Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Introduction To Amino Acids and Proteins - 1 - (Autosaved)
Загружено:
Twaiba Admani0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
15 просмотров10 страницThis document discusses protein chemistry and the structure and functions of proteins and their building blocks, amino acids. It covers the 20 common amino acids, their classification, structures, and ionization properties. Key points include that proteins are made of amino acids, which contain an amino group and carboxyl group. Amino acids exist as dipolar ions at neutral pH and can form peptide bonds. The 20 amino acids are classified based on polarity and charge of their R groups. Disulfide bonds and different structural levels of proteins are also mentioned.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
introduction to Amino acids and proteins _1_ [Autosaved]
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThis document discusses protein chemistry and the structure and functions of proteins and their building blocks, amino acids. It covers the 20 common amino acids, their classification, structures, and ionization properties. Key points include that proteins are made of amino acids, which contain an amino group and carboxyl group. Amino acids exist as dipolar ions at neutral pH and can form peptide bonds. The 20 amino acids are classified based on polarity and charge of their R groups. Disulfide bonds and different structural levels of proteins are also mentioned.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
15 просмотров10 страницIntroduction To Amino Acids and Proteins - 1 - (Autosaved)
Загружено:
Twaiba AdmaniThis document discusses protein chemistry and the structure and functions of proteins and their building blocks, amino acids. It covers the 20 common amino acids, their classification, structures, and ionization properties. Key points include that proteins are made of amino acids, which contain an amino group and carboxyl group. Amino acids exist as dipolar ions at neutral pH and can form peptide bonds. The 20 amino acids are classified based on polarity and charge of their R groups. Disulfide bonds and different structural levels of proteins are also mentioned.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 10
Protein chemistry
Learning goals
• To know different classes of proteins and their functions
• To know the structure and naming of all 20 protein amino acids
• To know the structure and properties of peptides and the particularly the structure of the
peptide bond.
• Ionization behavior of amino acids and peptides at different pH’s.
• To know the general pKa’s of amino acids: their carboxyls, aminos, the R-group weak acids.
• To know the different levels of protein structures
Functions of Proteins
Proteins perform many different functions in the body
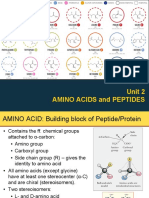
Amino Acids
• are the building blocks of proteins.
• contain a carboxylic acid group and an amino group on the
alpha () carbon.
• Each AA contain a different side group (R).
• Amino acids in solution at neutral pH exist predominantly
as dipolar ions
• Also called zwitterions if the number of positive and
negative charges are equal).
• In the dipolar form, the amino group is protonated (-NH3+) and
the carboxyl group is deprotonated (-COO-).
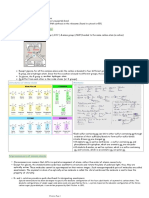
• The ionization state of an amino acid varies with pH
Ionization of amino acids state as a function of pH
Classification of Amino
•
Acids
There are 20 common amino acids found in human proteins.
• The 20 AA’s are classified into five groups based on polarity and charge of the R group
i. Non– polar aliphatic R- groups
ii. Polar uncharged R groups
iii. Aromatic R groups
iv. Positively charged R groups
v. Negatively Charged R groups
• Glycine in non-chiral
• Proline – imino acid (five membered ring
structure, rigid in confirmation): the amino
group is secondary not primary as other
amino acids
• The hydrocarbon R groups in Ala, Val, Leu,
Met and Ile , often involved in hydrophobic
interaction for stabilizing protein structure
+
• Disulfide bonds: SH group of two Cys in proteins can be oxidized to form a
covalent disulfide bond
• Disulfide bonds play special role in the structures of many proteins by
forming covalent links
• Phe & Tyr: Benzene rings
• Tryptophan: indole ring
• The OH- group in Tyr is an important
funtional group in proteins
(Phosphorylation, hydrogenation etc)
• NB: Phe is purely hydrophobic, whereas
Tyr and Trp are less so coz of their OH
and NH groups.
