Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Roles of Hormones
Загружено:
hafizah_90Исходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Roles of Hormones
Загружено:
hafizah_90Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Roles of Hormones
a) Explain the role of hormones during pregnancy b) Explain the role of hormones during parturition / birth process c) Explain the role of hormones during lactation
THE ROLE OF HORMONES DURING PREGNANCY
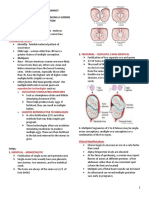
Hormonal changes during 1st trimester The chorion secretes hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) which maintains the corpus luteum, ensuring secretion of progesterone & estrogens-absence of this hormonal override during pregnancy-resulting in menstruation & loss of the embryo HCG level is so high & some is excreted in urine-its presence is the basis of a common early pregnancy test Progesterone - initiates increased mucus in the cervix ( forming a protective plug ); - stimulates growth of the maternal portion of placenta; - maintains the endometrium; - prevents ovulation & menstrual cycling; - stimulates breasts enlargement
CHAPTER : REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
THE ROLE OF HORMONES DURING PREGNANCY
Estrogens are important for development of uterus, foetus & mammary glands Starting at week 5, the chorion secretes hCG which stimulates: - secretion of estrogens & progesterone by corpus luteum; - entry of amino acids into cells of embryo ( for protein synthesis ); - development of mammary glands; - glucose & lipid metabolisms in the mother
CHAPTER : REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
THE ROLE OF HORMONES DURING PREGNANCY
Hormonal changes during 2nd trimester hCG level declines & corpus luteum deteriorates Placenta secretes own progesterone & estrogens ( maintaining pregnancy ) Hormonal changes during 3rd trimester Estrogens reach highest level during last weeks of pregnancy This will induce the birth process
CHAPTER : REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
THE ROLE OF HORMONES DURING PARTURITION / BIRTH PROCESS During pregnancy, progesterone & estrogens are secreted High level of progesterone prevents contractions of uterus ( prevents birth of immature baby ) But estrogens reach highest level during last weeks of pregnancy This triggers formation of oxytocin receptors on uterus Oxytocin - secreted by foetus & mothers posterior pituitary - stimulates contractions of uterus - stimulates placenta to secrete prostaglandins
Prostaglandins enhance contractions of uterus The contractions stimulate release of more oxytocin & prostaglandins ( +ve feedback ) Contractions become stronger & more frequent
CHAPTER : REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
THE ROLE OF HORMONES DURING PARTURITION / BIRTH PROCESS
Feedback mechanism
CHAPTER : REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
PARTURITION / BIRTH PROCESS Parturition ( birth process ) occurs as a result of the strong, rhythmic contractions ( labour ) 3 stages of parturition: i. dilation of cervix - opening up & thinning of cervix - ending with complete dilation - amnion ruptures - contractions get stronger
CHAPTER : REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
PARTURITION / BIRTH PROCESS ii. delivery of baby - continuous strong contractions force foetus down and out of the uterus & vagina - aided by mothers pushing - the umbilical cord is then cut and clamped
CHAPTER : REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
