Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Carmelen Bhey, Almeda Ryan A Barrinuevo Abdul Bashier Suliek
Загружено:
Vash SuleikИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Carmelen Bhey, Almeda Ryan A Barrinuevo Abdul Bashier Suliek
Загружено:
Vash SuleikАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Carmelen bhey, Almeda Ryan A Barrinuevo Abdul Bashier Suliek
When you hear the term "diabetes insipidus," you may assume it's related to what'scommonly known as "sugar" diabetes, or diabetes mellitus. While the disorders sharea name and have some common signs, in fact diabetes mellitus (type 1 and type 2)and diabetes insipidus are unrelated. Diabetes insipidus (DI) is a disorder characterized by intense thirst and by theexcretion of large amounts of urine (polyuria). In most cases, it's the result of your body not properly producing, storing or releasing a key hormone, but diabetesinsipidus can also occur when your kidneys are unable to properly respond to thathormone.
Diabetes insipidus is not the disorder of the glucose or sugar regulation, that is diabetes mellitus. Diabetes insipidus is a disorder of body water regulation They have both POLYURIA and POLYDIPSIA
Free water loss Decrease production of ADH by the Hypothalamus Decrease secretion of ADH by posterior pituitary gland Decrease renal response to ADH
Normally, your kidneys remove excess body fluids from your bloodstream. This fluidwaste is stored in your bladder as urine. When your fluid regulation system is working properly, your kidneys make less urine when your body water is decreased, such asthrough perspiration, in order to conserve fluid.The volume and composition of your body fluids remain balanced through acombination of oral intake and excretion in the kidneys. The rate of fluid intake islargely governed by thirst, although your habits can increase your intake far above theamount necessary. The rate of fluid excreted by your kidneys is greatly influenced bythe production of anti-diuretic hormone (ADH), also called vasopressin
Your body makes ADH in the hypothalamus and stores the hormone in your pituitarygland, a small gland located in the base of your brain. ADH is released into your bloodstream when necessary. ADH then concentrates the urine by triggering thekidney tubules to reabsorb water back into your bloodstream rather than excretingwater into your urine. Diabetes insipidus occurs when this system is disrupted and your body can't regulatehow it handles fluids. The way in which your system is disrupted determines whichform of diabetes insipidus you have
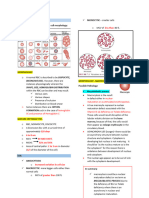
Polydispsia Polyuria Hypernatremia Hyperosmolar (increase osmolarity of blood>295mOsm/kg Tachycardia
Neurogenic Nephrogenic
Central DI Caused by any organic lesion that interfere witch ADH synthesis,transport or release - stroke - tumors - injury
Replace free water with hypotonic solution to equal urinary losses - PNSS - hormonal repalcement with desmopressin acetare an analogue of ADH - orally - intravenously - nasal spray - chlorpropramide(diabenese) helps the ADH that is circulating to work better and stimulates endogenous release of ADH
Condition where adequate ADH levels are present but kidney fail to respons appropriately Lithium is common cause of NDI - blocks the effect of ADH on the kidneys renal tubules
If oral intake cannot keep up with urinary loss Severe fluid vol. deficit Weight loss Constipation Poor skin turgor Hypotension Tachycardia Shock
Water deprivation test. This test helps determine the cause of diabetesinsipidus. You'll be asked to stop drinking fluids two to three hours before thetest so that your doctor can measure changes in your body weight, urine outputand urine composition when fluids are withheld. In some cases your doctor may also measure blood levels of ADH during this test. Urinalysis is the physical and chemical examination of urine. If your urine is less concentrated (meaning the amount of water excreted is highand the salt and waste concentrations are low)
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan.An MRI of the head is anoninvasive procedure that uses powerful magnets and radio waves toconstruct detailed pictures of brain tissues. Your doctor may want to performan MRI to look for abnormalities in or near the pituitary gland.
Low sodium diet No more than 3 per day may helps decrease urine out put Thiazide diuretics Hydrochlorothiazide(HCTZ) Chlorothiazide(DIURIL) These medication slow kidney filtration rate allowing for more absorption of free water.
