Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Clinical Chem Presentation On Beta Enolase
Загружено:
Marina Bridgemohan0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
67 просмотров18 страницОригинальное название
clinical chem presentation on beta enolase
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
67 просмотров18 страницClinical Chem Presentation On Beta Enolase
Загружено:
Marina BridgemohanАвторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 18
What is beta enolase deficiency?
• It is a autosomal recessive disorder and a new
metabolic myopathy of distal glycolysis that it is
caused by a deficiency of the enzyme beta enolase.
Characteristics of the enzyme
• The enzyme beta-enolase is present in skeletal and
heart muscle so its known as a muscle specific enzyme.
• enolase is the enzyme catalyzing the ninth step of
glycolysis, the mechanism.
• involves the transfer of a phosphoryl group from
phosphoenolpyruvate which are formed by the actions
of enolase in the glycolysis i.e. is the conversion of 2-
phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate.
• It is a dimeric enzyme which exists in different
isoforms resulting from various combinations of
three subunits, alpha, gamma and beta
• Enolase is a enzyme catalying the ninth step in the of
the glycolytic pathway
• over 90% of enolase activity is accounted for by
the beta-enolase subunit
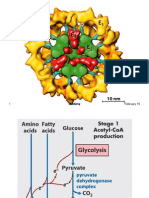
Role in the glycolytic pathway
Role in glycolosis
Enolase enyzme Beta unit of enolase enzyme
Causes
• Genetic conditions (mutation)
• Metabolic conditions (The optimum pH for this
enzyme is 6.5)
• Congenital conditions (at birth)
Genetic conditions
• inherited as autosomal recessive traits
• The beta subunit is encoded by a gene (ENO3) on
chromosome 17.
• Glycogen storage disease XIII (GSD13) has defects in
the ENO3 gene at locus 17pter-p12 coding for beta-
enolase.
• The decreased expression of ENO3 may be
associated with its role in glycolysis, and potentially
suggests a reduced requirement for energy.
Epidemiology
• GSD XIII is still represented:
• Discovered in 2001
• by a single patient, a 47-year-old Italian man with
adult onset
• chronically elevated serum creatine kinase.
• No rise of serum lactate was observed
• observed with the ischemic forearm exercise
• Ultrastructural analysis showed focal sarcoplasmic
accumulation of glycogen beta particles
Signs and symptoms
• Beta enolase deficiency includes the 6 symptoms
listed below:
• Myalgia (muscle pain)
• Exercise intolerance
• Muscle weakness
• Easy muscle fatigue
Myalgia (muscle pain)
Muscle weakness
Muscle weakness
Relationship with other disease
• β-Enolase protein plays a major role and also acts as
marker in many disorders such as
• Rhabdomyosarcoma,
• Muscular Dystrophy
• Congenital Dystrophy
• Epistaxis,
• Osteosarcoma
• Malaria
• Acute Myocardial Infarction
• Pneumoniae
• Also beta enolase is progressive in muscular
dystrophy and other neuromuscular diseases. But no
evidence it there to say it is the actual cause of these
deficiency
Treatment
• The important mechanism in treating any disease is
targeting the malfunctioning protein structure with
suitable ligands also known as potential drug
candidates
• Nonaethylene Glycol was found to be the best ligand
which returned an Energy value of -95.82
• Nonaethylene Glycol could be acted as a potential
drug candidate against β-Enolase protein.