PARTURITION / BIRTH PROCESS iii. delivery of placenta - continuing contraction expel the placenta & associated membranes ( the afterbirth )
CHAPTER : REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
THE ROLE OF HORMONES DURING LACTATION
Milk production that occurs in the mammary glands
An aspect of postnatal care unique to mammals
The breasts contain mammary glands
Alveoli of mammary glands will produce milk, that is secreted into mammary ducts which open at the nipple
During pregnancy, progesterone stimulates development of mammary alveoli Estrogens stimulate development of mammary ducts
CHAPTER : REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
THE ROLE OF HORMONES DURING LACTATION
CHAPTER : REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
THE ROLE OF HORMONES DURING LACTATION
When placenta is discharged after birth, levels of estrogens & progesterone decrease This allows mothers anterior pituitary to secrete prolactin { no lactation during pregnancy since prolactin secretion is inhibited }
Prolactin stimulates mammary alveoli to produce milk ( ~ 2 days after birth )
Mammary secretion for first few days is the colostrum ( thick, yellowish fluid with high protein content & rich in maternal antibodies-IgG)
CHAPTER : REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
THE ROLE OF HORMONES DURING LACTATION
Suckling of baby stimulates the nerve endings in the nipples to send signals which trigger anterior pituitary to release more prolactin The signals also trigger posterior pituitary to release oxytocin Oxytocin stimulates contraction of smooth muscles surrounding mammary glands, thus controlling release of milk
CHAPTER : REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT
Вам также может понравиться
- Nutritional Composition of Breast MilkДокумент24 страницыNutritional Composition of Breast MilkSamuel Bagas Wahyu SantosoОценок пока нет
- Management of First Stage of LabourДокумент35 страницManagement of First Stage of LabourPragati BholeОценок пока нет
- Essential Intrapartum and Newborn Care 1Документ5 страницEssential Intrapartum and Newborn Care 1Genierose YantoОценок пока нет
- Post Natal CareДокумент94 страницыPost Natal CareZekariyas MulunehОценок пока нет
- Abnormaluterineaction 100515015711 Phpapp01Документ40 страницAbnormaluterineaction 100515015711 Phpapp01Seema Vashisht100% (1)
- Physiologic Changes of Pregnancy (Normal) : Local (I.e., Confined To The Systemic (I.e., Affecting TheДокумент9 страницPhysiologic Changes of Pregnancy (Normal) : Local (I.e., Confined To The Systemic (I.e., Affecting TheAli Longasa CortezОценок пока нет
- Baby Friendly Hospital InitiativeДокумент38 страницBaby Friendly Hospital InitiativeSudhir SinghОценок пока нет
- 02 Fertilization & ImplantationДокумент24 страницы02 Fertilization & ImplantationAugust Ridlof RiwuОценок пока нет
- Enzymes Mechanism of Enzyme ActionДокумент3 страницыEnzymes Mechanism of Enzyme Actionkl42c4300Оценок пока нет
- Prostaglandins: By: Pharm.D. InternДокумент21 страницаProstaglandins: By: Pharm.D. InternaneenaОценок пока нет
- Physiology of Pregnancy 050918Документ75 страницPhysiology of Pregnancy 050918Anonymous 96LTCx100% (2)
- PartogramДокумент20 страницPartogramKasumba ChandaОценок пока нет
- Reproductive Physiology (Female)Документ23 страницыReproductive Physiology (Female)هدى قحطان جليل100% (1)
- Exclusive Breast Feeding PDFДокумент2 страницыExclusive Breast Feeding PDFAndreaОценок пока нет
- MCN Lect Multiple Pregnancy Hydramnios PosttermДокумент5 страницMCN Lect Multiple Pregnancy Hydramnios PosttermAmethystОценок пока нет