Iv fluid replacement Oral fluid replacement i&o Daily weight
Urine specific gravity (1.005-1.030) urine specific gravity<1.005 Serum osmolality(285-295 mOsm/kg) Serum osmolality >295
DI
Neurogenic cause
Nephrogenic cause
Decrease ADH secretion Kidney tubules fail to reabsorb Plasma hyperosmolality
Increase urination of dilute urine nocturia, decreasing urine specific gravity dehydration
Stimulate thirst center
polydipsia
Вам также может понравиться
- Anti Illegal FORMДокумент14 страницAnti Illegal FORMVash Suleik0% (3)
- HeadacheДокумент16 страницHeadacheKevinVunОценок пока нет
- Physiological Regulation of Arterial Blood PressureДокумент36 страницPhysiological Regulation of Arterial Blood PressureFrancesОценок пока нет
- Managemnet Arterial UlcersДокумент24 страницыManagemnet Arterial UlcersMohamad Zulfikar100% (1)
- GK Today 2016 General Sciences PDFДокумент294 страницыGK Today 2016 General Sciences PDFHasan Shaikh100% (2)
- C - Quick Access Table - Combining Forms To Definitions 1Документ19 страницC - Quick Access Table - Combining Forms To Definitions 1neuronurseОценок пока нет
- CirculatorySystem GizmoДокумент4 страницыCirculatorySystem GizmoNashly Ramirez50% (2)
- Urinary Tract Infection Nursing-Care-PlanДокумент3 страницыUrinary Tract Infection Nursing-Care-PlanRnspeakcomОценок пока нет
- Diabetes InsipidusДокумент11 страницDiabetes InsipidusAnil Yadav100% (1)
- CNS Congenital AnomaliesДокумент74 страницыCNS Congenital AnomaliesMoh DrhusseinyОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 EpidemiologyДокумент7 страницChapter 5 EpidemiologyJohn Rick OrineОценок пока нет
- CSF and Blood Brain BarrierДокумент67 страницCSF and Blood Brain BarrierPhysiology by Dr Raghuveer100% (1)
- Fulminant Hepatic Failure: Nattaphol UransilpДокумент27 страницFulminant Hepatic Failure: Nattaphol UransilpChacha TasyaОценок пока нет
- Reye's SyndromeДокумент11 страницReye's SyndromeChristine Go100% (1)
- ThalassemiaДокумент93 страницыThalassemiaHafdzi MaulanaОценок пока нет
- Thyroid DisordersДокумент21 страницаThyroid DisordersSuliman GarallehОценок пока нет
- Mastitis: By: Hj. Fatimah Usman, OBGYN (C)Документ12 страницMastitis: By: Hj. Fatimah Usman, OBGYN (C)David TurnerОценок пока нет
- Atrial MyxomaДокумент36 страницAtrial MyxomaPrince Jevon YapОценок пока нет
- Congestive Heart FailureДокумент43 страницыCongestive Heart Failure568563100% (1)
- Seizures in Children CMEДокумент43 страницыSeizures in Children CMEGideon K. Mutai100% (1)
- Surviving Sepsis Campaign 2016 Guidelines Presentation FinalДокумент60 страницSurviving Sepsis Campaign 2016 Guidelines Presentation FinalCocosul Cocosului CocosaruluiОценок пока нет
- CVAДокумент13 страницCVAAmlan jyoti thanapatiОценок пока нет
- Hemorrhagic StrokeДокумент57 страницHemorrhagic StrokeAnonymous oEbVOEОценок пока нет
- Insulin and Oral Hypoglycemic DrugsДокумент30 страницInsulin and Oral Hypoglycemic DrugsAngga NugrahaОценок пока нет
- Neurological DisordersДокумент11 страницNeurological DisordersFatima AsimОценок пока нет
- Introduction To HematologyДокумент61 страницаIntroduction To HematologyThis is PonyОценок пока нет
- JBI Critical AppraisalДокумент19 страницJBI Critical AppraisalAndi Indahwaty SidinОценок пока нет
- SAMДокумент108 страницSAMAlimyon Abilar MontoloОценок пока нет
- Lecture On Anemias and Polycythemias by Dr. RoomiДокумент30 страницLecture On Anemias and Polycythemias by Dr. RoomiMudassar Roomi100% (1)
- Rhemuatoid Arthritis: Post RN BSN 1 Semester JCON Pushpa Kumari Abdul Hafeez Raza Muhammad Ghulam Murtaza 20/11/2020Документ19 страницRhemuatoid Arthritis: Post RN BSN 1 Semester JCON Pushpa Kumari Abdul Hafeez Raza Muhammad Ghulam Murtaza 20/11/2020shewo.pirtamОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular DiseaseДокумент33 страницыCardiovascular Diseasejoyce lakshmanОценок пока нет
