Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Mycoplasma: BY: Raunak Prasad
Загружено:
Raunak Prasad0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
13 просмотров6 страницMycoplasma are the smallest prokaryotic organisms that can be grown in cell-free culture medium. They lack a cell wall and exist in filamentous, granular, or spherical forms. Mycoplasma are cultured between 35-37°C in enriched broth and take 2-3 weeks to form fried-egg shaped colonies. They cause pneumonia by penetrating host cell membranes and utilizing gliding motility. Symptoms include cough, fever, and malaise. Diagnosis involves specific antibiotic treatment with macrolides or doxycycline. Contamination in labs is monitored using staining, PCR, or enzymatic methods to detect the organisms.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
MYCOPLASMA
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документMycoplasma are the smallest prokaryotic organisms that can be grown in cell-free culture medium. They lack a cell wall and exist in filamentous, granular, or spherical forms. Mycoplasma are cultured between 35-37°C in enriched broth and take 2-3 weeks to form fried-egg shaped colonies. They cause pneumonia by penetrating host cell membranes and utilizing gliding motility. Symptoms include cough, fever, and malaise. Diagnosis involves specific antibiotic treatment with macrolides or doxycycline. Contamination in labs is monitored using staining, PCR, or enzymatic methods to detect the organisms.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
13 просмотров6 страницMycoplasma: BY: Raunak Prasad
Загружено:
Raunak PrasadMycoplasma are the smallest prokaryotic organisms that can be grown in cell-free culture medium. They lack a cell wall and exist in filamentous, granular, or spherical forms. Mycoplasma are cultured between 35-37°C in enriched broth and take 2-3 weeks to form fried-egg shaped colonies. They cause pneumonia by penetrating host cell membranes and utilizing gliding motility. Symptoms include cough, fever, and malaise. Diagnosis involves specific antibiotic treatment with macrolides or doxycycline. Contamination in labs is monitored using staining, PCR, or enzymatic methods to detect the organisms.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 6
MYCOPLASMA
BY: Raunak Prasad
General Characteristics
❏ Smallest unicellular ❏ It differs from viruses as it ❏ Bounded by a
prokaryotic (GRAM POS) has RNA and DNA trilaminar
organisms that can membrane- sterols,
grown in cell free lipids
culture medium
❏ Requires cholesterol for ❏ Can exist in three
forms - filament,
growth, hence also why
granular, and
it’s a facultative spherical
❏ Devoid of cell wall (and anaerobe.
even its precursors) ❏ Fried egg or
mulberry colonies
on agar
❏ Occurs as saprophytes in
❏ It differs from viruses soil and sewage.
as it has RNA and DNA
How Mycoplasma is cultured
❏ Mycoplasma can be cultured on liquid or solid medium
❏ Most optimal growth between 35-37°C
❏ Medium of growth should be enriched with 20% horse/ human
serum
❏ Culture media requires PPLO broth and sugar. In this broth, we
can determine the growth due to the pH changes (which is
caused by the carbohydrate metabolism)
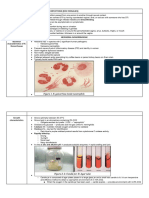
The central opaque area
❏ Takes 2-3 weeks
extends into the medium. In
❏ Colonies can be seen under microscope- Diene’s staining addition the periphery flat
technique and translucent.
❏ When it reaches 56°C or above it is killed by the heat in 30
minutes
How it causes diseases/ pathogenesis
❏ Usually the most important this disease causes is Pneumonia
❏ Transmission of droplets of nasopharyngeal secretion in close contacts, where the mycoplasma may
remain in the throat for more than 2 months after recovery
❏ When mycoplasma comes in contact with the mucus membranes, it penetrates the mucosal gel
coating of the epithelium (this is aided by the gliding motility and its minute size)
❏ Mycoplasma is pathogenic in nature utilizing the close facilitation between M.pneumoniae and its host
cell
Common symptoms
● Generalized aches and pains
● Fever at 102°F
● Sore throat or cough
● Headaches
● Chills
● Earache
● General malaise
● Nasal congestion with coryza
Diagnosis for Mycoplasma
Only certain antibiotics are useful ,as cell wall synthesis
inhibitors will be ineffective
For children: If macrolides are not effective enough, they
must be treated with corticosteroids to
Macrolides like erythromycin, Clarithromycin, manage the extra inflammation. Such
Roxithromycin, azithromycin include:
Prednisolone
Methylprenisolone
For adults:
Doxycycline, tetracycline, quinolones
HOW WE CAN MONITOR THE CONTAMINATION FOR MYCOPLASMA IN HUMAN IPC LABS
❏ Mycoplasma must be looked at, as they affect cell metabolism, gene expression, antigenicity.
