Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Drug Used For The Treatment of Cough - DR - Anila
Загружено:
rameshbmcОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Drug Used For The Treatment of Cough - DR - Anila
Загружено:
rameshbmcАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
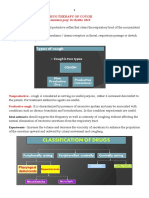
Drugs used for the
treatment of cough
Dr AneeIa KhaIid
ARNING OBJ%IV$
Classification of drugs used for the non
specific treatment of cough
Define the term Expectorant and
mucolytic
Describe the mechanism of action,
adverse effects and clinical uses of
Expectorants
Antitussives
Iassification of drugs used for
non specific treatment of cough
1. ough suppressants
entraIIy acting Antitussives
PeripheraI Antitussives
2. ough expectorants
3. Antihistamines
4. BronchodiIators
1) OUGH $UPPR$$AN%$ (Anti-
tussives)
1- entraIIy acting Antitussives
Narcotic antitussive
Opiates
Codeine
Pholcodine
Hydrocodone
Non narcotic antitussives
Opiates
Dextromethorphan
Levopropozyphene
Noscapine
Non-Opiates
Diphenhydramine
Benzonatate
2- PeripheraI Antitussives
1 DemuIcents
Linctus
Lozenges
Liquorice
2 InhaIation
Water aerosol inhalation
Benzoin
Menthol
3 ocaI anaesthetics
Benzonatate
Lignocaine (only in special circumstances)
2) ough xpectorants
1 Drugs acting RefIexIy
pecacuanha
Ammonium chloride
Potassium odide
2 Drugs Acting DirectIy
Potassium odide
Guaiphenesin
3 MucoIytics
Acetylcysteine
Bromhexine (Bisolvon)
Carbocisteine
Methylcysteine
Definition of MucoIytic and
xpectorant
MucoIytic
A mucolytic is a drug that breaks down thick
mucus, making it thinner and easier to cough
out.
xpectorant
An expectorant is a drug which makes the cough
more productive by loosening and liquefying
bronchial secretions.
Also known as Mucokinetics
Antitussives
Antitussives are substances that specifically
inhibit or suppress the action of cough
1) Depression of medullary centre or associated
higher centers.
2) ncreases threshold of the cough centre.
3) nterruption of tussal impulses peripherally in
the respiratory tract.
4) nhibition of conduction along the motor
pathways.
Narcotic Antitussives
odeine and PhoIcodeine
An opium alkaloid similar to morphine
less potent then morphine as analgesic and
respiratory depressant.
60% effective orally then parentrally as an
analgesic and respiratory depressant.
A standard antitussive
A small fraction of administered codeine is
metabolized to morphine which is responsible
for analgesic effects of codeine.
MOA of odeine:
Directly suppresses cough centre by binding to
distinct receptors in Medulla.
Suppresses cough for about 6 hrs.
Dosage: 15 mg
Adverse effects of odeine:
n therapeutic doses minimum side effects
Sedations, nausea, constipation
At higher doses respiratory depression and
drowsiness can occur.
Contraindicated in asthmatic patients and
patients with diminished respiratory reserves.
Pholcodeine has similar efficacy as
codeine with longer duration of action of
12hrs
t has no analgesic or addiction property
Non Narcotic Antitussives
Dextromethorphan Hydrobromide
A synthetic compound.
t is a dextrorotatory sterioisomer of a
methylated derivative of levorphenol.
Strong and partial agonist.
As effective antitussive as codeine.
MOA:
1. Controls cough spasm by depressing
cough centre in medulla
2. ncrease the threshold for coughing
Advantages of Dextromethorphan
No effect on ciliary activity
No CNS depression
No addiction potential
No constipation
Dosage: 15- 30mg three or four times daily.
%oxicity:
Toxic doses may cause.
Stupor, ataxia, respiratory depression,
convulsion in children and death with abuse of
its purified powder.
Contraindicated in children below 6 yrs of age
and also in patients taking Monoamine oxidase
inhibittors.
evopropoxyphene
t is a sterioisomer of weak opioid agonist
dextropropoxyphene.
t is devoid of opioid effects
Sedation is the only adverse effect
Dosage: 50-100mg 4hrly
Noscapine
An opium alkaloid
No narcotic, analgesic or dependance
inducing properties.
