Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Grammar Unit 31
Загружено:
api-38261990 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
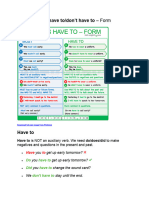
408 просмотров18 страницHave to and must Agenda Learning Objectives Example Set A for where to use 'have to'. Example Set B for comparing must with have to. Example Set C for comparing Mustn't and don't have. Example Set D for using have got to instead of have to.
Исходное описание:
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документHave to and must Agenda Learning Objectives Example Set A for where to use 'have to'. Example Set B for comparing must with have to. Example Set C for comparing Mustn't and don't have. Example Set D for using have got to instead of have to.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
408 просмотров18 страницGrammar Unit 31
Загружено:
api-3826199Have to and must Agenda Learning Objectives Example Set A for where to use 'have to'. Example Set B for comparing must with have to. Example Set C for comparing Mustn't and don't have. Example Set D for using have got to instead of have to.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 18
Grammar – Unit 31
Have to and must
Agenda
Learning objectives
Example Set A for where to use ‘have to’.
Example Set B for comparing must with have to.
Example Set C for comparing Mustn’t and don’t have .
Example Set D for using have got to instead of have to
Have to and must 2
Agenda
Learning objectives
Example Set A for where to use ‘have to’.
Example Set B for comparing must with have to.
Example Set C for comparing Mustn’t and don’t have .
Example Set D for using have got to instead of have to
Have to and must 3
Learning Objectives
Where to use have to.
Comparing have to and must.
Comparing mustn’t and don’t have.
Use of have got to instead of have to.
Have to and must 4
Agenda
Learning objectives
Example Set A for where to use ‘have to’.
Example Set B for comparing must with have to.
Example Set C for comparing Mustn’t and don’t have .
Example Set D for using have got to instead of have to
Have to and must 5
Example Set A
I have to do something = it is necessary
You have to turn left here.
to do it, I am obliged to do it;
You can’t turn right here. You have
to turn left.
I have to wear glasses for reading.
George can’t come out with us this evening.
He has to work late.
Last week Tina broke her arm and had to go to
hospital.
I haven’t had to go to the doctor for ages
Have to and must 6
Continue ….
We use do/does/did in questions and negative sentences ( for the
present and past simple):
What do I have to do to get a new driving license? (not What
have I to do?)
Karen doesn’t have to work Saturdays. (not Karen hasn’t to)
Why did you have to leave early?
Have to and must 7
Continue
You can use have to with will and might/may:
If the pain gets worse, you’ll have to go to the doctor.
I might have to work late tomorrow evening. or I may have to
work…
(= it’s possible that I will have to)
Have to and must 8
Agenda
Learning objectives
Example Set A for where to use ‘have to’.
Example Set B for comparing must with have to.
Example Set C for comparing Mustn’t and don’t have .
Example Set D for using have got to instead of have to
Have to and must 9
Example Set B
Must is similar to have to:
It’s later than I thought. I must go. or I have to go.
You can use must to give your own opinion (for example, to say what
you think is necessary, or to recommend someone to do
something).
Have to and must 10
Continue
Have to is also possible:
I haven’t spoken to Sue for ages. I must phone her. ( =I say this
is necessary)
Mark is a really nice person. You must meet him. (I recommend
this)
Have to and must 11
Continue ….
We use have to (not must) to say what someone is obliged to do. The
speaker is not giving his/her own opinion:
I have to work from 8.30 to 5.30 every day. (a fact, not an
opinion)
Jane has to travel a lot for her work.
Have to and must 12
Continue ….
But must is often used in written rules and instructions:
Applications for the job must be received by 18 May.
(exam instruction) You must write your answers in ink.
You cannot use must to talk about the past:
We had to leave early. (not we must)
Have to and must 13
Agenda
Learning objectives
Example Set A for where to use ‘have to’.
Example Set B for comparing must with have to.
Example Set C for comparing Mustn’t and don’t have .
