Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Unit1 KOM
Загружено:
velavansuИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Unit1 KOM
Загружено:
velavansuАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Classification of Kinematic Pairs
1. According to the type of relative motion between the elements
(a) Sliding pair. (b) Turning pair. (c) Rolling pair. (d) Screw pair. (e) Spherical pair
2. According to the type of contact between the elements (a) Lower pair. sliding pairs, turning pairs and screw pairs form lower pairs. (b) Higher pair. A pair of friction discs, toothed gearing, belt and rope drives, ball and roller bearings and cam and follower are the examples of higher pairs.
3.According to the type of closure
(a) Self closed pair. Thelower pairs are self closed pair. (b) Force - closed pair. The cam and follower is an example of force closed pair, as it is kept in contact by the forces exerted by spring and gravity.
Kinematic Chain When the kinematic pairs are coupled in such a way that the last link is joined to the first link to transmit definite motion (i.e. completely or successfully constrained motion), it is called a kinematic chain.
In other words, a kinematic chain may be defined as a combination of kinematic pairs, joined in such a way that each link forms a part of two pairs and the relative motion between the links or elements is completely or successfully constrained.
If each link is assumed to form two pairs with two adjacent links, then the relation between the number of pairs ( p ) forming a kinematic chain and the number of links ( l ) may be expressed in the form of an equation : l=2p4 Since in a kinematic chain each link forms a part of two pairs, therefore there will be as many links as the number of pairs.
Another relation between the number of links (l) and the number of joints ( j ) which constitute a kinematic chain is given by the expression :
Consider the arrangement of four links A B, BC, CD and DA as shown in Fig In this case l = 4, p = 4, and j = 4 From equation (i), l=2p4 4=244=4 i.e. L.H.S. = R.H.S. From equation (ii),
A chain having more than four links is known as compound kinematic chain
The following types of joints are usually found in a chain : 1. Binary joint. When two links are joined at the same connection, the joint is known as binary joint. For example, a chain as shown in Fig has four links and four binary joins at A, B,C and D. In order to determine the nature of chain, i.e. whether the chain is a locked chain (or structure) or kinematic chain or unconstrained chain, the following relation between the number of links and the number of binary joints, as given by A.W. Klein, may be used :
j = Number of binary joints, h = Number of higher pairs, and l = Number of links. When h = 0, the equation (i), may be written as
2. Ternary joint. When three links are joined at the same connection, the joint is known as ternary joint. It is equivalent to two binary joints as one of the three links joined carry the pin for the other two links. For example, a chain, as shown in Fig, has six links. It has three binary joints at A, B and D and two ternary joints at C and E. Since one ternary joint is equivalent to two binary joints, therefore equivalent binary joints in a chain, as shown in Fig. are 3 + 2 2 = 7 Let us now determine whether this chain is a kinematic chain or not. We know that l = 6 and j = 7, therefore from equation
Number of Degrees of Freedom for Plane Mechanisms In the design or analysis of a mechanism, one of the most important concern is the number of degrees of freedom (also called movability) of the mechanism. It is defined as the number of input parameters (usually pair variables) which must be independently controlled in order to bring the mechanism into a useful engineering purpose. It is possible to determine the number of degrees of freedom of a mechanism directly from the number of links and the number and types of joints which it includes.
Consider a four bar chain, as shown in Fig. A little consideration will show that only one variable such as is needed to define the relative positions of all the links. In other words, we say that the number of degrees of freedom of a four bar chain is one
Now, let us consider a five bar chain, as shown in Fig. In this case two variables such as 1 and 2 are needed to define completely the relative positions of all the links. Thus, we say that the number of degrees of freedom is two. the number of degrees of freedom of a mechanism is given by
This equation is called Kutzbach criterion for the movability of a mechanism having plane motion.