Diagnosis
• Elevated creatine kinase
• High 2-phosphoglycerate
• Low phosphoenolpyruvate
• Absence of pyruvic acids
Вам также может понравиться
- Hepatic Encephalopathy, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandHepatic Encephalopathy, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Subcellular Organelles DiseasesДокумент38 страницSubcellular Organelles DiseasesAttiba RizwanОценок пока нет
- Enzymology Medics 2011 5 (Compatibility Mode)Документ8 страницEnzymology Medics 2011 5 (Compatibility Mode)TennidoxОценок пока нет
- The Steroidogenic PathwayДокумент47 страницThe Steroidogenic Pathwaysusan64Оценок пока нет
- Inborn Error of Metabolism - ايهДокумент74 страницыInborn Error of Metabolism - ايهAyaОценок пока нет
- Progeria Park Ref Zel AdreДокумент47 страницProgeria Park Ref Zel AdreAbdullah FaisalОценок пока нет
- Iem - LectureДокумент73 страницыIem - LectureAmirhossein SheikhiОценок пока нет
- Nsaids: On Teroidal Nti Nflammatory RugДокумент61 страницаNsaids: On Teroidal Nti Nflammatory RugNdayishimiye ErnestОценок пока нет
- Inherited Metabolic Disorders Are Genetic Conditions That Result in Metabolism ProblemsДокумент10 страницInherited Metabolic Disorders Are Genetic Conditions That Result in Metabolism ProblemsLance CornistaОценок пока нет
- Genetic Toxic and Acquired Metabolic DiseasesДокумент37 страницGenetic Toxic and Acquired Metabolic DiseasesQuenee Joyce CabelloОценок пока нет
- Drugs Affecting EndocrineДокумент17 страницDrugs Affecting Endocrinemusamugabazi68Оценок пока нет
- Non Steroidal Anti Inflammatory Drugs: NsaidsДокумент58 страницNon Steroidal Anti Inflammatory Drugs: NsaidsmahamoudОценок пока нет
- Inborn Errors in MetabolismДокумент18 страницInborn Errors in MetabolismAkhil Hothi100% (1)
- Disorders of Glycogen Metabolism: Glycogen Storage Disease Dr. George WandoloДокумент23 страницыDisorders of Glycogen Metabolism: Glycogen Storage Disease Dr. George WandoloVel VicОценок пока нет
- University of Gujrat: Amina Tariq 17161560-015 Metabolism 25 APRIL 2019Документ4 страницыUniversity of Gujrat: Amina Tariq 17161560-015 Metabolism 25 APRIL 2019Amina TariqОценок пока нет
- Endothelial Dysfunction in Diabetic Erectile DysfunctionДокумент11 страницEndothelial Dysfunction in Diabetic Erectile DysfunctionILham SyahОценок пока нет
- AndrogensДокумент63 страницыAndrogensSantu Prashu0% (1)
- Maple Syrup Urine Disease (Msud)Документ8 страницMaple Syrup Urine Disease (Msud)Syed HanzalaОценок пока нет
- Adrenal Gland Physiology DR MMДокумент52 страницыAdrenal Gland Physiology DR MMP.D. MihirangaОценок пока нет
- Nitric Oxide: Dr. Abrar M Babateen Clinical Nutrition Department Faculty of Applied Medical SciencesДокумент25 страницNitric Oxide: Dr. Abrar M Babateen Clinical Nutrition Department Faculty of Applied Medical SciencesTasneem KutbiОценок пока нет
- 1st Year FND21, BIOCHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF CELL-II - 24022021Документ26 страниц1st Year FND21, BIOCHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF CELL-II - 24022021Egg TorОценок пока нет
- Inborn Error of MetabolismДокумент16 страницInborn Error of MetabolismIvy NОценок пока нет
- 863 Clinical Importance of EnzymesДокумент20 страниц863 Clinical Importance of EnzymesNickson WafulaОценок пока нет
- Congenital Adrenal HyperplasiaДокумент27 страницCongenital Adrenal HyperplasiaJunbek nov23Оценок пока нет
- Pyruvate Dehydrogenase LectureДокумент34 страницыPyruvate Dehydrogenase LectureFerasKarajehОценок пока нет
- Diabetic Neuropathy - Clinical and ManagementДокумент58 страницDiabetic Neuropathy - Clinical and ManagementChristian ThamОценок пока нет
- Glycogen Storage Disease (GSD) Type IVДокумент26 страницGlycogen Storage Disease (GSD) Type IVAnonymous t5TDwdОценок пока нет