❏ Once Mycoplasma enters IPC labs, it can be difficult to eradicate them.
❏ They cause cross contamination, and are highly infectious.
❏ To test for Mycoplasma in IPC labs, staining methods are used like fluorescent or PCR, and even
enzymatic. One of the fastest and newest methods developed is the use of Hoechst dyes.
❏ Enzymatic labeling using DNA polymerase I and modified nucleotides utilizing nicks in the
mycoplasmas’ DNA. Modified nucleotides are incorporated into mycoplasmas’ DNA and subsequently
visualized by immunofluorescence microscopy.
Вам также может понравиться
- BSC 204 Notes FinalsДокумент11 страницBSC 204 Notes FinalsWil LynОценок пока нет
- My Co PlasmaДокумент70 страницMy Co Plasmatummalapalli venkateswara raoОценок пока нет
- My Co PlasmaДокумент35 страницMy Co PlasmaPawan KatiyarОценок пока нет
- XENOPUSДокумент11 страницXENOPUSpranky neyneyОценок пока нет
- Bac NotesДокумент22 страницыBac NotesK PrashasthaОценок пока нет
- 745 MycoplasmaДокумент79 страниц745 MycoplasmadrbhaveshparmarОценок пока нет
- Cell Wall-Deficient & Spirochetes and Miscellaneous BacteriaДокумент33 страницыCell Wall-Deficient & Spirochetes and Miscellaneous BacteriaJienelle ManaloОценок пока нет
- BMY4301 - MollicutesДокумент7 страницBMY4301 - MollicutesMUHAMMAD FIKQRAN SHAH BIN SHAHRIZAD / UPMОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Identification of MoldsДокумент57 страницLaboratory Identification of MoldsMary Shikha ShaikeОценок пока нет
- CryptococcusДокумент57 страницCryptococcusማላያላም ማላያላምОценок пока нет
- Questions To ReviewДокумент3 страницыQuestions To ReviewReign ChristyneОценок пока нет
- Unit - 9 - Mycoplasma by Dr. Kirtika PadaliaДокумент22 страницыUnit - 9 - Mycoplasma by Dr. Kirtika PadaliaDj RiskОценок пока нет
- Chlamydia and MycoplasmaДокумент5 страницChlamydia and MycoplasmaMico Jan GurionОценок пока нет
- 2 - 3 - CNS TumorsДокумент14 страниц2 - 3 - CNS TumorsNajeebОценок пока нет
- QMS MicrobiologyДокумент21 страницаQMS MicrobiologyDr-Shubhaneel NeogiОценок пока нет
- Leprosy PPT ManyaДокумент25 страницLeprosy PPT Manyakhushi.gupta2122Оценок пока нет
- Pavi SivaДокумент17 страницPavi Sivaraasuraasu201Оценок пока нет
- 2 Basic Concepts in VirologyДокумент5 страниц2 Basic Concepts in VirologyJascha MoralОценок пока нет
- Microbiology: Atypical Bacteria: Chlamydia, Mycoplasms, LegionellaДокумент4 страницыMicrobiology: Atypical Bacteria: Chlamydia, Mycoplasms, LegionellaPatricia Mae de JesusОценок пока нет
- Bacterial EndosporesДокумент37 страницBacterial EndosporesGabriel TambweОценок пока нет
- Lesson 17 ChlamydiaceaeДокумент4 страницыLesson 17 ChlamydiaceaeLittle CloudОценок пока нет
- Medical Parasitology: 01 TaxonomyДокумент8 страницMedical Parasitology: 01 TaxonomyMonesa Christy VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- Hema2 M1 TransДокумент6 страницHema2 M1 TransvnicasantiagoОценок пока нет
- Hema 2Документ35 страницHema 2Angela ReyesОценок пока нет
- Bacteria Part2 StructureДокумент3 страницыBacteria Part2 StructureYezza Mae D. LucbanОценок пока нет
- Mtap - BacteriologyДокумент11 страницMtap - BacteriologyMoira Pauline LibroraniaОценок пока нет
- Mycoplasmas: Hugh B FackrellДокумент35 страницMycoplasmas: Hugh B FackrellMuhamad Abdul MubdiОценок пока нет
- Hema LectureДокумент8 страницHema LectureTrisha ManayaОценок пока нет
- Streptococcus-Midterm - 2ND SemДокумент6 страницStreptococcus-Midterm - 2ND Semrhenzyl ganoОценок пока нет
- Viral and Bacterial GenomeДокумент20 страницViral and Bacterial GenomeRoliane RugaОценок пока нет
- History of MicrobiologyДокумент64 страницыHistory of MicrobiologyHOPEОценок пока нет
- Materi 3 - 2022-Converted-CompressedДокумент41 страницаMateri 3 - 2022-Converted-CompressedYossi SiburianОценок пока нет
- Gram StainingДокумент30 страницGram StainingSolomon Fallah Foa Sandy100% (1)
