Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
02 Monitoring
Загружено:
Lino Alleje Cruz IIIИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
02 Monitoring
Загружено:
Lino Alleje Cruz IIIАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
POSTECH DP&NM Lab
Network Monitoring
J. Won-Ki Hong Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering POSTECH Tel: 054-279-2244 Email: jwkhong@postech.ac.kr
POSTECH DP&NM Lab
Table of Contents
Introduction Monitored Types of Information Network Monitoring Configurations Network Monitoring Methods Performance Monitoring
Performance Indicators Performance Monitoring Functions
Fault Monitoring
Problems of Fault Monitoring Fault Monitoring Functions
Accounting Monitoring
2
POSTECH DP&NM Lab
Introduction
Network monitoring is concerned with observing and analyzing the status and behavior of the end systems, intermediate systems, and subnetworks that make up the network to be managed Issues in network monitoring
what to monitor?
define what is to be monitored
how to monitor?
how to obtain information from managed resources
what to do with the monitored information?
how the monitored information is used in various management functional areas
POSTECH DP&NM Lab
Monitored Types of Information
Static information
hardly changes current configuration information
e.g., the number and identification of ports on a router
Dynamic information
changes frequently information related to events in the network
e.g., change of state, transmission/reception of packets
Statistical information
derived from dynamic information
e.g., average number of packets transmitted per unit time
4
POSTECH DP&NM Lab
Organization of a Management Information Base
MANAGEMENT INFORMATION BASE (MIB) Statistical data base Call_Blocked Time_Delay Packet_Loss Throughput Abstraction of state and event variables Dynamic data base State_Variable Event_Variable Sensor activation and data collection Sensor data base Buffer Switch_server Source Server Station_Info Switch_Buffer Switch_Source Configuration data base Static data base Status_Sensor Derived_Status_Sensor Event_Sensor
POSTECH DP&NM Lab
Monitoring System Components
monitoring application
includes the functions of monitoring that are visible to the user
e.g., performance, fault, accounting
manager function
performs the basic monitoring function of retrieving information
agent function
gathers and records management information for one or more network elements and delivers the information to the monitor
managed objects
mgmt information that represents resources and their activities
monitoring agent
generates summaries and statistical analysis of mgmt information
6
POSTECH DP&NM Lab
Functional Architecture for Network Monitoring
Monitoring application Manager function Monitoring application Manager function Monitoring agent
Agent function Managed objects
Agent function Managed objects
...
Agent function Managed objects
(a) manager-agent model
(b) A model for summarization 7
POSTECH DP&NM Lab
Network Monitoring Configurations
Monitoring application Manager function Agent function Managed objects (a) Managed resources in manager system Monitoring application Manager function Monitoring application Manager function Monitoring application Manager function
Subnetwork or internet
Agent function Managed objects (b) Resources in agent system
Subnetwork or internet
Subnetwork or internet Agent function LAN observed traffic (c) External monitor
Agent function LAN
(d) proxy monitor agent 8
POSTECH DP&NM Lab
Network Monitoring Methods
Polling
a request-response interaction between a manager and agent a manager sends request to an agent which processes the request and responds with information from its MIB a manager may use polling to
learn about the configuration it is managing obtain periodically an update of conditions investigate an area in detail after being altered to a problem
Event Reporting
information flow is initiated from the agent to manager an agent may generate report periodically to give the manager its current status or whenever a significant event (e.g., change of a state) or an unusual event (e.g., fault) occurs good for detecting problems as soon as they occur
9
POSTECH DP&NM Lab
Performance Monitoring
Measuring the performance of the network (or performance monitoring) is absolutely required in NM
to detect & fix problems that cause performance degradation to better plan network upgrades
