became part of
mainstream.
• A paramilitary is a semi-militarized force whose
organizational structure, tactics, trainings, subculture, and
(often) function are similar to those of a professional
military, and which is not included as part of a state’s
formal armed forces
• Militia – a military forces that engages in rebel or terrorist
activities, typically in opposition to a regular army.
Refeences
• https://www.slideshare.net/CarlPatrickTadeo1
/human-cultural-variation-social-differences
Вам также может понравиться
- Module 1 Human VariationДокумент36 страницModule 1 Human VariationGian ApolinarioОценок пока нет
- Understand Culture Lesson1Документ25 страницUnderstand Culture Lesson1Archi ArchiОценок пока нет
- Notes For UCSPДокумент2 страницыNotes For UCSPNionel TabigneОценок пока нет
- Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsДокумент26 страницUnderstanding Culture, Society and PoliticsIdieh Azodnem100% (2)
- Ethnocentrism Cultural RelativismДокумент2 страницыEthnocentrism Cultural RelativismApple ColipanoОценок пока нет
- Ucsp Quiz ReviewerДокумент4 страницыUcsp Quiz ReviewerEjay VillaverОценок пока нет
- Understanding Culture, Society and Politics LESSON TWO: Understanding The Nature of Culture, Society and PoliticsДокумент4 страницыUnderstanding Culture, Society and Politics LESSON TWO: Understanding The Nature of Culture, Society and PoliticsDream CatcherОценок пока нет
- Q1 Mod. 3looking Back at HumanДокумент7 страницQ1 Mod. 3looking Back at HumanHat DogОценок пока нет
- Hand Outs PlagiarismДокумент4 страницыHand Outs PlagiarismwyrmczarОценок пока нет
- World LiteratureДокумент3 страницыWorld LiteratureJOBELLE MALIHANОценок пока нет
- Genetic Engineering: By: Faiza Rashid Lecturer City University of Science and Information Technology, Peshawar, PakistanДокумент19 страницGenetic Engineering: By: Faiza Rashid Lecturer City University of Science and Information Technology, Peshawar, PakistanFaiza RashidОценок пока нет
- Ucspol ReviewerДокумент10 страницUcspol ReviewerMA. ANGELA NISSI QUIROZОценок пока нет
- Understanding Culture Society and PoliticsДокумент173 страницыUnderstanding Culture Society and PoliticsMaxine PearlОценок пока нет
- Philosophy of Human Person Lecture #1 - Philosophical ReflectionДокумент2 страницыPhilosophy of Human Person Lecture #1 - Philosophical ReflectionAntonio DelgadoОценок пока нет
- Reaction PaperДокумент17 страницReaction PaperLouis NavarroОценок пока нет
- Writing Reaction Paper EappДокумент23 страницыWriting Reaction Paper EappShen EugenioОценок пока нет
- Reaction Paper HandoutДокумент1 страницаReaction Paper Handoutsherilyn peyra0% (1)
- Philippine Politics and Governance SpeechДокумент2 страницыPhilippine Politics and Governance SpeechPoala Hannah MateoОценок пока нет
- L2Документ116 страницL2Rufin KrysОценок пока нет
- Hand Outs ResearchДокумент11 страницHand Outs ResearchJulieSanchezErsandoОценок пока нет
- Module 3 SAMURAI DAUGHTERSДокумент9 страницModule 3 SAMURAI DAUGHTERSMicaela Cea MortilОценок пока нет
- Understanding Culture, Society & Politics: Quarter 1 - Week 2Документ12 страницUnderstanding Culture, Society & Politics: Quarter 1 - Week 2Michael JunioОценок пока нет
- Comparative ConfucianismДокумент4 страницыComparative ConfucianismMarchell DennОценок пока нет
- World LiteraturesДокумент40 страницWorld LiteraturesJanine Vega CalayoОценок пока нет
- UCSP Notes Week 1Документ4 страницыUCSP Notes Week 1Tristan Magno FelipeОценок пока нет
- Module 3 Creative WritingДокумент13 страницModule 3 Creative WritingMione AlmeydaОценок пока нет
- Jose GarciaДокумент29 страницJose GarciaAQUA VINES (official youtube channel)Оценок пока нет