Example Set D for using have got to instead of have to
Have to and must 14
Example Set C
Mustn’t and don’t have to are completely different:
You mustn’t do something =it is necessary You don’t have to do something =
that you do not do it (so don’t do it): you don’t need to do it (but you can if
you want):
You must keep it a secret. You
mustn’t tell anyone. (=don’t tell You don’t have to tell him,
anyone) but you can If you want to.
I promised I would be on time. I don’t have to be at the
I mustn’t be late. (=I must be meeting, But I think I’ll go
on time) anyway.
Have to and must 15
Agenda
Learning objectives
Example Set A for where to use ‘have to’.
Example Set B for comparing must with have to.
Example Set C for comparing Mustn’t and don’t have .
Example Set D for using have got to instead of have to
Have to and must 16
Example Set D
You can use have got to instead of have to. So you can say:
I’ve got to work tomorrow. Or I have to work tomorrow
When has Liz got to go? or When does Liz have to go?
Have to and must 17
Summary
Learning objectives
Example Set A for where to use ‘have to’.
Example Set B for comparing must with have to.
Example Set C for comparing Mustn’t and don’t have .
Example Set D for using have got to instead of have to
Have to and must 18
Вам также может понравиться
- Grammar Unit 41Документ21 страницаGrammar Unit 41api-3826199100% (1)
- Have To and MustДокумент1 страницаHave To and MustAdrián SuárezОценок пока нет
- Unit 6: Modal Verbs Prof. Ana María MellidesДокумент22 страницыUnit 6: Modal Verbs Prof. Ana María MellidesMariolyta Llanos OdarОценок пока нет
- Have To, Must, Should-Obligation, Prohibition, Necessity, AdviceДокумент5 страницHave To, Must, Should-Obligation, Prohibition, Necessity, AdviceKenedy Omar Monroy PoconОценок пока нет
- Must-Mustn't, Have To-Don't Have ToДокумент9 страницMust-Mustn't, Have To-Don't Have ToSusana GarciaОценок пока нет
- MustДокумент5 страницMustionica porumbОценок пока нет
- A2 Grammar Modals ZarifJamalДокумент28 страницA2 Grammar Modals ZarifJamalalisinaalipoorОценок пока нет
- Obligation and SuggestionДокумент6 страницObligation and SuggestionNAN MONTES ROSALESОценок пока нет
- MODALSДокумент3 страницыMODALSMiroslava MassielОценок пока нет
- Modals of Necessity and SuggestionДокумент6 страницModals of Necessity and SuggestionMujahed BrijieahОценок пока нет
- Must, Have To, Don't Have To, Mustn'tДокумент5 страницMust, Have To, Don't Have To, Mustn'tUmay TalayОценок пока нет
- Makalah Physic TeacingДокумент10 страницMakalah Physic TeacingnindyaОценок пока нет
- Should-Shouldn't MotulДокумент10 страницShould-Shouldn't MotulOsmara CatzinОценок пока нет
- Grammar Unit 1Документ17 страницGrammar Unit 1api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Modal Verbs: Intermediate Unit 7Документ36 страницModal Verbs: Intermediate Unit 7DanielaОценок пока нет
- Present SimpleДокумент16 страницPresent Simpleanup0% (1)
- Modalverbs 130910201649 Phpapp01Документ19 страницModalverbs 130910201649 Phpapp01fiorela 13Оценок пока нет
- Grammar Unit 24Документ18 страницGrammar Unit 24api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- THEORY-must:have To: Should:ought ToДокумент3 страницыTHEORY-must:have To: Should:ought ToQuỳnh Anh LêОценок пока нет
- Must Mustn't Needn'tДокумент8 страницMust Mustn't Needn'tOsvaldo MxОценок пока нет
- 7C Grammar BankДокумент3 страницы7C Grammar BankRovshen BayramovОценок пока нет