Equally effective antitussive as codeine
Useful for spasmodic cough.
Headache and nausea are usual side
effects
Contraindicated in asthamatic patients.
Benzonatate
Chemically related to tetracaine.
MOA:
Reduces the cough reflex by anesthetizing
the stretch receptors in the respiratory
passages, Lungs and Pleura.
t has some central effects also.
Adverse effects:
Headache, Dizziness, Pruritus
Nasal Congestion, burning of eyes &
tightness in chest.
P%ORAN%$
These are the drugs which make the cough
more productive by loosening and
liquefying bronchial secretions.
Also known as Mucokinetics.
Guaiphenesin
t is a derivative of Guaiacol
Obtained from wood or synthetically prepared
MOA. Decrease sputum viscosity and increase
sputum volume thereby decreasing difficulty in
expectoration
onIy FDA Approved expectorant .
Adverse effects. Nausea, gastric disturbances
drowsiness and rash.
IPAUANHA
$ource: Natural alkaloid obtained from
roots of cephaelis acuminata contains:
Cephaeline
Emetine
MOA.
Loosening & liquefying mucosa
soothing irritated bronchial mucosa.
t also has emetic & amoebicidal properties.
Uses. Mainly used for emesis in accidental
poisoning.
ontraindications
Semiconscious, Unconscious or
convulsing person
Corrosive poisoning or kerosine poisoning.
MucoIytics
MOA of MucoIytics:
Mucolytics open disulphide bonds in the
mucoproteins present in the sputum
making it less viscid.
Bromhexine:
MOA: t depolymerizes the
polysaccharides directly as well as by
liberating lysosomal enzymes which
breaks down the fiber network in the
tenacious sputum.
Particularly useful for mucous plugs.
Adverse effects:
Rhinorrhoea, lacrimation, and gastric
irritation.
Antihistamines
Chlorphenaramine 2-5mg
Diphenhydramine 5-25mg
Promethazine 15-25mg
Anti histamines provides relief in cough
due to sedative and anticholinergic action.
They lack selectivity for cough centres
They have been promoted for treatment of
cough in allergic states.
No efficacy in Asthma
BronchodiIators
Bronchodilators by clearing secretions
through increase in surface velocity of
airflow during cough relieves .
Should be used only when element of
bronchoconstriction is present and not
routinely
Fixed dose combination of bronchodilators
with anti tussives not preferred .
$peciaI conditions
Cough may be useful or useless.
No roIe of Antitussives
Asthma
young infants
Congestive cardiac failure
Bronchiactasis, COPD, Tuberculosis.
Antitussives may be prescribed
For dry unproductive cough that is
hazardous or is disturbing sleep.
( hernias, piles, after surgical procedures
esp cataract surgery).
Pholcodeine along with diphenhydramine
is useful.
n whooping cough or in pertusis.
Bronchodilator along with
Diphenhydramine is useful.
Вам также может понравиться
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)От EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Drug Used For The Treatment of Cough - DR - AnilaДокумент28 страницDrug Used For The Treatment of Cough - DR - AnilaShaan Rules100% (1)
- Pharmacology Respiratory DrugsДокумент51 страницаPharmacology Respiratory DrugsAngel DamoОценок пока нет
- Drugs For CoughДокумент18 страницDrugs For CoughAbraham BanjoОценок пока нет
- Cough: PHR Sangita ShakyaДокумент21 страницаCough: PHR Sangita ShakyaCurex QAОценок пока нет
- Cholinergic Antagonists: DR - Ch. Shanmukha Sai RaghavДокумент12 страницCholinergic Antagonists: DR - Ch. Shanmukha Sai RaghavShanmukh SaiОценок пока нет
- Respiratory PharmacologyДокумент34 страницыRespiratory PharmacologyHirpâsà MămoОценок пока нет
- AnesthesiaДокумент12 страницAnesthesiaعلي الاسديОценок пока нет