If there are no two degree of freedom pairs (i.e. higher pairs), then h = 0. Substituting h = 0 in equation , we have
Application of Kutzbach Criterion to Plane Mechanisms
Вам также может понравиться
- Unit IДокумент33 страницыUnit IThe sky BlueОценок пока нет
- Note 1440423033Документ17 страницNote 1440423033Siva GaneshОценок пока нет
- Mechanism 69869Документ28 страницMechanism 69869Abi DemОценок пока нет
- MCQ Tom I - Unit - I and IIДокумент39 страницMCQ Tom I - Unit - I and IIHasan AL-BahraniОценок пока нет
- Kom NotesДокумент15 страницKom NoteselangandhiОценок пока нет
- Lee Brekke Et Al - Knots and Links of Nonabelian StringДокумент17 страницLee Brekke Et Al - Knots and Links of Nonabelian StringPomac232Оценок пока нет
- MECHANISMS AND KINEMATICS FUNDAMENTALSДокумент24 страницыMECHANISMS AND KINEMATICS FUNDAMENTALSrajeshОценок пока нет
- Plot displacement curves from position diagramsДокумент9 страницPlot displacement curves from position diagramsReyner LozaОценок пока нет
- Introduction: Mechanisms and MachinesДокумент5 страницIntroduction: Mechanisms and Machineschala nigussieОценок пока нет
- Louis Kauffman - From Knots To Quantum Groups (And Back)Документ26 страницLouis Kauffman - From Knots To Quantum Groups (And Back)Sprite090Оценок пока нет
- Kinematic MachinesДокумент18 страницKinematic MachinesGamini SureshОценок пока нет
- Kinematics of MechanicsДокумент34 страницыKinematics of MechanicsErasmo Israel Garcia Ochoa100% (1)
- Chapter One: Simple Link Compound LinkДокумент9 страницChapter One: Simple Link Compound Linkusman yimerОценок пока нет
- Unit 1Документ44 страницыUnit 1Prabal SinghОценок пока нет
- 3 - Chapter MechanicalДокумент18 страниц3 - Chapter MechanicalPrudhivi KumarОценок пока нет
- Forward Kinematics1Документ6 страницForward Kinematics1adireyОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2 Degrees of FreedomДокумент105 страницLecture 2 Degrees of FreedombourneОценок пока нет
- Determining Kinematic ChainsДокумент3 страницыDetermining Kinematic ChainsRanjit RajendranОценок пока нет
- 2nd Lec Theory of Machines2 - ShahДокумент29 страниц2nd Lec Theory of Machines2 - ShahHaroonОценок пока нет
- Constraints On Motion: Degrees Ot Freedom: Answers To Revl8lon ExerciseДокумент9 страницConstraints On Motion: Degrees Ot Freedom: Answers To Revl8lon ExerciseAnonymous LU3Dz3TKtVОценок пока нет
- Kinematics of MachineryДокумент64 страницыKinematics of MachineryStar SathishОценок пока нет
- Kom-Unit - IДокумент17 страницKom-Unit - IJagadeesh Babu VadapalliОценок пока нет
- Types of Constrained MotionДокумент3 страницыTypes of Constrained MotionTasnuva SharminОценок пока нет
- SSC-Theory of MachineДокумент75 страницSSC-Theory of MachineSteph Dela MujerОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ58 страницChapter 3ketemaОценок пока нет
- Yidun Wan - Effective Theory of Braid Excitations of Quantum Geometry in Terms of Feynman DiagramsДокумент23 страницыYidun Wan - Effective Theory of Braid Excitations of Quantum Geometry in Terms of Feynman DiagramsMopadDeluxeОценок пока нет
- Basic Concepts: Dedison Gasni, PH.DДокумент39 страницBasic Concepts: Dedison Gasni, PH.DAnggiaAnggrainiPutriОценок пока нет
- Aim: - To Study Various Types of Links, Pairs, Chain and Mechanism, Inversion of Mechanism For TheoryДокумент6 страницAim: - To Study Various Types of Links, Pairs, Chain and Mechanism, Inversion of Mechanism For TheoryAvinash RОценок пока нет