- Feeding of High Risk Neonates: Feeding of LBW Infants: How Is It Different?Документ22 страницыFeeding of High Risk Neonates: Feeding of LBW Infants: How Is It Different?sandeepv08Оценок пока нет
- RH Disease and ABO IncompatibilityДокумент21 страницаRH Disease and ABO Incompatibilityjeezislove617Оценок пока нет
- Gavino and Aguilera (Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive Organ)Документ4 страницыGavino and Aguilera (Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive Organ)Allyne GavinoОценок пока нет
- Hormones in Human Reproduction: Group 1Документ36 страницHormones in Human Reproduction: Group 1Accel YcoОценок пока нет
- Active Management of LabourДокумент4 страницыActive Management of LabourHytham AtiaОценок пока нет
- 22 Cephalo-Pelvic DisproportionДокумент32 страницы22 Cephalo-Pelvic DisproportionNirupama KsОценок пока нет
- Newborn Assessment by DR Dahir123Документ84 страницыNewborn Assessment by DR Dahir123Najjuma BettyОценок пока нет
- Neonate: Learning Guide - 2Документ41 страницаNeonate: Learning Guide - 2osamaОценок пока нет
- Infants Nutritional NeedsДокумент5 страницInfants Nutritional NeedsSukQin KongОценок пока нет
- Male Reproductive System FinalДокумент5 страницMale Reproductive System FinalJohn Dale Lulu CruzОценок пока нет
- Fertilisation Implantation NotesДокумент4 страницыFertilisation Implantation NotesShaun JinОценок пока нет
- Exclusive Breast Milk Nutrition For Baby 0-6 Month Only !Документ4 страницыExclusive Breast Milk Nutrition For Baby 0-6 Month Only !WindayaniayuОценок пока нет
- Physiological Changes During PregnancyДокумент44 страницыPhysiological Changes During PregnancyvrutipatelОценок пока нет
- Amphibolic Nature of Krebs Cycle: How What We Are Is What We EatДокумент33 страницыAmphibolic Nature of Krebs Cycle: How What We Are Is What We EatMargaret SannohОценок пока нет
- Pregnancy Induced HypertensionДокумент52 страницыPregnancy Induced HypertensionJoy GloryОценок пока нет
- S2-OB-Maternal Physio PDFДокумент14 страницS2-OB-Maternal Physio PDFSheena PasionОценок пока нет
- Reflexes NeonatalДокумент15 страницReflexes Neonataldr parveen bathla100% (1)
- FERTILIZATIONДокумент73 страницыFERTILIZATIONSavita Hanamsagar100% (1)
- Emergency ContraceptionДокумент7 страницEmergency Contraceptionyogita_itsme7560Оценок пока нет
- Anemia in PregnancyДокумент53 страницыAnemia in PregnancysyafahalimОценок пока нет
- Female Sex HormonesДокумент20 страницFemale Sex HormonesAlina ShahОценок пока нет
- Breast Problems After DeviveryДокумент19 страницBreast Problems After DeviverySanthosh.S.UОценок пока нет
- Early Initiation of BreastfeedingДокумент2 страницыEarly Initiation of BreastfeedingMutia Salindri Putri100% (1)
- Physiology of LaborДокумент16 страницPhysiology of LaborRodrerick De lafuentesОценок пока нет
- Physiology of Female Reproductive System 01092010Документ57 страницPhysiology of Female Reproductive System 01092010Azry MustapaОценок пока нет
- OBG DrugsДокумент85 страницOBG Drugsvivekkumar05468Оценок пока нет
- Diagnosis and Mangement of Abnormal LabourДокумент55 страницDiagnosis and Mangement of Abnormal LabourVirda Maharani100% (3)
- Cystocele & RectoceleДокумент26 страницCystocele & RectoceleAlmasОценок пока нет
- Spontaneous Abortion PPДокумент47 страницSpontaneous Abortion PPSurgeon Raza HamidОценок пока нет
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Physiology of MenstruationДокумент6 страницPhysiology of MenstruationgmindalanoОценок пока нет
- Essential Newborn CareДокумент67 страницEssential Newborn CareTadesse MuhammedОценок пока нет