- Ucsp 22Документ53 страницыUcsp 22Ariel PagoboОценок пока нет
- Human Biocultural and Social EvolutionДокумент19 страницHuman Biocultural and Social EvolutionDebora Chantengco-VirayОценок пока нет
- Inquiry Vs ResearchДокумент12 страницInquiry Vs ResearchJulie Anne Portal - OdascoОценок пока нет
- In Literature: Philippine National ArtistsДокумент51 страницаIn Literature: Philippine National ArtistsLady AnnEОценок пока нет
- UCSP Q2 M6 Lecture NotesДокумент4 страницыUCSP Q2 M6 Lecture NotesML CreationsОценок пока нет
- Reading & Writing WK 5Документ6 страницReading & Writing WK 5JeninaS.LimОценок пока нет
- Ologic Time Scale 93922Документ18 страницOlogic Time Scale 93922Ms.AwoОценок пока нет
- The Waraynon's Variety of Patrons Dividing The Dialects Among Their InfluencesДокумент187 страницThe Waraynon's Variety of Patrons Dividing The Dialects Among Their InfluencesAileen MontejoОценок пока нет
- UCSP - Learning Tasks - Week 3Документ3 страницыUCSP - Learning Tasks - Week 3Althea Mitzi DimafelixОценок пока нет
- Pre-Colonial Philippine LiteratureДокумент32 страницыPre-Colonial Philippine LiteratureEsther A. EdaniolОценок пока нет
- Activity Sheet: General BiologyДокумент4 страницыActivity Sheet: General BiologyCarrie Lhee BoadoОценок пока нет
- Exposure and VulnerabilityДокумент17 страницExposure and VulnerabilityDivine Ora CaasiОценок пока нет
- Images" or "Imagery".: ST NDДокумент6 страницImages" or "Imagery".: ST NDRutchelОценок пока нет
- Quantitative ResearchДокумент5 страницQuantitative ResearchDekzie Flores MimayОценок пока нет
- Ucsp MidtermsДокумент4 страницыUcsp MidtermsTintin Levida100% (1)
- How Fossil Fuels Are FormedДокумент6 страницHow Fossil Fuels Are FormedLehaz KakakhelОценок пока нет
- Understanding CultureДокумент4 страницыUnderstanding CultureKnotsNautischeMeilenproStundeОценок пока нет
- Critical PaperДокумент1 страницаCritical PaperLAZO Mark AngeloОценок пока нет
- General Biology 2 NotesДокумент97 страницGeneral Biology 2 NotesMacky NohayОценок пока нет
- Writing The RRLДокумент15 страницWriting The RRLIanne FabianОценок пока нет
- UCSPДокумент9 страницUCSPE-dlord M-alabananОценок пока нет
- Competency Calendar For Creative WritingДокумент3 страницыCompetency Calendar For Creative WritingJS SocoОценок пока нет
- Nature of Inquiry and Research (First Quarter - Week 2)Документ42 страницыNature of Inquiry and Research (First Quarter - Week 2)Ron Adrian AbustanОценок пока нет
- Activity For Evolution Part 1Документ6 страницActivity For Evolution Part 1lala735Оценок пока нет
- Ucsp - Change and AdaptationДокумент50 страницUcsp - Change and AdaptationKyle RicardoОценок пока нет
- Lesson 2 Fiction and CNFДокумент45 страницLesson 2 Fiction and CNFEsther A. EdaniolОценок пока нет
- Biographical ContextДокумент37 страницBiographical ContextLea May VillajuanОценок пока нет
- Ucsp LM PDFДокумент124 страницыUcsp LM PDFAivonny Peñaranda CorbitaОценок пока нет
- Reviewer of Ucsp 2019Документ5 страницReviewer of Ucsp 2019rizalyn alegreОценок пока нет
- History of Life On EarthДокумент45 страницHistory of Life On EarthJedaiah Arnigo AsoyОценок пока нет
- Antonym ExamplesДокумент3 страницыAntonym ExamplesFernando Labucay Fariñas Jr100% (1)
- Wilbur C. Go NHS: Classroom Daily Health Monitoring Tool For Covid-19 Grade Level: - 12 - Section: Onyx IДокумент2 страницыWilbur C. Go NHS: Classroom Daily Health Monitoring Tool For Covid-19 Grade Level: - 12 - Section: Onyx IFernando Labucay Fariñas JrОценок пока нет
- Biology Activity 5. Web Page Reading and Exercise (Week 4)Документ1 страницаBiology Activity 5. Web Page Reading and Exercise (Week 4)Fernando Labucay Fariñas JrОценок пока нет