Problems in selecting and using appropriate indicators (or metrics)
too many indicators in use the meaning of most indicators are not yet clearly understood some indicators are supported by some manufacturers only frequently, the indicators are accurately measured but incorrectly interpreted by human or mgmt application the calculation of indicators takes too much time
10
POSTECH DP&NM Lab
Network Performance Indicators
Service-oriented
Availability: the percentage of time that a network system, a
component, or an application is available for a user
Response Time: how long it takes for a response to appear at
a users terminal after a user action calls for it
Accuracy: the percentage of time that no errors in the
transmission and delivery of information
Efficiency-oriented
Throughput: the rate at which application-oriented events (e.g.,
file transfers) occur
Utilization: the percentage of the theoretical capacity of a
resource (e.g., transmission line, switch, CPU) that is being used
11
POSTECH DP&NM Lab
Elements of Response Time
TO Workstation Network interface (e.g., router) SI Server
Network
SO WI TI RT = TI + WI + SI + CPU + WO + SO + TO WO CPU
RT = response time TI = inbound terminal delay WI = inbound queuing time SI = inbound service time
CPU = CPU process delay WO = outbound queuing time SO = outbound service time TO = outbound terminal delay
12
POSTECH DP&NM Lab
Performance Monitoring Functions
Performance Measurement
the actual gathering of statistics about network traffic & timing typically performed by agents within network devices e.g., amount of data in and out of a node, number of connections, traffic per connection
Performance Analysis
analyzing the gathered data and presenting it e.g., total, average, min, max, histogram
Synthetic Traffic Generation
generating artificial traffic load permits the network to be observed under a controlled load
13
POSTECH DP&NM Lab
Typical Performance-Related Questions
Performance measurements can be used to answer a number of questions
Why is the response so slow? (a very loaded question!) Why is the retransmission rate so high? Is traffic evenly distributed among network users or are there source-destination pairs with unusually heavy traffic? What is the percentage of each type of packet? What is the channel utilization and throughput? What is the effect of traffic load on utilization, throughput & time delays? When does traffic load start to degrade system performance? What is the maximum capacity of the channel under normal operating conditions? How many active users are necessary to reach this maximum?
14
POSTECH DP&NM Lab
Fault Monitoring
To detect faults as quickly as possible after they occur and to identify the cause of the fault so that correctional action may be taken Problems of Fault Monitoring
Fault Detection Problems
Unobservable faults: e.g., deadlock, device not monitorable Partially observable faults: insufficient to pinpoint the problem Uncertainty in observation: not clear what the problem is
Fault Isolation Problems
Multiple potential causes Too many related observations Interference between diagnosis and local recovery procedures Absence of automated testing tools
15
POSTECH DP&NM Lab
What happens when the T1 link fails?
802.5 802.3
Client
Router
Router
Server
MUX
T1
MUX
PBX
PBX
802.3
Heterogeneous Network Environment
16
POSTECH DP&NM Lab
Propagation of Failures to Higher Layers
Application failure
Transport failure
Client Server Data link failure Transmission Mux Mux break Router Router 17
POSTECH DP&NM Lab
Fault Monitoring Functions
Logging
record important events and errors logs should be accessible by managers (e.g., via polling)
Event Reporting
sending events, errors to managers sending alarms to manager to warn possible problems
Diagnostic Functions
connectivity test (e.g., traceroute) response-time test liveness test (e.g., ping) protocol integrity test loopback test
18
POSTECH DP&NM Lab
Accounting Monitoring
Keeping track of users usage of network resources
communication facilities computer hardware software and systems services
Usage may need to be broken down by account, by project, or by individual user for appropriate accounting purposes
19
POSTECH DP&NM Lab
Summary
Network monitoring is the most basic aspect of NM The purpose of network monitoring is to gather information about the status and behavior of network elements Information to be gathered include