- Therapy of Diabetic Neuropathy With MecobalaminДокумент29 страницTherapy of Diabetic Neuropathy With MecobalaminKristina FergusonОценок пока нет
- New Estrogen and ProgesteroneДокумент39 страницNew Estrogen and ProgesteroneWegrimel AriegaraОценок пока нет
- Androgens, Anabolic Steroids and Antiandrogens: Dr. D. K. Brahma Department of Pharmacology NEIGRIHMS, ShillongДокумент16 страницAndrogens, Anabolic Steroids and Antiandrogens: Dr. D. K. Brahma Department of Pharmacology NEIGRIHMS, ShillongAbhijeet BhagatОценок пока нет
- Peripheral Nerve and Muscular WeaknessДокумент17 страницPeripheral Nerve and Muscular WeaknessSamuel kuriaОценок пока нет
- Anemia: Erythropoietin DeficiencyДокумент14 страницAnemia: Erythropoietin DeficiencyHaifa ibrahimОценок пока нет
- Adrenocorticosteroids & Adrenocortical Antagonists: Namwase Hadijja KatabiraДокумент77 страницAdrenocorticosteroids & Adrenocortical Antagonists: Namwase Hadijja KatabiraSamson100% (1)
- Topic Menopause and AdrenopauseДокумент88 страницTopic Menopause and AdrenopauseWikrom Keng WromKiОценок пока нет
- Seminar MenopauseДокумент51 страницаSeminar MenopauseKelvin SuОценок пока нет
- NsaidДокумент51 страницаNsaidDebasis Sahoo100% (1)
- Hormon AdrenalДокумент76 страницHormon AdrenalgitafazaОценок пока нет
- Glycogen Storage Disease (GSD) Type IVДокумент26 страницGlycogen Storage Disease (GSD) Type IVAnonymous t5TDwdОценок пока нет
- Genetics of Metabolic Disorders IДокумент17 страницGenetics of Metabolic Disorders IGagan DhaliwalОценок пока нет
- Curriculum Vitae: Nama: Natsir Akil Riwayat PendidikanДокумент50 страницCurriculum Vitae: Nama: Natsir Akil Riwayat PendidikanSelica ErlindiОценок пока нет
- Neurophysiology & NeurotoxicologyДокумент5 страницNeurophysiology & NeurotoxicologyTaufik PamisОценок пока нет
- Alzheimer's Disease: SymptomsДокумент8 страницAlzheimer's Disease: Symptomsbosun88Оценок пока нет
- Concepts of Andropause Subject SemДокумент55 страницConcepts of Andropause Subject SemSyam RJОценок пока нет
- Glycogen Sto DisДокумент41 страницаGlycogen Sto DisMidhun BalajiОценок пока нет
- Pathology Biochemical and Molecular Basis of Some Mendelian DisordersДокумент5 страницPathology Biochemical and Molecular Basis of Some Mendelian DisordersAmna Baig0% (1)
- Inborn Errors of Amino Acid Metabolism: (Advanced Nutrition)Документ8 страницInborn Errors of Amino Acid Metabolism: (Advanced Nutrition)Deepshikha PatelОценок пока нет
- Isoenzymes Multienzyme ComplexДокумент20 страницIsoenzymes Multienzyme ComplexAnisam Abhi100% (2)
- Drugs Affecting Reproduction: DR - R - PrameelaДокумент76 страницDrugs Affecting Reproduction: DR - R - PrameelaRamadi PrameelaОценок пока нет
- Glycogen Storage DiseaseДокумент19 страницGlycogen Storage DiseaseRold Brio SosОценок пока нет
- SteroidsДокумент25 страницSteroidsalhusien.abd2000Оценок пока нет
- Motor Neurone Disease: J GormallyДокумент14 страницMotor Neurone Disease: J GormallyBambang SutrisnoОценок пока нет
- CorticosteroidsДокумент40 страницCorticosteroidsBusy worldОценок пока нет
- Noshaba MSДокумент3 страницыNoshaba MSKb AliОценок пока нет
- Journal Club: Paolo Dametto January 2013Документ42 страницыJournal Club: Paolo Dametto January 2013Олег ЕвсюковОценок пока нет
- Biological Importance of Enzymes 254263Документ11 страницBiological Importance of Enzymes 254263Musharaf RehmanОценок пока нет
- Female Sex HormonesДокумент28 страницFemale Sex HormonesAbdimalik AliОценок пока нет
- Alzheimer's DiseaseДокумент29 страницAlzheimer's DiseaseKeVz Nicdao100% (1)
- Gonadal Hormones 62594Документ98 страницGonadal Hormones 62594TES SENОценок пока нет
- Uremic EncephalophatyДокумент48 страницUremic EncephalophatySindi LadayaОценок пока нет