- English - Examples of Educational Multimedia ResourcesДокумент4 страницыEnglish - Examples of Educational Multimedia ResourcesFernando Labucay Fariñas JrОценок пока нет
- Farinas Activity 3Документ1 страницаFarinas Activity 3Fernando Labucay Fariñas JrОценок пока нет
- English Task 1 News-Print and Non-Print Media - FARINAS.Документ4 страницыEnglish Task 1 News-Print and Non-Print Media - FARINAS.Fernando Labucay Fariñas JrОценок пока нет
- TLE10 Q2 Mod1 Configuring-Computer-System-and-Network v3Документ43 страницыTLE10 Q2 Mod1 Configuring-Computer-System-and-Network v3Bernadeth Irma Sawal Caballa100% (1)
- Application Letter JapsДокумент1 страницаApplication Letter JapsFernando Labucay Fariñas JrОценок пока нет
- True or False: Write PAK If The Statement Is Correct and GANERN If It Is NotДокумент1 страницаTrue or False: Write PAK If The Statement Is Correct and GANERN If It Is NotFernando Labucay Fariñas JrОценок пока нет
- Certification - Authority To TravelДокумент1 страницаCertification - Authority To TravelFernando Labucay Fariñas JrОценок пока нет
- True or False: Write PAK If The Statement Is Correct and GANERN If It Is NotДокумент1 страницаTrue or False: Write PAK If The Statement Is Correct and GANERN If It Is NotFernando Labucay Fariñas JrОценок пока нет
- Jobsheet No 1 2Документ1 страницаJobsheet No 1 2Fernando Labucay Fariñas JrОценок пока нет
- First Periodical Grade 7 SY. 2017-2018Документ3 страницыFirst Periodical Grade 7 SY. 2017-2018Fernando Labucay Fariñas JrОценок пока нет
- 2nd Assessment Grade 12 CSSДокумент3 страницы2nd Assessment Grade 12 CSSFernando Labucay Fariñas JrОценок пока нет
- Jobsheet No 3Документ1 страницаJobsheet No 3Fernando Labucay Fariñas JrОценок пока нет
- Europe FinaleДокумент9 страницEurope FinaleFernando Labucay Fariñas JrОценок пока нет
- MIS-OR-MODULE-6.pdf Version 3Документ21 страницаMIS-OR-MODULE-6.pdf Version 3Kindred Binondo63% (8)
- Jobsheet No 3Документ1 страницаJobsheet No 3Fernando Labucay Fariñas JrОценок пока нет
- Jobsheet No 6Документ1 страницаJobsheet No 6Fernando Labucay Fariñas JrОценок пока нет
- Jobsheet No 4Документ1 страницаJobsheet No 4Fernando Labucay Fariñas JrОценок пока нет
- Remarks: o Competent o Not ComptetentДокумент1 страницаRemarks: o Competent o Not ComptetentFernando Labucay Fariñas JrОценок пока нет
- Jobsheet No 6Документ1 страницаJobsheet No 6Fernando Labucay Fariñas JrОценок пока нет
- Jobsheet No 1 2Документ1 страницаJobsheet No 1 2Fernando Labucay Fariñas JrОценок пока нет
- Kinds of Materials Emp. Lesson 3Документ8 страницKinds of Materials Emp. Lesson 3Fernando Labucay Fariñas JrОценок пока нет
- Strategies For Different Learning StylesДокумент1 страницаStrategies For Different Learning Stylesapi-268185812Оценок пока нет
- 03 Basic Computer NetworkДокумент36 страниц03 Basic Computer Networknellaidenison3548Оценок пока нет
- Kinds of Materials Emp. Lesson 3Документ8 страницKinds of Materials Emp. Lesson 3Fernando Labucay Fariñas JrОценок пока нет
- Image Placement. Emp. Lesson 3Документ10 страницImage Placement. Emp. Lesson 3Fernando Labucay Fariñas JrОценок пока нет
- 3rd Grading Exam 11 CSS 2019-2020 With AnswerДокумент3 страницы3rd Grading Exam 11 CSS 2019-2020 With AnswerFernando Labucay Fariñas JrОценок пока нет
- Bugis Street CsiДокумент8 страницBugis Street CsiMichelle LeeОценок пока нет
- Transgender Community BelonginДокумент11 страницTransgender Community BelonginMarta Cañero PérezОценок пока нет
- Punk and Politics HumphreysДокумент15 страницPunk and Politics Humphreysapi-436684116Оценок пока нет
- We Deserve Better ReportДокумент37 страницWe Deserve Better ReportBreakOUT100% (1)