- Pharma-Respiratory DrugsДокумент56 страницPharma-Respiratory DrugsZainab ArshadОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 - Drugs Actiong On Respiratory SystemДокумент6 страницChapter 6 - Drugs Actiong On Respiratory SystemMohit SoniОценок пока нет
- Respiratory DrugsДокумент6 страницRespiratory DrugsCurtney PedriaОценок пока нет
- Cough (Antitussive) DrugsДокумент15 страницCough (Antitussive) DrugsBeer DilacsheОценок пока нет
- Respiratory System DrugsДокумент5 страницRespiratory System DrugsHamad AlshabiОценок пока нет
- CoughДокумент16 страницCoughRwapembe StephenОценок пока нет
- Obat Batuk Flu AsmaДокумент23 страницыObat Batuk Flu AsmaArya PratamaОценок пока нет
- Pulmonary Pharmacology Anticoughing AgentsДокумент10 страницPulmonary Pharmacology Anticoughing AgentsanaОценок пока нет
- Opiod Analgesics &antagonistsДокумент58 страницOpiod Analgesics &antagonistsVictoria ChepkorirОценок пока нет
- Oxymetazoline 2Документ8 страницOxymetazoline 2Febry Dian SinagaОценок пока нет
- Pharmacotherapy of CoughДокумент51 страницаPharmacotherapy of CoughIqra Butt100% (3)
- Defn: Periodic Spasm of Bronchial Smooth Muscles, Increased Secretion, andДокумент5 страницDefn: Periodic Spasm of Bronchial Smooth Muscles, Increased Secretion, andSambit BeheraОценок пока нет
- Opioids 160224153327Документ27 страницOpioids 160224153327Dr.Aman SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Clinical Pharmacology Reviewer. RespiДокумент4 страницыClinical Pharmacology Reviewer. RespiSister RislyОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology - Respiratory DrugsДокумент61 страницаPharmacology - Respiratory DrugsBenjamin Joel Breboneria100% (5)
- Drugs Used in The Treatment of CoughДокумент12 страницDrugs Used in The Treatment of CoughMaryam NisaОценок пока нет
- MorningДокумент9 страницMorningCamelle DiniayОценок пока нет
- AntitussivesДокумент5 страницAntitussivesAditya PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Dr. Rishi Pal: Asstt. ProfessorДокумент40 страницDr. Rishi Pal: Asstt. ProfessortamaОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент186 страницDrug StudyTheresa Sombilla FacunlaОценок пока нет
- Printed Material ModuleeeeДокумент56 страницPrinted Material ModuleeeeShang MacarayonОценок пока нет
- Autonomic Nervous System-2Документ8 страницAutonomic Nervous System-2محمد علي حميدОценок пока нет
- PHARMACOLOGY VOLUME 1 UNIT 4 Drugs Acting On Respiratory SystemДокумент44 страницыPHARMACOLOGY VOLUME 1 UNIT 4 Drugs Acting On Respiratory SystemAkhilesh TiwariОценок пока нет
- Respiratory DrugsДокумент56 страницRespiratory DrugsIra G. Delos Santos100% (1)
- Anticholinergic DrugsДокумент22 страницыAnticholinergic Drugs502-s21-027Оценок пока нет
- Over The CounterDrugstherapeuticsДокумент46 страницOver The CounterDrugstherapeuticsemmanuelkdei1994Оценок пока нет
- Over The CounterDrugstherapeuticsДокумент46 страницOver The CounterDrugstherapeuticsJenel WelchОценок пока нет
- Asma Bronkial & Copd: Bagian Farmakologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas TadulakoДокумент38 страницAsma Bronkial & Copd: Bagian Farmakologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas TadulakoPutri PrimandiniОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology - Respiratory SystemДокумент13 страницPharmacology - Respiratory System22bgu0805msОценок пока нет
- Drugs Acting On The Pulmonary System 2: Dr. Dita Hasni, M.BiomedДокумент24 страницыDrugs Acting On The Pulmonary System 2: Dr. Dita Hasni, M.BiomedYeny ElfiyantiОценок пока нет
- Course Task 9Документ24 страницыCourse Task 9Katrina AballaОценок пока нет
- Drugs Used in The Management of COPDДокумент6 страницDrugs Used in The Management of COPDASWINI GОценок пока нет