Aromatic cpds Contain conjugated planar ring systems with delocalized pi
electron clouds instead of discrete alternating single and double bonds
Вам также может понравиться
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionОт EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2)
- Amino AcidsДокумент17 страницAmino AcidsANAND sОценок пока нет
- Aminoacidclassification 150616095122 Lva1 App6892Документ50 страницAminoacidclassification 150616095122 Lva1 App6892Archisman Mukherjee FAPSIANОценок пока нет
- BIO 203 Biochemistry I by Seyhun YURDUGÜL, PH.D.: The Chemistry of Amino AcidsДокумент54 страницыBIO 203 Biochemistry I by Seyhun YURDUGÜL, PH.D.: The Chemistry of Amino AcidsYasin Çağrı KılıçerОценок пока нет
- Theory 1127762Документ25 страницTheory 1127762Shirin GulОценок пока нет
- Lecture 4 Amino AcidsДокумент32 страницыLecture 4 Amino AcidsShorif Ahmed100% (2)
- Amino Acids: Mehwish NawazДокумент45 страницAmino Acids: Mehwish NawazMehwish NawazОценок пока нет
- 01 Amino AcidsДокумент22 страницы01 Amino AcidsFatish BanguraОценок пока нет
- Protein Merged (DR Addis)Документ825 страницProtein Merged (DR Addis)Gashaw DestaОценок пока нет
- Amino Acids and PeptidesДокумент35 страницAmino Acids and PeptidesJim Jose AntonyОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry 3 PDFДокумент101 страницаBiochemistry 3 PDFDBT2A F1055 KALISVARIОценок пока нет
- Csir-Ugc NetДокумент205 страницCsir-Ugc NetCogvid ProjectОценок пока нет
- Amino AcidДокумент29 страницAmino AcidNurhayati HasanahОценок пока нет
- Amino Acids: SY: 2020-2021 Prof. Joy Z. AvanteДокумент35 страницAmino Acids: SY: 2020-2021 Prof. Joy Z. AvanteJohn Raniel IsidroОценок пока нет
- Amino Acids: SY: 2020-2021 Prof. Joy Z. AvanteДокумент35 страницAmino Acids: SY: 2020-2021 Prof. Joy Z. AvanteJohn Raniel IsidroОценок пока нет
- 5 Asam Amino PDFДокумент76 страниц5 Asam Amino PDFputri zelОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1 Biochemistry 2023-2024Документ26 страницLecture 1 Biochemistry 2023-2024fatimakareem0623Оценок пока нет
- Proteins, Peptides and Amino AcidsДокумент50 страницProteins, Peptides and Amino AcidsJawad AliОценок пока нет
- Amino AcidsДокумент33 страницыAmino AcidsANAND sОценок пока нет
- Biochem - Chapter 2 - Amino AcidsДокумент37 страницBiochem - Chapter 2 - Amino AcidsRayonesh RayanaОценок пока нет
- 4a ProteinДокумент37 страниц4a ProteinblezyjoymОценок пока нет
- 2022 - B353 - L1 - Amino Acids 1Документ19 страниц2022 - B353 - L1 - Amino Acids 1nemanashimitahОценок пока нет
- Biochem Module 3 - Amino AcidsДокумент15 страницBiochem Module 3 - Amino AcidsAnothando GobaОценок пока нет
- Proteins and Amino AcidsДокумент53 страницыProteins and Amino Acidssash34Оценок пока нет
- Unit 2 Amino Acids and PeptidesДокумент23 страницыUnit 2 Amino Acids and PeptidesAndrei PusungОценок пока нет
- Proteins and Amino AcidsДокумент50 страницProteins and Amino Acidsraddag100% (2)
- Amino Acids, Peptides, and ProteinsДокумент26 страницAmino Acids, Peptides, and Proteinsabdullah aliОценок пока нет
- ProteinsДокумент106 страницProteinscpagente01Оценок пока нет
- Protein StructureДокумент16 страницProtein StructurecarnevermelhaОценок пока нет
- L02 - Amino AcidsДокумент33 страницыL02 - Amino AcidsLeroy ChengОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry Chapter 4Документ16 страницBiochemistry Chapter 4Jayson AguilarОценок пока нет
- Structure of Amino AcidsДокумент32 страницыStructure of Amino AcidswithneyОценок пока нет
- Amino Acids and PeptidesДокумент40 страницAmino Acids and PeptidesDaniel LuchendoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 - ProteinДокумент34 страницыChapter 3 - ProteinPJ1-0619 Florence Binti IstemОценок пока нет
