Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Components of Communication
Загружено:
Abdullah Nasir0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
19 просмотров9 страницCommunications Skills Lecture
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документCommunications Skills Lecture
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
19 просмотров9 страницComponents of Communication
Загружено:
Abdullah NasirCommunications Skills Lecture
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 9
Components of communication
Context
Every message (Oral or written), begins with context. Context is a very
broad field that consists of different aspects such as country, culture and
organization. Every organization, culture and country communicate
information in their own way. The sender chooses the message to
communicate within a context.
Another aspect of context is external stimulus. The sources of external
stimulus include; meeting, letter, memo, telephone call, fax, note, email
and even a casual conversation. The external stimulus motivates you to
respond and this response may be oral or written.
Internal stimuli include your opinion, attitude, likes, dislikes, emotions,
experience, education and confidence. These all have multifaceted
influence on the way you communicate your ideas.
Sender/Encoder
Encoder is a person who sends the message. In oral
communication the encoder is speaker, and in written
communication writer is the encoder. A sender makes use of
symbols (words or graphic or visual) to convey the message
and produce the required response. For instance , a training
manager conducting training for new batch of employees.
Sender may be an individual or a group or an organization.
The views, background, approach, skills, competencies, and
knowledge of the sender have a great impact on the message.
The verbal and non-verbal symbols chosen are essential in
ascertaining interpretation of the message by the recipient in
the same terms as intended by the sender.
Receiver/Decoder
The person to whom the message is sent is called
receiver/decoder. Receiver may be a listener or a reader
depending on the choice of medium by sender to transmit
the message. Receiver is also influenced by the context;
internal and external stimuli.
Receiver is the person who interprets the message; so the
chances of mis-communication because of receivers’
perception, opinion, attitude and personality are high if your
receiver is educated and has good communication skills.
Message
Message is the information that is exchanged between
sender and receiver. It is the key idea that the sender wants
to communicate. It is a sign that elicits the response of
recipient. The first task is to decide what you want to
communicate and what would be the content of your
message; what are the main points of your message and
what other information to include. The central idea of the
message must be clear. While writing the message, encoder
should keep in mind all aspects of context and the receiver
(How he will interpret the message). Messages can be
intentional and unintentional.
Medium
Medium is a means used to exchange / transmit the message. The sender must
choose an appropriate medium for transmitting the message else the message might
not be conveyed to the desired recipients. The choice of appropriate medium of
communication is essential for making the message effective and correctly
interpreted by the recipient. The choice of communication medium varies
depending upon the features of communication. For instance , written medium is
chosen when a message has to be conveyed to a small group of people, while an
oral medium is chosen when spontaneous feedback is required from the recipient as
misunderstandings are cleared then and there. The oral medium, to convey your
message, is effective when your message is urgent, personal or when immediate
feedback is desired. While, when your message is long, technical and needs to be
documented, then written medium should be preferred.
Medium is the channel through which encoder sends his message. It may be print,
electronic, or sound or a person such as a postman. The choice of medium totally
depends on the nature of you message and contextual factors. Choice of medium is
also influenced by the relationship between the sender and receiver.
Feedback
Response or reaction of the receiver to a message is called
feedback.
Feedback is the main component of communication process
as it permits the sender to analyze the efficacy of the
message. It helps the sender in confirming the correct
interpretation of message by the decoder. Feedback may be
verbal (oral) or non-verbal (smiles, sighs, action, silence,
etc.). It may take written form also. (memos, reports, etc).
ACTIVITY
Have a group discussion on a topic of your own choice and
reason out your communication from the following
perspectives:
• What was the context?
• Which medium was used?
• Did you get any feedback?
• Did you face any problems while communicating?
• Was there any non-verbal communication? If yes, how?