- BIO 151 2018-2019 Student Lecture Guide - Lecture 5 - Structure and Organization of BacteriaДокумент3 страницыBIO 151 2018-2019 Student Lecture Guide - Lecture 5 - Structure and Organization of BacteriaDoctor ChetanneОценок пока нет
- Micro GramNegCocci MD2021Документ5 страницMicro GramNegCocci MD2021Patricia Mae de JesusОценок пока нет
- Bacteria and ArcheaДокумент9 страницBacteria and ArcheaQuintin MangaoangОценок пока нет
- Module 9.4 + Microbio + Study GuideДокумент33 страницыModule 9.4 + Microbio + Study GuideMikhail LamayoОценок пока нет
- Chlorophyta PDFДокумент102 страницыChlorophyta PDFabhishek sharmaОценок пока нет
- Crypto Cocco SisДокумент32 страницыCrypto Cocco SisLincy JohnyОценок пока нет
- Mojza Biology NotesДокумент102 страницыMojza Biology NotesShumyla JahanzaibОценок пока нет
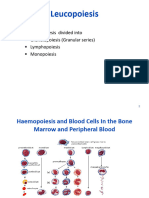
- LeucopoiesisДокумент97 страницLeucopoiesiscaroline vaughanОценок пока нет
- Agents of Opportunistic MycosesДокумент6 страницAgents of Opportunistic MycosesReinDePabloОценок пока нет
- Campy Lo Bacterio SisДокумент14 страницCampy Lo Bacterio SisHarikrishnan NamОценок пока нет
- They Also Play The Role of Virulence Factors: Transmission Is Person To Person by Respiratory AerosolДокумент5 страницThey Also Play The Role of Virulence Factors: Transmission Is Person To Person by Respiratory Aerosolsm5315213Оценок пока нет
- Chloroplast Transformation and Its Applications To Plant ImprovementДокумент29 страницChloroplast Transformation and Its Applications To Plant Improvementjajati keshari nayakОценок пока нет
- MIC211 - Introduction To Mycology & Superficial and Cutaenous MycosesДокумент15 страницMIC211 - Introduction To Mycology & Superficial and Cutaenous Mycosesmrbaldonado0144valОценок пока нет
- Parasitic Inclusions in ErythrocytesДокумент27 страницParasitic Inclusions in ErythrocytesLian Marie ViñasОценок пока нет
- Basic Concept of Mycology PDFДокумент56 страницBasic Concept of Mycology PDFSjsjОценок пока нет
- MP Week 2 Part 2 NotesДокумент5 страницMP Week 2 Part 2 NotesDara BilocuraОценок пока нет
- Tissueculture 3 171212101129Документ40 страницTissueculture 3 171212101129khawarkhubaibОценок пока нет
- MycoplasmaДокумент2 страницыMycoplasmaaminshafihassan902Оценок пока нет
- PlasmidДокумент19 страницPlasmidAleena MustafaОценок пока нет
- Microbiology Casi Lec 2Документ3 страницыMicrobiology Casi Lec 2Stevens MacabidangОценок пока нет
- Week 4. Subcutaneous MycosesДокумент59 страницWeek 4. Subcutaneous MycosesAsdfghjklОценок пока нет
- Week 6 Blood and Tissue FlagellatesДокумент7 страницWeek 6 Blood and Tissue FlagellatesaemancarpioОценок пока нет
- Lab Diagnosis and TreatmentДокумент22 страницыLab Diagnosis and TreatmentDavid lufafaОценок пока нет
- Materi 5Документ29 страницMateri 5Rafif Abdikah UtamaОценок пока нет
- MBBS Leptospirosis StudentДокумент26 страницMBBS Leptospirosis StudentCatherine JosephОценок пока нет
- Neisseria 160915072903Документ26 страницNeisseria 160915072903HARSH BAGDIОценок пока нет
- Ena Shroom PublishedДокумент17 страницEna Shroom PublishedRaunak PrasadОценок пока нет
- Business Management Paper 2 HL Markscheme PDFДокумент28 страницBusiness Management Paper 2 HL Markscheme PDFRaunak Prasad100% (1)
- Newman Projection State of MindДокумент4 страницыNewman Projection State of MindRaunak PrasadОценок пока нет
- All MS Jun08Документ96 страницAll MS Jun08Raunak PrasadОценок пока нет
- General Certificate of Education Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelДокумент4 страницыGeneral Certificate of Education Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelRaunak PrasadОценок пока нет
- Arenes - Benzene Chemistry 1 MSДокумент16 страницArenes - Benzene Chemistry 1 MSRaunak PrasadОценок пока нет
- NMR Spectroscopy 1 QPДокумент13 страницNMR Spectroscopy 1 QPRaunak PrasadОценок пока нет