- Grammar Unit 49Документ16 страницGrammar Unit 49api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Grammar Unit 38Документ17 страницGrammar Unit 38api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Grammar Rules Simplified: Have To, Must, Mustn't, Don't Have To, Needn't Have, Didn't Need ToДокумент1 страницаGrammar Rules Simplified: Have To, Must, Mustn't, Don't Have To, Needn't Have, Didn't Need ToLarbi NadiaОценок пока нет
- Present Continuous: Grammar Unit 1Документ15 страницPresent Continuous: Grammar Unit 1பாலரத்தினம் தமிழன்Оценок пока нет
- Should, Ought To, Had Better: Should and Ought To Are Also Used To Shows Responsibility or DutyДокумент8 страницShould, Ought To, Had Better: Should and Ought To Are Also Used To Shows Responsibility or Dutymichelle gomezОценок пока нет
- MUST Musnt Dont Have To Have ToДокумент6 страницMUST Musnt Dont Have To Have ToAgung Prasetyo WibowoОценок пока нет
- Mixed ModalsДокумент6 страницMixed ModalsMiroslava MassielОценок пока нет
- Modal Verbs (Obligation - Suggestion) Unit 8Документ9 страницModal Verbs (Obligation - Suggestion) Unit 8Alejandro QuintanaОценок пока нет
- New EraДокумент2 страницыNew EraKarim MohamedОценок пока нет
- Expressing ObligationДокумент28 страницExpressing ObligationAlfiani Mar'atussalehahОценок пока нет
- 01-Ingles-U4-7b-Teorico-Modal VerbsДокумент11 страниц01-Ingles-U4-7b-Teorico-Modal VerbsMartina CastilloОценок пока нет
- Pref - 6 - Grammar 3.6 - Revisión Del IntentoДокумент8 страницPref - 6 - Grammar 3.6 - Revisión Del IntentoJaneth SanabriaОценок пока нет
- 235 - 7 - English Grammar in Use. Murphy R., 2019, 5th, - 394p - (1) - 74-75Документ2 страницы235 - 7 - English Grammar in Use. Murphy R., 2019, 5th, - 394p - (1) - 74-75Ana BoviОценок пока нет
- Semana 16 SummaryДокумент4 страницыSemana 16 SummaryGehanire Azcona CardenasОценок пока нет
- Can, Have To, MustДокумент5 страницCan, Have To, MustLuis InaganОценок пока нет
- English, Group 1-1......Документ12 страницEnglish, Group 1-1......Maria Ruiz LinoОценок пока нет
- Must-Vs-Have-To FBДокумент3 страницыMust-Vs-Have-To FBO̾swaldo A̾rrietaОценок пока нет
- Ingles Explicacion de Todos Must Cant Have To EtcДокумент6 страницIngles Explicacion de Todos Must Cant Have To EtcMar TinОценок пока нет
- Modals of Obligation: Have To & MustДокумент25 страницModals of Obligation: Have To & MustLiizeth RuiizОценок пока нет
- Obligation & NecessityДокумент7 страницObligation & Necessitymazidah xiuОценок пока нет
- MustДокумент3 страницыMustChiosa AdinaОценок пока нет
- Grammar Unit 48Документ16 страницGrammar Unit 48api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Asking Giving SuggestionДокумент30 страницAsking Giving Suggestionhermanelly ramadhaniОценок пока нет
- Custom Avatar App by SlidesgoДокумент12 страницCustom Avatar App by SlidesgoMariia KaverinaОценок пока нет
- Have ToДокумент4 страницыHave ToIonela VieruОценок пока нет
- Must vs. Have To: Use of Must NotДокумент8 страницMust vs. Have To: Use of Must NotRuxandra PleseaОценок пока нет
- UNIT. 3.should Must Have ToДокумент14 страницUNIT. 3.should Must Have TochofsohОценок пока нет
- Modal VerbSSSSZZZZZДокумент4 страницыModal VerbSSSSZZZZZClara ArejaОценок пока нет
- Bahasa Inggris BisnisДокумент4 страницыBahasa Inggris Bisniskura bearОценок пока нет
- English Grammar Today: Must: FormsДокумент7 страницEnglish Grammar Today: Must: FormsBondfriendsОценок пока нет
- Obligation and Necessity (Modals)Документ8 страницObligation and Necessity (Modals)Muhammad Farhan100% (1)
- Modal Verbs Exercise 2Документ4 страницыModal Verbs Exercise 2Vân ChiОценок пока нет
- Grammar Models X 3Документ13 страницGrammar Models X 3A KennedyОценок пока нет
- Must, Have To, ShouldДокумент13 страницMust, Have To, Shouldoppareul1999Оценок пока нет