- Amino Acids and ProteinsДокумент62 страницыAmino Acids and ProteinsSolar Adhikari100% (1)
- Chapter 3: Amino Acids & Peptides: Dr. Bacolod, Chuckie Miguel A. Silliman University Medical SchoolДокумент30 страницChapter 3: Amino Acids & Peptides: Dr. Bacolod, Chuckie Miguel A. Silliman University Medical SchoolThea Cheruve TomentosОценок пока нет
- Bio Chemistry Lecture NotesДокумент26 страницBio Chemistry Lecture Notesshavindrap2000Оценок пока нет
- Chem (Lec) Reviewer ProteinsДокумент14 страницChem (Lec) Reviewer Proteinsjomorales7298pamОценок пока нет
- Structures of Amino AcidsДокумент32 страницыStructures of Amino AcidsUsman GhaniОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1 - Aminoacids. Peptides. ProteinsДокумент33 страницыLecture 1 - Aminoacids. Peptides. ProteinsEiad SamyОценок пока нет
- Lif101 6Документ34 страницыLif101 6Shubham MauryaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 - Amino Acids Peptides & ProteinsДокумент43 страницыChapter 3 - Amino Acids Peptides & Proteinsdaniel3676Оценок пока нет
- 3 Amino AcidsДокумент25 страниц3 Amino AcidsrlznrecurОценок пока нет
- Click To Edit Master Title Style: Lecture 1: Introduction To Medical Biochemistry and Protein ChemistryДокумент36 страницClick To Edit Master Title Style: Lecture 1: Introduction To Medical Biochemistry and Protein ChemistryMohammed EzzatОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Introduction To ProteinsДокумент43 страницыChapter 5 Introduction To Proteinstania.delafuenteОценок пока нет
- Amino Acid ClassificationДокумент26 страницAmino Acid ClassificationAloke SahaОценок пока нет
- Amino AcidsДокумент21 страницаAmino AcidsIsabella LopezОценок пока нет
- Chapter3 Without VOДокумент62 страницыChapter3 Without VOrmf92r4wbrОценок пока нет
- Protein FileДокумент7 страницProtein FilePhia JesalvaОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry Chapter III PROTEINДокумент137 страницBiochemistry Chapter III PROTEINJonnel BarcelaОценок пока нет
- 13 Proteins and Nucleic AcidsДокумент27 страниц13 Proteins and Nucleic AcidsJerik ChristofferОценок пока нет
- Amino AcidsДокумент94 страницыAmino AcidsDr.Santosh Kumar100% (3)
- Lec 6Документ27 страницLec 6Sreemanti DeyОценок пока нет
- BCH 201 Amino Acids and Titration Curve 2-1-1Документ52 страницыBCH 201 Amino Acids and Titration Curve 2-1-1JoyОценок пока нет
- Amino Acids & Proteins Chemistry-2017Документ212 страницAmino Acids & Proteins Chemistry-2017ShadowStormОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 - ProteinsДокумент115 страницChapter 3 - ProteinsOlsen TrinidadОценок пока нет
- Module On Amino Acids Proteins 1st Sem 21 22Документ44 страницыModule On Amino Acids Proteins 1st Sem 21 22Balangat Regine L.Оценок пока нет
- BSC 450 CH 3 NotesДокумент22 страницыBSC 450 CH 3 NotesMaddie NОценок пока нет
- Unit Ii Amino Acids and Their Characteristics: Karthika Gopakumar TF, CBT Anna UniversityДокумент27 страницUnit Ii Amino Acids and Their Characteristics: Karthika Gopakumar TF, CBT Anna Universitysharon123456manjuОценок пока нет
- Summary of Proteins (Biochemistry)Документ12 страницSummary of Proteins (Biochemistry)Xie LianОценок пока нет
- Solution EquilibriumДокумент55 страницSolution EquilibriumTwaiba AdmaniОценок пока нет
- Chemical Equilibrium - Le Chatliers PrincipleДокумент37 страницChemical Equilibrium - Le Chatliers PrincipleTwaiba AdmaniОценок пока нет
- Business Unit 2 Part 2Документ45 страницBusiness Unit 2 Part 2Twaiba AdmaniОценок пока нет
- Maarya Jan2021 FeesДокумент2 страницыMaarya Jan2021 FeesTwaiba AdmaniОценок пока нет
- Business Unit 2 Notes Part 1Документ25 страницBusiness Unit 2 Notes Part 1Twaiba AdmaniОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 Notes BiologyДокумент117 страницUnit 1 Notes BiologyTwaiba AdmaniОценок пока нет