- Drugs in Respiratory SystemДокумент120 страницDrugs in Respiratory SystemRidhaОценок пока нет
- Pharmacological Treatment of Respiratory DisordersДокумент8 страницPharmacological Treatment of Respiratory DisorderssaraiОценок пока нет
- 6 OpioidsДокумент23 страницы6 Opioidsphoto copyhemnОценок пока нет
- Cough: Drug Therapy of CoughДокумент4 страницыCough: Drug Therapy of CoughAbdul HameedОценок пока нет
- Acetyl Cystein HospitalДокумент17 страницAcetyl Cystein HospitalSabaОценок пока нет
- ANTIEMETICSДокумент21 страницаANTIEMETICSanaya khan StudentОценок пока нет
- Asthma MedicationДокумент6 страницAsthma Medicationmomina arshidОценок пока нет
- Opioid Induced PruritusДокумент2 страницыOpioid Induced PruritusJavierОценок пока нет
- лекция №3Документ88 страницлекция №3THE TOXICОценок пока нет
- Drugs Affecting The Respiratory SystemДокумент151 страницаDrugs Affecting The Respiratory SystemMajestic RavenОценок пока нет
- Lo 4 Sk1 Rhinitis AlergiДокумент4 страницыLo 4 Sk1 Rhinitis AlergiFullyОценок пока нет
- Pre Medications AnaesthesiaДокумент34 страницыPre Medications AnaesthesiastadolinОценок пока нет
- 3 ParasympatholyticsДокумент35 страниц3 ParasympatholyticsSudhakar LakavathОценок пока нет
- Lect 1 - Respiratory 1Документ23 страницыLect 1 - Respiratory 1mohammed sarkawtОценок пока нет
- Pharmacological Control of PainДокумент9 страницPharmacological Control of Painn28h7sr2bmОценок пока нет
- Autonomics and CNS PlusДокумент131 страницаAutonomics and CNS PlusMiguel TolentinoОценок пока нет
- Premedicantdrugs1 170216071329Документ49 страницPremedicantdrugs1 170216071329Sagar BhardwajОценок пока нет
- Drugs Used For Bronchial AsthmaДокумент81 страницаDrugs Used For Bronchial AsthmaJinTaoОценок пока нет
- Lecture 16-17 - Opioids AnalgesicsДокумент20 страницLecture 16-17 - Opioids AnalgesicsJedoОценок пока нет
- Respiratory DrugsДокумент19 страницRespiratory DrugsBryan MedranoОценок пока нет
- Tricuspid Stenosis (TS)Документ8 страницTricuspid Stenosis (TS)rameshbmcОценок пока нет
- Hypertension FinalДокумент64 страницыHypertension FinalrameshbmcОценок пока нет
- Mitral RegurgitationДокумент22 страницыMitral Regurgitationrameshbmc100% (1)
- Aortic Regurgitation (Ar)Документ18 страницAortic Regurgitation (Ar)rameshbmc100% (1)
- Mitral StenosisДокумент29 страницMitral Stenosisrameshbmc100% (4)
- Aortic Stenosis (As)Документ20 страницAortic Stenosis (As)rameshbmc100% (1)
- Cardiovascular Diseases: DR Raveendra K.R Assistant Professor Department of Medicine BMC BangaloreДокумент34 страницыCardiovascular Diseases: DR Raveendra K.R Assistant Professor Department of Medicine BMC BangalorerameshbmcОценок пока нет
- Tricuspid Regurgitation (TR)Документ7 страницTricuspid Regurgitation (TR)rameshbmcОценок пока нет
- Rheumatic FeverДокумент24 страницыRheumatic FeverrameshbmcОценок пока нет
- Pulmonary Valve DiseasesДокумент2 страницыPulmonary Valve DiseasesrameshbmcОценок пока нет
- Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD)Документ55 страницIschemic Heart Disease (IHD)rameshbmc100% (5)
- Liver Funtion Test (D)Документ24 страницыLiver Funtion Test (D)rameshbmcОценок пока нет
- Infective Endocarditis IeДокумент26 страницInfective Endocarditis IeAnthie FitriОценок пока нет
- Mitral Valve Prolapse (MVP)Документ9 страницMitral Valve Prolapse (MVP)rameshbmcОценок пока нет
- Ophthalmia NeonatorumДокумент15 страницOphthalmia NeonatorumrameshbmcОценок пока нет
- Infective Endocarditis (Ie)Документ26 страницInfective Endocarditis (Ie)rameshbmc100% (1)
- Nios Environment Material Mrunal OrgДокумент643 страницыNios Environment Material Mrunal OrgVinod KumarОценок пока нет