- Artificial Synaptic Rewiring Demonstrates That Distinct Neural Circuit Configurations Underlie Homologous BehaviorsДокумент18 страницArtificial Synaptic Rewiring Demonstrates That Distinct Neural Circuit Configurations Underlie Homologous BehaviorsRaunak PrasadОценок пока нет
- BET Proteins Exhibit Transcriptional and Functional Opposition in The Epithelial-To-Mesenchymal TransitionДокумент24 страницыBET Proteins Exhibit Transcriptional and Functional Opposition in The Epithelial-To-Mesenchymal TransitionRaunak PrasadОценок пока нет
- Tsokos LSN 5-6 To 5-8 Test ReviewДокумент11 страницTsokos LSN 5-6 To 5-8 Test ReviewRaunak PrasadОценок пока нет
- Assignment 10Документ13 страницAssignment 10Raunak PrasadОценок пока нет
- Assignment 10 V2aДокумент10 страницAssignment 10 V2aRaunak PrasadОценок пока нет
- Summary Sheet: Functions: Sketching Modulus GraphsДокумент3 страницыSummary Sheet: Functions: Sketching Modulus GraphsRaunak PrasadОценок пока нет
- Summary Sheet: Probability: 4 1 P (Total 5) 16 4Документ3 страницыSummary Sheet: Probability: 4 1 P (Total 5) 16 4Raunak PrasadОценок пока нет
- Friendly Bacteria: BY: Raunak PrasadДокумент6 страницFriendly Bacteria: BY: Raunak PrasadRaunak PrasadОценок пока нет
- Ibz Mo - Personal StatementsДокумент3 страницыIbz Mo - Personal StatementsRaunak PrasadОценок пока нет
- Summary Sheet: ProofДокумент3 страницыSummary Sheet: ProofRaunak PrasadОценок пока нет
- Apoptosis: By: Raunak PrasadДокумент7 страницApoptosis: By: Raunak PrasadRaunak PrasadОценок пока нет
- Assignment 07 PDFДокумент13 страницAssignment 07 PDFRaunak PrasadОценок пока нет
- Personal Statement 2Документ2 страницыPersonal Statement 2Raunak PrasadОценок пока нет
- 2 IR SpectrosДокумент32 страницы2 IR SpectrosRaunak PrasadОценок пока нет
- 2 IR SpectrosДокумент32 страницы2 IR SpectrosRaunak PrasadОценок пока нет
- A Collection of TOEFL Reading Comprehension Tests 352Документ1 страницаA Collection of TOEFL Reading Comprehension Tests 352luisaОценок пока нет
- Acid Fast StainingДокумент13 страницAcid Fast StainingDhanushika Sakthi VBОценок пока нет
- Black DeathДокумент15 страницBlack DeathAlex KibalionОценок пока нет
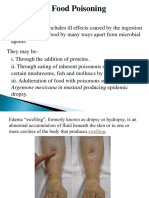
- Food Poisoning and IntoxicationsДокумент26 страницFood Poisoning and IntoxicationslakshmijayasriОценок пока нет
- Peta SensitivitasДокумент1 страницаPeta SensitivitasInstalasi Farmasi TPTОценок пока нет
- Microbiology Lab Report: Negative Staining of Staphylococcus AureusДокумент4 страницыMicrobiology Lab Report: Negative Staining of Staphylococcus AureusMuhammed ElRakabawiОценок пока нет
- Liberation of InoculaДокумент2 страницыLiberation of InoculaXenave JohnsonОценок пока нет
- IspaДокумент30 страницIspahary anggoroОценок пока нет
- Mad Cow DiseaseДокумент40 страницMad Cow DiseaseSathiyaraj Srinivasan100% (1)
- Campeel IutДокумент86 страницCampeel IutRosa TorresОценок пока нет
- InfectiousДокумент28 страницInfectiousVarshitha VenkateshОценок пока нет
- BMJ 335 7630 CR 01147 Vaginal DischargeДокумент5 страницBMJ 335 7630 CR 01147 Vaginal DischargeHassan Abdullah AL-balushiОценок пока нет
- Antimicrobial Effectiveness Tests: We Provide Health and Safety in A Visible FormДокумент1 страницаAntimicrobial Effectiveness Tests: We Provide Health and Safety in A Visible FormNanda Hendra PratamaОценок пока нет
- Genital UlcersДокумент17 страницGenital UlcersCLEMENTОценок пока нет
- HeiQ Pure - ViroblockДокумент66 страницHeiQ Pure - ViroblockAyrton Da SilvaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 176. Superficial Cutaneous Infections and Pyodermas PDFДокумент36 страницChapter 176. Superficial Cutaneous Infections and Pyodermas PDFTresia SimalangoОценок пока нет
- Nipah Virus Infection-GuidelinesДокумент7 страницNipah Virus Infection-GuidelinesSIVAPRASADОценок пока нет
- Cornell University: Dairy Foods Science NotesДокумент2 страницыCornell University: Dairy Foods Science NotesTanishka AggarwalОценок пока нет
- Scaling and PerionomicsДокумент13 страницScaling and PerionomicsRavikant KurmiОценок пока нет