- Dulux Firepro Epoxy Intumescent Application GuideДокумент10 страницDulux Firepro Epoxy Intumescent Application GuideAlpha DekoОценок пока нет
- LOVIBOND Reagents Suited For HachДокумент6 страницLOVIBOND Reagents Suited For HachKacem BenaoumeurОценок пока нет
- Finalreport PDFДокумент47 страницFinalreport PDFNelCamHerОценок пока нет
- Bits F111-Course HandoutДокумент3 страницыBits F111-Course HandoutPPОценок пока нет
- Aircraft Materials BrochureДокумент6 страницAircraft Materials BrochureAdnan ColoОценок пока нет
- MSDS Songnox - 1680Документ8 страницMSDS Songnox - 1680Seshagiri KalyanasundaramОценок пока нет
- Desalination Technologies, 4th Level, ERE414, 2023, ChapterДокумент49 страницDesalination Technologies, 4th Level, ERE414, 2023, ChapterMohamed HatemОценок пока нет
- Lignocellulosic Biomass A Sustainable Platform For Production of Bio-Based - Isikgor2015 PDFДокумент62 страницыLignocellulosic Biomass A Sustainable Platform For Production of Bio-Based - Isikgor2015 PDFNatasha Mgt JoharОценок пока нет
- TSO C72cДокумент6 страницTSO C72cRobert FlorezОценок пока нет
- Alloy 276 Spec SheetДокумент3 страницыAlloy 276 Spec SheetermusatОценок пока нет
- ARMENANTE Ny Adsorption With Granular Activated Carbon PDFДокумент103 страницыARMENANTE Ny Adsorption With Granular Activated Carbon PDFpippo2378793Оценок пока нет
- Acacia ReactorДокумент11 страницAcacia ReactorPedrin Cha OlivosОценок пока нет
- Fuel Cells Article in ISOFT by Inderraj GulatiДокумент6 страницFuel Cells Article in ISOFT by Inderraj GulatiInderraj_Gulati100% (1)
- 1.TDS MIXO Plast D100Документ2 страницы1.TDS MIXO Plast D100mohamed ragabОценок пока нет
- AQA GCSE Chem Combined End of Topic C1Документ9 страницAQA GCSE Chem Combined End of Topic C1joeОценок пока нет
- Science10 Q4 M3 W5 6 1Документ10 страницScience10 Q4 M3 W5 6 1Reyydell DelimaОценок пока нет
- Capillary Elevation in Capillary TubesДокумент2 страницыCapillary Elevation in Capillary TubesJeffries ThabangОценок пока нет
- Bomba Goulsd Ic-125Документ3 страницыBomba Goulsd Ic-125ELMERОценок пока нет
- Lab 4: An Acyclic Process ObjectivesДокумент1 страницаLab 4: An Acyclic Process ObjectivesFnur FatihahОценок пока нет
- Radio-Analytical TechniquesДокумент30 страницRadio-Analytical TechniquesMohammad Zamir TaqwaОценок пока нет
- Catalyst: Generalized Expression For The Effectiveness Factor of Porous PelletsДокумент3 страницыCatalyst: Generalized Expression For The Effectiveness Factor of Porous PelletsEduardo Antonio Burgos RuidíasОценок пока нет
- BS en 10222-2 - 2017 PDFДокумент32 страницыBS en 10222-2 - 2017 PDFАртем Титов75% (4)
- Lydia 1-S2.0-S0022391320301669-MainДокумент9 страницLydia 1-S2.0-S0022391320301669-MainCherifОценок пока нет
- Herbert Brown and Edward N. Peters' : Abstract: 80% or (503 000)Документ5 страницHerbert Brown and Edward N. Peters' : Abstract: 80% or (503 000)Liz HansОценок пока нет
- Alphabetic List of Iran Refinery Plant PDFДокумент108 страницAlphabetic List of Iran Refinery Plant PDFBambang Kardito100% (1)
- ChemicalsДокумент72 страницыChemicalsMrudulaОценок пока нет
- Attachment - 1 Document No. 081113B-CL-303-R0 Permissible Elastic Bend Limit Calculation (48in Hassyan Gas Pipeline Location Class 4)Документ4 страницыAttachment - 1 Document No. 081113B-CL-303-R0 Permissible Elastic Bend Limit Calculation (48in Hassyan Gas Pipeline Location Class 4)ISRAEL PORTILLOОценок пока нет
- Entropy Examples and EquationsДокумент2 страницыEntropy Examples and EquationsRome BautistaОценок пока нет
- Separating Solids From LiquidsДокумент4 страницыSeparating Solids From LiquidsRizal RusydiОценок пока нет