- Adrenal Gland Physiology (DRДокумент77 страницAdrenal Gland Physiology (DRapi-3769252100% (4)
- Surgical Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux in Adults - UpToDateДокумент22 страницыSurgical Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux in Adults - UpToDateJuan InsignaresОценок пока нет
- DKA Handout1Документ59 страницDKA Handout1aleОценок пока нет
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2017-18Документ3 страницыGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2017-18raj royelОценок пока нет
- Physics and Imaging in Radiation OncologyДокумент6 страницPhysics and Imaging in Radiation Oncologydarr artОценок пока нет
- Patient Information Leaflet: (Etonogestrel)Документ4 страницыPatient Information Leaflet: (Etonogestrel)A VHRSEОценок пока нет
- Salmonella Typhi 2012Документ60 страницSalmonella Typhi 2012Mohd Syaiful Mohd ArisОценок пока нет
- Endodontics Pain Control in Endodontics: Differential Diagnosis of Dental PainДокумент4 страницыEndodontics Pain Control in Endodontics: Differential Diagnosis of Dental Painريام الموسويОценок пока нет
- Paramedic Pediatric Scenario 2017Документ3 страницыParamedic Pediatric Scenario 2017Chad StreetОценок пока нет
- Pedia Nursing Resource Unit - FinalДокумент69 страницPedia Nursing Resource Unit - FinalDaryl Adrian RecaidoОценок пока нет
- Axa Group Corporate PresentationДокумент35 страницAxa Group Corporate PresentationRajneesh VermaОценок пока нет
- Insulin SensitizersДокумент17 страницInsulin SensitizersGautam SharmaОценок пока нет
- An Unconscious Patient With A DNR TattooДокумент2 страницыAn Unconscious Patient With A DNR TattoonadaОценок пока нет
- Case Study 5 Dengue Fever CorrectedДокумент13 страницCase Study 5 Dengue Fever CorrectedyounggirldavidОценок пока нет
- Minor AilmentsДокумент14 страницMinor AilmentsGazala100% (1)
- Essential Oils Pocket Reference - Fifth EditionДокумент206 страницEssential Oils Pocket Reference - Fifth Editionbianca7893% (88)
- Autism Recovery CHINESE 2018.10.23 PDFДокумент245 страницAutism Recovery CHINESE 2018.10.23 PDFcelinescuwgОценок пока нет
- HNPДокумент47 страницHNPSyifa RabiahОценок пока нет
- The GINA 2019 Asthma Treatment Strategy For Adults and Adolescents 12... Download Scientific DiagramДокумент1 страницаThe GINA 2019 Asthma Treatment Strategy For Adults and Adolescents 12... Download Scientific DiagramFatih AryaОценок пока нет
- Worksheet TherapyДокумент2 страницыWorksheet TherapymermerytaОценок пока нет
- Mental Rubrics by Farookh MasterДокумент589 страницMental Rubrics by Farookh MasterPranesh Peter91% (22)
- Pathophysiology of InflammationДокумент50 страницPathophysiology of InflammationElla Jones0% (1)
- An Approach To A Floppy InfantДокумент33 страницыAn Approach To A Floppy InfantayunisallehОценок пока нет
- Multiple Personality Disorder: Is It Fact or Fiction?: Deguzman 1Документ10 страницMultiple Personality Disorder: Is It Fact or Fiction?: Deguzman 1Eliza Philline De GuzmanОценок пока нет
- Complications of Insulin TherapyДокумент16 страницComplications of Insulin TherapyIngrid NicolasОценок пока нет
- PMLS Lesson 5Документ7 страницPMLS Lesson 5Althea EspirituОценок пока нет
- BLOOD DONATION (Autosaved)Документ11 страницBLOOD DONATION (Autosaved)Anisa Fitri RachmaОценок пока нет
- Textbook of Gynaecological OncologyДокумент58 страницTextbook of Gynaecological OncologyMarco Vinicio Benavides Osorto100% (2)
- Drugs Used in Heart FailureДокумент33 страницыDrugs Used in Heart FailureLynx Kee Bayating100% (1)
- Guia NICE 2011 AutismoДокумент51 страницаGuia NICE 2011 Autismomecho9002Оценок пока нет
- Medication AdministrationДокумент8 страницMedication AdministrationMarku LeeОценок пока нет