- Endocrin E Diseases: by Group 3Документ53 страницыEndocrin E Diseases: by Group 3Ash AshОценок пока нет
- Fetal CirculationДокумент28 страницFetal CirculationNelai GoОценок пока нет
- MCH 161118045354Документ38 страницMCH 161118045354SrideviRaviОценок пока нет
- Female External GenitaliaДокумент9 страницFemale External Genitaliabuhari rabiuОценок пока нет
- Fetal Biophysical Profile PDFДокумент2 страницыFetal Biophysical Profile PDFVickiОценок пока нет
- Misoprostol - PPT 1Документ61 страницаMisoprostol - PPT 1Hussein AminОценок пока нет
- Malpresentation and Malposition - ShoulderДокумент5 страницMalpresentation and Malposition - ShoulderNishaThakuri100% (1)
- Intrauterine Fetal Death: Prepared By: Roshni Adhikari Roshani Sunar Sabina Ranabhat Sadhana DevkotaДокумент15 страницIntrauterine Fetal Death: Prepared By: Roshni Adhikari Roshani Sunar Sabina Ranabhat Sadhana DevkotaRoshni SunarОценок пока нет
- Digestive System DisordersДокумент11 страницDigestive System DisordersDanie CabahugОценок пока нет
- RATHNAДокумент30 страницRATHNAhaisuresh100% (1)
- FertilizationДокумент6 страницFertilizationKristine Castillo100% (1)
- Preventing The Hazards of ImmobilityДокумент23 страницыPreventing The Hazards of ImmobilitySUBI BABUОценок пока нет
- Fertilization and Implantation Copy To StudentsДокумент40 страницFertilization and Implantation Copy To StudentsRiya SinghОценок пока нет
- Weekly PlanДокумент1 страницаWeekly PlanSenawi AbdullahОценок пока нет
- 1 MondayДокумент20 страниц1 Mondayhafizah_90Оценок пока нет
- W31Документ22 страницыW31hafizah_90Оценок пока нет
- Cuti Sempena Tahun Baru Hijrah Isnin 3/10/2016Документ8 страницCuti Sempena Tahun Baru Hijrah Isnin 3/10/2016hafizah_90Оценок пока нет
- Year 5 (The Big Bully) RPH SampleДокумент5 страницYear 5 (The Big Bully) RPH SampleSenawi AbdullahОценок пока нет
- W17Документ13 страницW17hafizah_90Оценок пока нет
- Quiz 2 Sce 3103Документ6 страницQuiz 2 Sce 3103hafizah_90Оценок пока нет
- Paper1 Yr2Документ8 страницPaper1 Yr2hafizah_90Оценок пока нет
- Suggested KBSR and KSSR Lesson Plan Format 1Документ5 страницSuggested KBSR and KSSR Lesson Plan Format 1hafizah_90Оценок пока нет
- Wors Search ToolДокумент1 страницаWors Search Toolhafizah_90Оценок пока нет
- Comparative Adjectives ExerciseДокумент1 страницаComparative Adjectives Exercisehafizah_90Оценок пока нет
- Backcross N Genetic CodeДокумент6 страницBackcross N Genetic Codehafizah_90Оценок пока нет
- Laporan 1 Page IsrajДокумент1 страницаLaporan 1 Page Israjhafizah_90Оценок пока нет
- Ujian Bahasa Inggeris Tahun 5Документ9 страницUjian Bahasa Inggeris Tahun 5hafizah_90100% (2)
- Brain Based LearningДокумент18 страницBrain Based Learninghafizah_90100% (1)
- Unsafe Substance Year 3Документ1 страницаUnsafe Substance Year 3hafizah_90Оценок пока нет
- Picture CardДокумент2 страницыPicture Cardhafizah_90Оценок пока нет
- How To Recycle Paper1Документ3 страницыHow To Recycle Paper1hafizah_90Оценок пока нет
- Latex Turned Into Rubber SheetДокумент1 страницаLatex Turned Into Rubber Sheethafizah_90Оценок пока нет
- English Writing For Different Text TypeДокумент13 страницEnglish Writing For Different Text Typehafizah_90Оценок пока нет
- Cystic FibrosisДокумент2 страницыCystic Fibrosishafizah_90Оценок пока нет
- Adaptations Related To Insect and Wind PollinationДокумент5 страницAdaptations Related To Insect and Wind Pollinationhafizah_90Оценок пока нет
- Questions of HeatДокумент1 страницаQuestions of Heathafizah_90Оценок пока нет
- GeneticДокумент7 страницGenetichafizah_90Оценок пока нет
- Human Foetal DevelopmentДокумент22 страницыHuman Foetal Developmenthafizah_90Оценок пока нет