Вам также может понравиться
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- IEEE Code of EthicsДокумент1 страницаIEEE Code of EthicsAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- Civic Virtues IДокумент14 страницCivic Virtues IAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- Safety & Risk IIДокумент22 страницыSafety & Risk IIAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Civic Virtues IIДокумент13 страницCivic Virtues IIAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- Micron Technical NoteДокумент28 страницMicron Technical NoteAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- Workplace Responsibility & Conflict of IntrestДокумент21 страницаWorkplace Responsibility & Conflict of IntrestAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Memorandum of Understanding Between Hitec Press Club and DsaДокумент1 страницаMemorandum of Understanding Between Hitec Press Club and DsaAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- IEEE Workshop On Android Application Development: Event Name DateДокумент1 страницаIEEE Workshop On Android Application Development: Event Name DateAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- From Collage To UniversityДокумент2 страницыFrom Collage To UniversityAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- World Youth Skills Day Celebrated On Every 15th JulyДокумент1 страницаWorld Youth Skills Day Celebrated On Every 15th JulyAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
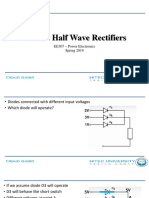
- 6b. 3 Phase Full Wave RectifiersДокумент11 страниц6b. 3 Phase Full Wave RectifiersAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- Unit 3: Safety, Responsibility As An EngineerДокумент24 страницыUnit 3: Safety, Responsibility As An EngineerAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- 11 Things Only HITONIANS Would Be Able To UnderstandДокумент2 страницы11 Things Only HITONIANS Would Be Able To UnderstandAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Electronic Workshop Project ProposalДокумент3 страницыElectronic Workshop Project ProposalAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Memorandum of Understanding Between Hitec Press Club and DsaДокумент1 страницаMemorandum of Understanding Between Hitec Press Club and DsaAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- AC-AC Controllers: EE307 - Power Electronics Spring 2019Документ22 страницыAC-AC Controllers: EE307 - Power Electronics Spring 2019Abdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2-3 Introduction To Computer SystemsДокумент66 страницLecture 2-3 Introduction To Computer SystemsAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- Nearly Twenty Years AgoДокумент3 страницыNearly Twenty Years AgoAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Types of Electrical CablesДокумент41 страницаTypes of Electrical CablesAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Switch Mode RegulatorsДокумент32 страницыSwitch Mode RegulatorsAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- Hitecuniversity: Department of Electrical EngineeringДокумент3 страницыHitecuniversity: Department of Electrical EngineeringAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- EC-110 Computing Fundamentals (2+1) : Introductory Lecture, Course Organisation andДокумент8 страницEC-110 Computing Fundamentals (2+1) : Introductory Lecture, Course Organisation andAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
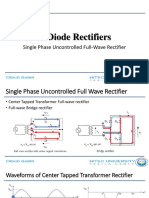
- 3.diode RectifiersДокумент14 страниц3.diode RectifiersAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- 6a. 3 Phase Have Wave RectifiersДокумент29 страниц6a. 3 Phase Have Wave RectifiersAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- DC-DC ChoppersДокумент24 страницыDC-DC ChoppersAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- 5b. Rectifiers With RL LoadДокумент20 страниц5b. Rectifiers With RL LoadAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- 3.full Wave RectifierДокумент15 страниц3.full Wave RectifierAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- 5a. Controlled RectifiersДокумент17 страниц5a. Controlled RectifiersAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- ThyristorsДокумент26 страницThyristorsAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- 2.power Semiconductor DiodesДокумент22 страницы2.power Semiconductor DiodesAbdullah NasirОценок пока нет
- Practice 16-11Документ3 страницыPractice 16-11Duy DươngОценок пока нет