static, dynamic and statistical information
Monitoring methods - polling & event reporting Monitoring functions
performance monitoring fault monitoring accounting monitoring
READ Chapter 2 of Textbook
20
Вам также может понравиться
- Action PlanДокумент3 страницыAction PlanLino Alleje Cruz IIIОценок пока нет
- Query 1Документ1 страницаQuery 1Lino Alleje Cruz IIIОценок пока нет
- Query 1Документ1 страницаQuery 1Lino Alleje Cruz IIIОценок пока нет
- Query 1Документ1 страницаQuery 1Lino Alleje Cruz IIIОценок пока нет
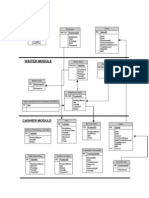
- POS Database PlanДокумент1 страницаPOS Database PlanLino Alleje Cruz IIIОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (120)
- A Scalable Framework For Provisioning Large-Scale IoT DeploymentsДокумент20 страницA Scalable Framework For Provisioning Large-Scale IoT Deploymentsselvakrishnan_sОценок пока нет
- Brand Focus - Starbucks Premium Pricing StrategyДокумент4 страницыBrand Focus - Starbucks Premium Pricing StrategyRitika SinghalОценок пока нет
- NP000194 - NP000200 - NP000203 - (Ct050-3-2-Wapp)Документ45 страницNP000194 - NP000200 - NP000203 - (Ct050-3-2-Wapp)Rupak ThapaОценок пока нет
- Open University Study BookДокумент146 страницOpen University Study BookjusticeОценок пока нет
- Fortios v7.0.9 Release NotesДокумент34 страницыFortios v7.0.9 Release NotesMichael Fabian Rennella MuñozОценок пока нет
- MBA (DS) - Introduction To Python ProgrammingДокумент144 страницыMBA (DS) - Introduction To Python ProgrammingSyed AmeenОценок пока нет
- Reference Manual v8.00 - A4Документ284 страницыReference Manual v8.00 - A4naidu9522Оценок пока нет
- Clean Wipe Symantec READMEДокумент2 страницыClean Wipe Symantec READMEShady El-MalataweyОценок пока нет
- Lecture 7Документ39 страницLecture 7Jose Luis CrОценок пока нет
- Payroll Voucher GuideДокумент32 страницыPayroll Voucher GuideVerry NoviandiОценок пока нет
- CTP HistoryДокумент125 страницCTP HistoryPavan SamudralaОценок пока нет
- Step Replace Module Flexi BSC NokiaДокумент19 страницStep Replace Module Flexi BSC Nokiarudibenget0% (1)
- A Water Pumping Control System With A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) PDFДокумент8 страницA Water Pumping Control System With A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) PDFsunnyday32Оценок пока нет
- Burp SuiteДокумент18 страницBurp SuiteCleber PimentaОценок пока нет
- Project DIVA Map Editor Readme Google TranslateДокумент16 страницProject DIVA Map Editor Readme Google TranslateImron Adi Laksono100% (1)
- All Softwares Serial NumbersДокумент136 страницAll Softwares Serial NumbersSohani0070% (1)
- First Term Question of CSC 383 DДокумент3 страницыFirst Term Question of CSC 383 DMd.AshikuzzamanОценок пока нет
- Case Study: Digital Learning and Employee Development at The Gulfistan Co., LTDДокумент5 страницCase Study: Digital Learning and Employee Development at The Gulfistan Co., LTDsharan chakravarthyОценок пока нет
- DevicemoveДокумент32 страницыDevicemoveUrvashiОценок пока нет
- 5G Open Innovation IPZ ApplicationДокумент7 страниц5G Open Innovation IPZ ApplicationNat LevyОценок пока нет
- Mastering 3D PrintingДокумент2 страницыMastering 3D PrintingTamás KissОценок пока нет
- Recommended Default Settings For A New PostgreSQL or EPAS Installation - WindowsДокумент5 страницRecommended Default Settings For A New PostgreSQL or EPAS Installation - WindowsGilberto MartinsОценок пока нет
- C Annun8 009Документ26 страницC Annun8 009Youssef EBОценок пока нет
- Beewi Product Guide 2011 4web PDFДокумент24 страницыBeewi Product Guide 2011 4web PDFcipdaleОценок пока нет
- Quality Requirements InterpretationДокумент76 страницQuality Requirements InterpretationMauro MLRОценок пока нет
- STQA Introduction PPT 3 (Unit 3)Документ43 страницыSTQA Introduction PPT 3 (Unit 3)Gowtham RajuОценок пока нет
- Oracle 9I-Performance Tuning: (Rev1.1) - January, 2009 - by Ergem PEKERДокумент26 страницOracle 9I-Performance Tuning: (Rev1.1) - January, 2009 - by Ergem PEKERKarla Fraser-LucasОценок пока нет
- Software Quality Factors and Software Quality Metrics To Enhance Software Quality AssuranceДокумент27 страницSoftware Quality Factors and Software Quality Metrics To Enhance Software Quality AssurancearijayantiОценок пока нет
- Uip Practical 1 To 7Документ10 страницUip Practical 1 To 7C052 Diksha PawarОценок пока нет
- Mission Critical, Vol.8-Num.5Документ81 страницаMission Critical, Vol.8-Num.5arturoncОценок пока нет