- CandidiasisДокумент27 страницCandidiasisfarmasi_hmОценок пока нет
- Antibacterial EnxofreДокумент5 страницAntibacterial EnxofreCarina MoitaОценок пока нет
- Microbial Genetics: Julia Hartati, DRДокумент21 страницаMicrobial Genetics: Julia Hartati, DRerwan_mivecОценок пока нет
- Rinderpest: ImportanceДокумент5 страницRinderpest: Importancekadek ayu ichaОценок пока нет
- 5-Article Text-20-1-10-20201008Документ6 страниц5-Article Text-20-1-10-20201008RY COURSE KELAS 11Оценок пока нет
- Penatalaksanaan Osteomielitis Kronis Disertai Fistula Ekstraoral Pada MandibulaДокумент4 страницыPenatalaksanaan Osteomielitis Kronis Disertai Fistula Ekstraoral Pada MandibulaFajriah SaraswatiОценок пока нет
- Lombok Immunizationand Traveller231017-Dr - Agus SomiaДокумент63 страницыLombok Immunizationand Traveller231017-Dr - Agus Somiarinaldy IX9Оценок пока нет
- Eng Tok VaccinesДокумент55 страницEng Tok VaccinesallemedizinОценок пока нет
- The Big Picture Book of Viruses. EP Rybicki & R KightleyДокумент106 страницThe Big Picture Book of Viruses. EP Rybicki & R KightleyDОценок пока нет
- Increases in COVID 19 Are Unrelated To Levels of Vaccination Across 68 Countries and 2947 Counties in The United StatesДокумент4 страницыIncreases in COVID 19 Are Unrelated To Levels of Vaccination Across 68 Countries and 2947 Counties in The United StatesKyle Becker95% (19)
- Literature Review Acute GastroenteritisДокумент8 страницLiterature Review Acute Gastroenteritisc5hzgcdj100% (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityОт EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (6)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseОт EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (69)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessОт EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessОценок пока нет
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainОт EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (65)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessОт Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (33)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincОт EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (137)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorОт EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorОценок пока нет
- Water: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationОт EverandWater: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (37)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseОт EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (52)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsОт EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (6)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldОт EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (597)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceОт EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (18)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionОт EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (812)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedОт EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (11)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouОт EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (62)
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorОт EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (139)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomОт EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (216)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainОт EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (111)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceОт EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (517)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveОт EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (66)