- Department of Sociology International Islamic University IslamabadДокумент21 страницаDepartment of Sociology International Islamic University IslamabadHatch HepzuttОценок пока нет
- Autism and TransgenderismДокумент12 страницAutism and TransgenderismprabhatdreamzОценок пока нет
- Woman or Warrior The Onstruction of Gender in Old Norse MythДокумент11 страницWoman or Warrior The Onstruction of Gender in Old Norse MythRavnhild RagnarsdottirОценок пока нет
- Ort 90 1 136Документ11 страницOrt 90 1 136Marta Cañero PérezОценок пока нет
- Ang Ladlad LGBT Party vs. Comelec (Equal Protection of Laws)Документ20 страницAng Ladlad LGBT Party vs. Comelec (Equal Protection of Laws)Yosi IsoyОценок пока нет
- Awareness Dates: Days: Weeks: Months: Synopsis and Key PointsДокумент27 страницAwareness Dates: Days: Weeks: Months: Synopsis and Key PointsKhushiОценок пока нет
- Transgender IndividualsДокумент10 страницTransgender IndividualsLINA AGRONOОценок пока нет
- LGBT SymbolsДокумент13 страницLGBT SymbolsTaher TimoumiОценок пока нет
- Sexuality and Gender PDFДокумент4 страницыSexuality and Gender PDFNeil Vincent BocoОценок пока нет
- Planning and LGBTQ Communities The Need For Inclusive Queer Spaces 2Документ14 страницPlanning and LGBTQ Communities The Need For Inclusive Queer Spaces 2fbutteОценок пока нет
- Group2 Literature BackgroundДокумент14 страницGroup2 Literature BackgroundJUDE VINCENT MACALOSОценок пока нет
- Anne-Fausto Sterling 'Should There Be Only Two Sexes?'Документ14 страницAnne-Fausto Sterling 'Should There Be Only Two Sexes?'infini02Оценок пока нет
- RestroomДокумент42 страницыRestroomAj RosalОценок пока нет
- What Is The Difference Between Sex and GenderДокумент8 страницWhat Is The Difference Between Sex and GenderIsaac UtuhОценок пока нет
- PGN112219Документ44 страницыPGN112219Philly Gay NewsОценок пока нет
- College Students' Acceptability of Same-Sex Marriage: An InquiryДокумент26 страницCollege Students' Acceptability of Same-Sex Marriage: An InquiryJaselle HoranОценок пока нет
- Regional LGBTI Survey For PublishingДокумент36 страницRegional LGBTI Survey For PublishingAineОценок пока нет
- 9 - Maroney Et Al (2019) - Emergence of A Transnational LGBTI PsychologyДокумент20 страниц9 - Maroney Et Al (2019) - Emergence of A Transnational LGBTI PsychologyJean AraújoОценок пока нет
- Drag, A Cultural Analysis On The Subculture of Crossdressing and ArtistryДокумент8 страницDrag, A Cultural Analysis On The Subculture of Crossdressing and ArtistryMarcoОценок пока нет
- Book Review - Deepti KalraДокумент4 страницыBook Review - Deepti KalraAmit AroraОценок пока нет
- Humanities Assignment JMДокумент4 страницыHumanities Assignment JMJM Renz Cobain DelantarОценок пока нет
- Homosexuality - PFOXДокумент305 страницHomosexuality - PFOXRuben MicleaОценок пока нет
- Running Head: Family Transgender Therapy 1Документ4 страницыRunning Head: Family Transgender Therapy 1JacobОценок пока нет
- Developing Multicultural Counseling Competence: A Systems ApproachДокумент28 страницDeveloping Multicultural Counseling Competence: A Systems ApproachaisyahwanzaukiОценок пока нет
- Addendum To Psychiatric - Mental Health Nurse Practitioner: Chapter #Документ26 страницAddendum To Psychiatric - Mental Health Nurse Practitioner: Chapter #Soojung Nam100% (6)
- Beyond The Gender BinaryДокумент2 страницыBeyond The Gender BinaryabhicueeОценок пока нет
- Unwanted Advances: Sexual Paranoia Comes to CampusОт EverandUnwanted Advances: Sexual Paranoia Comes to CampusРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (22)
- The Masonic Myth: Unlocking the Truth About the Symbols, the Secret Rites, and the History of FreemasonryОт EverandThe Masonic Myth: Unlocking the Truth About the Symbols, the Secret Rites, and the History of FreemasonryРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (14)