- Urinary Incontinence: 2 PathophysiologyДокумент8 страницUrinary Incontinence: 2 PathophysiologyZiedTrikiОценок пока нет
- Acute Coronary Syndrome: Aminah DalimuntheДокумент48 страницAcute Coronary Syndrome: Aminah Dalimunthesintesis obatОценок пока нет
- Huntington'S Disease: Dhakal, Gerbabuena, Jittwatanatakool, Jordan, KarnДокумент25 страницHuntington'S Disease: Dhakal, Gerbabuena, Jittwatanatakool, Jordan, KarnIrene JordanОценок пока нет
- Atherosclerosis 2 2017 (Modified)Документ64 страницыAtherosclerosis 2 2017 (Modified)Remo B AbyОценок пока нет
- Nutrition Wound Healing10!20!10Документ28 страницNutrition Wound Healing10!20!10Jathen22Оценок пока нет
- Diabetes MellitusДокумент8 страницDiabetes MellitusJaja RamosОценок пока нет
- NUR 104 Nursing Process MY NOTESДокумент77 страницNUR 104 Nursing Process MY NOTESmeanne073100% (1)
- Thyroid GlandДокумент30 страницThyroid GlandahmedkomranОценок пока нет
- DIABETIC COMA - Clinical Features and ManagementДокумент54 страницыDIABETIC COMA - Clinical Features and ManagementRitesh SinghОценок пока нет
- Head Injury: Manali H. Solanki F.Y. M.Sc. Nursing J G College of NursingДокумент31 страницаHead Injury: Manali H. Solanki F.Y. M.Sc. Nursing J G College of NursingWaqar AhmedОценок пока нет
- Cva Case PDFДокумент39 страницCva Case PDFEmsy Ni ThelayОценок пока нет
- Imuune Thrombocytopenia (Itp)Документ34 страницыImuune Thrombocytopenia (Itp)Roshandiep GillОценок пока нет
- 4 - Guidelines For HIV Care and Treatment in Infants and ChildrenДокумент136 страниц4 - Guidelines For HIV Care and Treatment in Infants and Childreniman_kundu2007756100% (1)
- Lung Cancer (Bronchogenic Carcinoma)Документ45 страницLung Cancer (Bronchogenic Carcinoma)Howell Thomas Montilla AlamoОценок пока нет
- GCS Assessment Aid English PDFДокумент1 страницаGCS Assessment Aid English PDFSila OntitaОценок пока нет
- Dissiminated Intravascular Coagulation PathoДокумент2 страницыDissiminated Intravascular Coagulation Pathoapi-341263362Оценок пока нет
- Classifications of Thyroid TumoursДокумент15 страницClassifications of Thyroid TumoursSandra LisaОценок пока нет
- Stroke MsДокумент57 страницStroke MsAishwarya ShahОценок пока нет
- Cerebral Malaria (CM) Prof. WBP Matuja, MuhasДокумент20 страницCerebral Malaria (CM) Prof. WBP Matuja, MuhasAnonymous TCZf45C10Оценок пока нет
- Legalandethicalissuesincriticalcarenursing 130411224544 Phpapp02Документ33 страницыLegalandethicalissuesincriticalcarenursing 130411224544 Phpapp02Guna RamyaОценок пока нет
- What Is ICU PsychosisДокумент6 страницWhat Is ICU PsychosisAngelicaMarieRafananОценок пока нет
- GoitreДокумент6 страницGoitreJohn Vladimir A. BulagsayОценок пока нет
- Liver Function Test FinalДокумент98 страницLiver Function Test FinalHussain AzharОценок пока нет
- Eye ExaminationДокумент23 страницыEye Examinationcynthia167Оценок пока нет
- Brain Death Role of Intensivist in Diagnosis and Preparation For Organ RetrievalДокумент86 страницBrain Death Role of Intensivist in Diagnosis and Preparation For Organ Retrievalharsha mummaka100% (1)
- Cellulitis: Clinical Review: Be The First To CommentДокумент9 страницCellulitis: Clinical Review: Be The First To CommentAnonymous 1nMTZWmzОценок пока нет
- Airway ObstructionДокумент35 страницAirway ObstructionJemicia AdamsОценок пока нет
- Chronic Diarrhea and Malabsorption SyndromesДокумент152 страницыChronic Diarrhea and Malabsorption SyndromesAndrei DumitruОценок пока нет
- History Taking: DR - Ahmed Gaber Ass. Prof of Neurology Ain Shams UniversityДокумент81 страницаHistory Taking: DR - Ahmed Gaber Ass. Prof of Neurology Ain Shams UniversityKhaled OssamaОценок пока нет
- Otitis Media Diagnosis and TreatmentДокумент19 страницOtitis Media Diagnosis and TreatmentreyhanrrОценок пока нет