- Most Essential Learning Competencies For Grade 10: Subject MelcДокумент2 страницыMost Essential Learning Competencies For Grade 10: Subject MelcCatherine FadriquelanОценок пока нет
- PerDev Q1 Module 2 Developing The Whole Person Ver1-ForCADILLAДокумент33 страницыPerDev Q1 Module 2 Developing The Whole Person Ver1-ForCADILLAJenny E. Forcadilla100% (4)
- Hanh Vi Nguoi Tieu Dung Bui Thi Phuong Hoa Chapter 3 Learning and Memory (Cuuduongthancong - Com)Документ31 страницаHanh Vi Nguoi Tieu Dung Bui Thi Phuong Hoa Chapter 3 Learning and Memory (Cuuduongthancong - Com)Huong Quach NgocОценок пока нет
- Teamwork and Leadefship - Drop The Ball ReflectionДокумент3 страницыTeamwork and Leadefship - Drop The Ball Reflectionapi-248093224Оценок пока нет
- Jane Austen: Performer - Culture & LiteratureДокумент15 страницJane Austen: Performer - Culture & LiteratureCarla ManuntaОценок пока нет
- Midterm ProjectДокумент3 страницыMidterm ProjectJoy QuerubinОценок пока нет
- Ecological Systems TheoryДокумент9 страницEcological Systems TheoryAce VenturaОценок пока нет
- Ideal Society EssayДокумент3 страницыIdeal Society Essayafhbgmmtc100% (2)
- Unit II Lesson 1 Social Reproduction or How Societies PersistДокумент35 страницUnit II Lesson 1 Social Reproduction or How Societies PersistVencent Costola ZaballeroОценок пока нет
- Grade 7Документ58 страницGrade 7Abdelhak Marouf86% (7)
- A Topical Approach To Life Span Development Santrock 7th Edition Test BankДокумент53 страницыA Topical Approach To Life Span Development Santrock 7th Edition Test BankStevenRichardsdesk100% (42)
- Slave ContractДокумент3 страницыSlave ContractJohnОценок пока нет
- BLANK-IPLAN (Format)Документ2 страницыBLANK-IPLAN (Format)That's Entertainment100% (1)
- Cognative Behavioural TherapyДокумент6 страницCognative Behavioural TherapyAshani Aarora100% (1)
- School-Based Management Assessment Process and Tool (SBM Apat) Leadership & GovernanceДокумент19 страницSchool-Based Management Assessment Process and Tool (SBM Apat) Leadership & GovernanceJivy100% (1)
- The Nunnery Scene Part 1Документ1 страницаThe Nunnery Scene Part 1parveezОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 Biological DevelopmentДокумент9 страницUnit 2 Biological DevelopmentJudel TanoОценок пока нет
- MED102 Test Prep 4Документ3 страницыMED102 Test Prep 4Earl PilarОценок пока нет
- MKT201 IndiДокумент8 страницMKT201 IndiPhạm Thu HằngОценок пока нет
- 08 OT Adult MH AOTA Exam PrepДокумент25 страниц08 OT Adult MH AOTA Exam PrepThirdy BullerОценок пока нет
- Interactive Metronome TrainingДокумент24 страницыInteractive Metronome TrainingHector GonzalesОценок пока нет
- The City in The City Berlin As A MagneriДокумент116 страницThe City in The City Berlin As A MagneriP ArchОценок пока нет
- Assertiveness FinlandДокумент2 страницыAssertiveness FinlandDivyanshi ThakurОценок пока нет
- (Caderno Sesc - Videobrasil 12) Vilém Flusser Et Al. - METAFLUXUS-Associação Cultural Videobrasil (2017)Документ170 страниц(Caderno Sesc - Videobrasil 12) Vilém Flusser Et Al. - METAFLUXUS-Associação Cultural Videobrasil (2017)ankebfОценок пока нет
- Trivial:: Hacked by Jon DavisДокумент1 страницаTrivial:: Hacked by Jon Davisseymour79Оценок пока нет
- Introduction To The Study of Consumer BehaviorДокумент22 страницыIntroduction To The Study of Consumer BehaviorTuhina MistryОценок пока нет
- ME4382 CourseWorkFormatДокумент3 страницыME4382 CourseWorkFormatMathiОценок пока нет
- The Impact of Softskill Training On Employee Performance and Its Implications On Organisational SuccessДокумент8 страницThe Impact of Softskill Training On Employee Performance and Its Implications On Organisational SuccessSRINATH RОценок пока нет
- Name: Mark Francis Zalsos BS Agriculture Major in Animal Science AN1-A ActivityДокумент5 страницName: Mark Francis Zalsos BS Agriculture Major in Animal Science AN1-A ActivityMark ZalsosОценок пока нет
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)От EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Рейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsОт EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsОценок пока нет
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityОт EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (32)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionОт EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (404)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDОт EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsОт EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)