- Should and ShouldnДокумент2 страницыShould and ShouldnSoAliveОценок пока нет
- Podemos Usar "Can" para Hablar Sobre Posibilidades Usamos "Can" para Dar y Conceder PermisoДокумент11 страницPodemos Usar "Can" para Hablar Sobre Posibilidades Usamos "Can" para Dar y Conceder PermisosergioОценок пока нет
- UNIT 6 LEVEL III - PDF PRESENTATIONДокумент41 страницаUNIT 6 LEVEL III - PDF PRESENTATIONCindy Paola SevillaОценок пока нет
- Test My English. Intermediate. How Good Are You?: Test My English, #2От EverandTest My English. Intermediate. How Good Are You?: Test My English, #2Оценок пока нет
- Overcoming Procrastination: 44 Actionable Tips to Take Control of Your LifeОт EverandOvercoming Procrastination: 44 Actionable Tips to Take Control of Your LifeРейтинг: 2 из 5 звезд2/5 (1)
- Eng Essential Unit 17Документ2 страницыEng Essential Unit 17api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Essential Eng Unit30Документ2 страницыEssential Eng Unit30api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Essential Eng Unit14Документ2 страницыEssential Eng Unit14api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Eng Essential Unit 21Документ2 страницыEng Essential Unit 21api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Eng Essential Unit 18Документ2 страницыEng Essential Unit 18api-38261990% (1)
- Essential Eng Unit29Документ2 страницыEssential Eng Unit29api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Essential Eng Quiz Unit1Документ4 страницыEssential Eng Quiz Unit1api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Eng Essential Unit15Документ2 страницыEng Essential Unit15api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Eng Essential Unit19Документ2 страницыEng Essential Unit19api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Essential Eng Quiz Unit 3Документ2 страницыEssential Eng Quiz Unit 3api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Eng Essential Unit12Документ2 страницыEng Essential Unit12api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Grammar Unit 47Документ14 страницGrammar Unit 47api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Eng Essential Unit16Документ2 страницыEng Essential Unit16api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Essential Eng Quiz Unit2Документ7 страницEssential Eng Quiz Unit2api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Grammar Unit 50Документ15 страницGrammar Unit 50api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Eng Essential Unit8Документ2 страницыEng Essential Unit8api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Eng Essential Unit10Документ2 страницыEng Essential Unit10api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Grammar Unit 54Документ18 страницGrammar Unit 54api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Eng Essential Quiz Unit6Документ2 страницыEng Essential Quiz Unit6api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Eng Essential Quiz Unit7Документ2 страницыEng Essential Quiz Unit7api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Grammar Unit 48Документ16 страницGrammar Unit 48api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Grammar Unit 49Документ16 страницGrammar Unit 49api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Grammar Unit 53Документ18 страницGrammar Unit 53api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Eng Essential Unit5Документ3 страницыEng Essential Unit5api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Grammar Unit 38Документ17 страницGrammar Unit 38api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Grammar Unit 24Документ18 страницGrammar Unit 24api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Grammar Unit 16Документ16 страницGrammar Unit 16api-3826199Оценок пока нет