- Ebstein Anomaly, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandEbstein Anomaly, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- A Simple Guide to Cerebral Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsОт EverandA Simple Guide to Cerebral Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Obstructive UropathyДокумент3 страницыObstructive UropathyVash SuleikОценок пока нет
- Parliamentary AND Presidential Government: Reported By: Jasmine SuleikДокумент11 страницParliamentary AND Presidential Government: Reported By: Jasmine SuleikVash SuleikОценок пока нет
- Chart CHNДокумент3 страницыChart CHNVash SuleikОценок пока нет
- Anaesthesia For Paediatric Robotic Assisted Thoracoscopic SurgeryДокумент6 страницAnaesthesia For Paediatric Robotic Assisted Thoracoscopic SurgeryPrabakaran ParameswaranОценок пока нет
- Soal Kelas 9 Agustus FixДокумент2 страницыSoal Kelas 9 Agustus FixYuli KurniatiОценок пока нет
- Blood Everywhere: A Case Study in BloodДокумент2 страницыBlood Everywhere: A Case Study in BloodAbdullahОценок пока нет
- OmrДокумент39 страницOmrabhijeetОценок пока нет
- Phylum Porifera - : Sycon, Spongilla, EuspongiaДокумент8 страницPhylum Porifera - : Sycon, Spongilla, EuspongiaCrazy about JunglesОценок пока нет
- Hiperakusis 2015Документ20 страницHiperakusis 2015Abdur ShamilОценок пока нет
- Red Blood Cell Disorders Part 1 and 2Документ7 страницRed Blood Cell Disorders Part 1 and 2babael.zuher123Оценок пока нет
- Corail Surgical Technique Revision 1Документ20 страницCorail Surgical Technique Revision 1Kaustubh KeskarОценок пока нет
- DEGLUTITIONДокумент39 страницDEGLUTITIONmamatha dОценок пока нет
- Block Diagram PT MonitorДокумент7 страницBlock Diagram PT MonitorAbabil Academy KannanОценок пока нет
- A Quick Guide To Grand Practical Exam in ElectrotherapyДокумент8 страницA Quick Guide To Grand Practical Exam in ElectrotherapyJohnpeter EsporlasОценок пока нет
- Respiratory FailureДокумент39 страницRespiratory FailureMuntasir BashirОценок пока нет
- Ab-5251 Willing Family (Ray Todd) 1980Документ35 страницAb-5251 Willing Family (Ray Todd) 1980ramanaОценок пока нет
- Myocardial InfarctionДокумент20 страницMyocardial InfarctionRio Ramon HilarioОценок пока нет
- Rapid Learning in RoboticsДокумент169 страницRapid Learning in RoboticsMatthew PadillaОценок пока нет
- Cells Structure & FunctionДокумент80 страницCells Structure & Functionderr barrОценок пока нет
- Haemonetics MCS+ Analyzer - User Manual PDFДокумент110 страницHaemonetics MCS+ Analyzer - User Manual PDFPedro Villanueva C.Оценок пока нет
- Bahan Ajajar English II KeperawatanДокумент49 страницBahan Ajajar English II KeperawatanEchingt TukaОценок пока нет
- 11 класс 4 модульДокумент4 страницы11 класс 4 модульYuriОценок пока нет
- Trauma and The Brain 1Документ14 страницTrauma and The Brain 1Syed Shams Haider MashhadiОценок пока нет
- Biotechnological Applications of Pectinases in Textile Processing and Bioscouring of Cotton Fibers PDFДокумент9 страницBiotechnological Applications of Pectinases in Textile Processing and Bioscouring of Cotton Fibers PDFAnonymous uUL0B5pncОценок пока нет
- Controlling Your Dopamine For Motivation, FocusДокумент111 страницControlling Your Dopamine For Motivation, Focuswnd cОценок пока нет
- Endoscopic InvestigationsДокумент1 страницаEndoscopic Investigationsgeorgeloto12Оценок пока нет
- PHILIPPINES Asthma Consensus Guidelines 2009Документ134 страницыPHILIPPINES Asthma Consensus Guidelines 2009Sirias_black50% (2)
- Fetal Movements As A Predictor of HealthДокумент8 страницFetal Movements As A Predictor of HealthWordtreader PtОценок пока нет
- Homeostasis and Hormonal Action: CAPE Biology Unit 2: Module 2 N.M. NarineДокумент6 страницHomeostasis and Hormonal Action: CAPE Biology Unit 2: Module 2 N.M. NarineLemontОценок пока нет