- Self-Pollination & Cross PollinationДокумент3 страницыSelf-Pollination & Cross Pollinationhafizah_90Оценок пока нет
- Field TripДокумент15 страницField Triphafizah_90Оценок пока нет
- 3 D PolyhedralДокумент24 страницы3 D Polyhedralhafizah_90Оценок пока нет
- Anatomy of Retina: by DR - Ashok Kumar ValuroutuДокумент49 страницAnatomy of Retina: by DR - Ashok Kumar ValuroutuanamariaboariuОценок пока нет
- Chap13 Lymphatic System PPT LecДокумент68 страницChap13 Lymphatic System PPT LecThea Gornez100% (1)
- FCPS NOV Paper 2 Oph 2012Документ13 страницFCPS NOV Paper 2 Oph 2012bahaashakirОценок пока нет
- Bladder Outlet Obstruction in Children PDFДокумент64 страницыBladder Outlet Obstruction in Children PDFalaaОценок пока нет
- The Human Fascial System by L Stecco J A Day HandoutsДокумент4 страницыThe Human Fascial System by L Stecco J A Day Handoutsnyaniso rahotepОценок пока нет
- Extraction: Department of Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryДокумент26 страницExtraction: Department of Oral and Maxillofacial SurgerySudip ChakrabortyОценок пока нет
- Slide Kuliah TyroidДокумент57 страницSlide Kuliah TyroidsuhandinataОценок пока нет
- Posterior AnatomyДокумент17 страницPosterior AnatomyAziz RanaОценок пока нет
- 2nd Quarter Summative Test No.1 in Science 6Документ1 страница2nd Quarter Summative Test No.1 in Science 6Marilou Kimayong100% (9)
- Gross Anatomy: ExampleДокумент7 страницGross Anatomy: ExampleJerwin TullaoОценок пока нет
- Anatomy - KeyДокумент18 страницAnatomy - KeyAnonymous MtKJkerbpUОценок пока нет
- Autoimmune NeurologicalДокумент385 страницAutoimmune Neurologicalbodeadumitru9261Оценок пока нет
- Pig DissectionДокумент8 страницPig DissectiondvinalОценок пока нет
- Anatomi Leher New UpdateДокумент9 страницAnatomi Leher New UpdateKarl ImanuelОценок пока нет
- PNFДокумент37 страницPNFPaul TucciОценок пока нет
- Sheehan SyndromeДокумент6 страницSheehan SyndromeArvie TagnongОценок пока нет
- Assessment of Patients With Renal Disorders Management of Urinary Tract DisordersДокумент16 страницAssessment of Patients With Renal Disorders Management of Urinary Tract DisordersJhosita Flora LarocoОценок пока нет
- Complete Denture ManualДокумент23 страницыComplete Denture ManualCitra PurnamasariОценок пока нет
- Nuggets Combined 2010Документ461 страницаNuggets Combined 2010Advaita SusarlaОценок пока нет
- Walla Ridges PDFДокумент5 страницWalla Ridges PDFmanuela castroОценок пока нет
- BiolistrikДокумент40 страницBiolistrikFajar Sartika HadiОценок пока нет
- Neurological AssessmentДокумент23 страницыNeurological AssessmentNavjot BrarОценок пока нет
- Human Excretory SystemДокумент51 страницаHuman Excretory SystemVinoj MnoОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and PhysiologyДокумент3 страницыAnatomy and PhysiologyChristopher bruncanoОценок пока нет
- The Human Heart: Learner's Book Pg. # 8-9Документ17 страницThe Human Heart: Learner's Book Pg. # 8-9hareem FatimaОценок пока нет
- 18 Sigwart Sumner Rooney Chapter 18Документ19 страниц18 Sigwart Sumner Rooney Chapter 18Haniza SaraОценок пока нет
- Cranial Nerve Test Cranial Nerve I: OlfactoryДокумент2 страницыCranial Nerve Test Cranial Nerve I: OlfactoryjisooОценок пока нет
- Function of The Circulatory SystemДокумент5 страницFunction of The Circulatory SystemChristine SegundoОценок пока нет
- Skeletal System Concept MapДокумент3 страницыSkeletal System Concept MapMariana Arévalo100% (1)
- Imunitas Alami Dan Imunitas AdaptifДокумент55 страницImunitas Alami Dan Imunitas AdaptifAnthony UchihaОценок пока нет