- Grammar Unit 17Документ17 страницGrammar Unit 17api-3826199100% (1)
- Excerpt From SUNDAY SUPPERS by Karen MordechaiДокумент21 страницаExcerpt From SUNDAY SUPPERS by Karen MordechaiThe Recipe Club0% (1)
- Ambalappuzha Krishna TempleДокумент1 страницаAmbalappuzha Krishna TempleManeeshОценок пока нет
- Ang Huling El Bimbo: Eraserheads/Riyalized Cover VersionДокумент2 страницыAng Huling El Bimbo: Eraserheads/Riyalized Cover VersionMichaela Bell ConcepcionОценок пока нет
- Matthew Cheah - Great Gatsby Journal - Google Docs 1Документ21 страницаMatthew Cheah - Great Gatsby Journal - Google Docs 1api-520774138Оценок пока нет
- The Day The Dancers CameДокумент8 страницThe Day The Dancers CamehyarojasguliОценок пока нет
- Emma Janes Maternity BraДокумент1 страницаEmma Janes Maternity BraforyoumumОценок пока нет
- Direct Application On Polyester Using PROsperse Disperse DyesДокумент4 страницыDirect Application On Polyester Using PROsperse Disperse DyesYanmei BiОценок пока нет
- English Module 3Документ23 страницыEnglish Module 3Rica100% (1)
- English 3 Unit 11 QUIZ NameДокумент1 страницаEnglish 3 Unit 11 QUIZ NameOllian300Оценок пока нет
- HelgaДокумент2 страницыHelgaMubashir RafiqueОценок пока нет
- Document List DrawingДокумент13 страницDocument List Drawingzat572000Оценок пока нет
- IDEO DTEdu v2 Toolkit+workbookДокумент129 страницIDEO DTEdu v2 Toolkit+workbookAdelina SilvaОценок пока нет
- Approaches To Literary CriticismДокумент2 страницыApproaches To Literary CriticismRangothri Sreenivasa SubramanyamОценок пока нет
- Manila Hankuk Academy Elementary Department 1 Semester / 2015 Writing Grade 6 Final Exam Name: - Score: - / 30 Parent's SignatureДокумент4 страницыManila Hankuk Academy Elementary Department 1 Semester / 2015 Writing Grade 6 Final Exam Name: - Score: - / 30 Parent's SignatureManila Hankuk AcademyОценок пока нет
- 1 Vocabulary VacationsДокумент7 страниц1 Vocabulary VacationsPaulina CondoriОценок пока нет
- Arts of CalabarzonДокумент2 страницыArts of Calabarzoniza suarezОценок пока нет
- Bali & Beyond Magazine December 2011Документ92 страницыBali & Beyond Magazine December 2011Bali and Beyond MagazineОценок пока нет
- Fun HomeДокумент3 страницыFun HomeJoshMooiweerОценок пока нет
- Sources and ApproachesДокумент9 страницSources and ApproachespavanОценок пока нет
- Finders Keepers: Week 1Документ1 страницаFinders Keepers: Week 1Tiso Blackstar GroupОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1-Ancient India, Raj-Ravi Verma, Indian Art FormДокумент8 страницAssignment 1-Ancient India, Raj-Ravi Verma, Indian Art FormRashi GambhirОценок пока нет
- Hatco FSHC Flav R SavorДокумент2 страницыHatco FSHC Flav R Savorwsfc-ebayОценок пока нет
- Animator Syllabus and CurriculamДокумент17 страницAnimator Syllabus and CurriculamBasavaraja B M BangaloreОценок пока нет
- Grisaille HandoutДокумент5 страницGrisaille Handoutandrewsrobert540Оценок пока нет
- JI Pitch NotationДокумент4 страницыJI Pitch NotationEl Roy M.T.Оценок пока нет
- Eating Habits in Great BritainДокумент4 страницыEating Habits in Great Britainsherylinla86% (7)
- Erotic PDF PicturesДокумент1 страницаErotic PDF PicturesCindy0% (2)
- Anglican and Episcopalian Church Music en GDДокумент19 страницAnglican and Episcopalian Church Music en GDAdrian ZambranoОценок пока нет
- Dashamgranth ChhandasДокумент12 страницDashamgranth ChhandassomapriyОценок пока нет
- G10 English Budget of Work 2nd QuarterДокумент5 страницG10 English Budget of Work 2nd Quarterryan castro100% (5)