- Rejected Princesses: Tales of History's Boldest Heroines, Hellions, & HereticsОт EverandRejected Princesses: Tales of History's Boldest Heroines, Hellions, & HereticsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (68)
- Lucky Child: A Daughter of Cambodia Reunites with the Sister She Left BehindОт EverandLucky Child: A Daughter of Cambodia Reunites with the Sister She Left BehindРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (54)
- Never Chase Men Again: 38 Dating Secrets to Get the Guy, Keep Him Interested, and Prevent Dead-End RelationshipsОт EverandNever Chase Men Again: 38 Dating Secrets to Get the Guy, Keep Him Interested, and Prevent Dead-End RelationshipsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (387)
- The Myth of Equality: Uncovering the Roots of Injustice and PrivilegeОт EverandThe Myth of Equality: Uncovering the Roots of Injustice and PrivilegeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (17)
- Making Gay History: The Half-Century Fight for Lesbian and Gay Equal RightsОт EverandMaking Gay History: The Half-Century Fight for Lesbian and Gay Equal RightsОценок пока нет
- Does Jesus Really Love Me?: A Gay Christian's Pilgrimage in Search of God in AmericaОт EverandDoes Jesus Really Love Me?: A Gay Christian's Pilgrimage in Search of God in AmericaРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (13)
- Unlikeable Female Characters: The Women Pop Culture Wants You to HateОт EverandUnlikeable Female Characters: The Women Pop Culture Wants You to HateРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (18)
- Braiding Sweetgrass: Indigenous Wisdom, Scientific Knowledge and the Teachings of PlantsОт EverandBraiding Sweetgrass: Indigenous Wisdom, Scientific Knowledge and the Teachings of PlantsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (1424)
- For the Love of Men: From Toxic to a More Mindful MasculinityОт EverandFor the Love of Men: From Toxic to a More Mindful MasculinityРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (56)
- Decolonizing Wellness: A QTBIPOC-Centered Guide to Escape the Diet Trap, Heal Your Self-Image, and Achieve Body LiberationОт EverandDecolonizing Wellness: A QTBIPOC-Centered Guide to Escape the Diet Trap, Heal Your Self-Image, and Achieve Body LiberationРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (22)
- Silent Tears: A Journey Of Hope In A Chinese OrphanageОт EverandSilent Tears: A Journey Of Hope In A Chinese OrphanageРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (29)
- You Can Thrive After Narcissistic Abuse: The #1 System for Recovering from Toxic RelationshipsОт EverandYou Can Thrive After Narcissistic Abuse: The #1 System for Recovering from Toxic RelationshipsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (16)
- Sex and the City and Us: How Four Single Women Changed the Way We Think, Live, and LoveОт EverandSex and the City and Us: How Four Single Women Changed the Way We Think, Live, and LoveРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (22)
- Unbound: My Story of Liberation and the Birth of the Me Too MovementОт EverandUnbound: My Story of Liberation and the Birth of the Me Too MovementРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (147)
- Tears of the Silenced: An Amish True Crime Memoir of Childhood Sexual Abuse, Brutal Betrayal, and Ultimate SurvivalОт EverandTears of the Silenced: An Amish True Crime Memoir of Childhood Sexual Abuse, Brutal Betrayal, and Ultimate SurvivalРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (136)