- MechanismsДокумент8 страницMechanismsJai BhavaniОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Physical Systems Modelling With Bond Graphs: Jan F. BroeninkДокумент31 страницаIntroduction To Physical Systems Modelling With Bond Graphs: Jan F. Broeninkusman_mani_7Оценок пока нет
- Chris - Knot TheoryДокумент20 страницChris - Knot Theoryremo remoОценок пока нет
- Mechanics of MachineДокумент31 страницаMechanics of MachineRanjit Rajendran100% (1)
- Denavit-Hartenberg Parameters - WikipediaДокумент19 страницDenavit-Hartenberg Parameters - Wikipediavikas16051998Оценок пока нет
- Kinematics of Machinery PDFДокумент40 страницKinematics of Machinery PDFkalirajgurusamy92% (26)
- Kinematics of Machinery Lecturer Notes All 5 UnitsДокумент45 страницKinematics of Machinery Lecturer Notes All 5 Unitskumaravel07Оценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes For Week One Kinematics of Mechanism 1Документ10 страницLecture Notes For Week One Kinematics of Mechanism 1John KimaniОценок пока нет
- Bond Graphs V2Документ31 страницаBond Graphs V2jorge_naranjo_4Оценок пока нет
- Fortescue1918 1 50Документ50 страницFortescue1918 1 50CARLOS ALBERTO GOMEZ REYESОценок пока нет
- The Royal SocietyДокумент18 страницThe Royal Society2ymmgОценок пока нет
- Kinematics of MachinesДокумент227 страницKinematics of Machinesdpksobs100% (4)
- Theory of Machines, MT 215: Kinematic FundamentalsДокумент29 страницTheory of Machines, MT 215: Kinematic FundamentalsmanecoОценок пока нет
- Shmuel Lifsches and Saharon Shelah - Random Graphs in The Monadic Theory of OrderДокумент37 страницShmuel Lifsches and Saharon Shelah - Random Graphs in The Monadic Theory of OrderJgfm2Оценок пока нет
- Knots - Richard HepworthДокумент59 страницKnots - Richard HepworthhGanieetОценок пока нет
- Squential Binding ModelsДокумент4 страницыSquential Binding ModelsAnil Choubey100% (1)
- Cartesian Tensor AnalysisДокумент10 страницCartesian Tensor AnalysissquirreldnaОценок пока нет
- Machine Dynamics - I Lecture Note: (Assist. Prof. Mechanical Engineering Department, VSSUT, Burla, Orissa, India)Документ70 страницMachine Dynamics - I Lecture Note: (Assist. Prof. Mechanical Engineering Department, VSSUT, Burla, Orissa, India)phb1986Оценок пока нет
- Group Theory TheoryДокумент1 страницаGroup Theory Theorygo9uОценок пока нет
- Sundance Bilson-Thompson, Jonathan Hackett and Louis H. Kau Man - Particle Topology, Braids and Braided BeltsДокумент21 страницаSundance Bilson-Thompson, Jonathan Hackett and Louis H. Kau Man - Particle Topology, Braids and Braided BeltsMopadDeluxeОценок пока нет
- Mechanisms and Machine Theory - Unit 0 and Unit 1Документ28 страницMechanisms and Machine Theory - Unit 0 and Unit 1Sangamesh ShettarОценок пока нет
- Kinematics of MachinesДокумент227 страницKinematics of MachinesstelandreouОценок пока нет
- Kinematics of Machines ExplainedДокумент227 страницKinematics of Machines Explainedborchec100% (2)
- Introduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11От EverandIntroduction to Non-Linear Mechanics. (AM-11), Volume 11Оценок пока нет
- Semi-Simple Lie Algebras and Their RepresentationsОт EverandSemi-Simple Lie Algebras and Their RepresentationsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Theory of Elastisity, Stability and Dynamics of Structures Common ProblemsОт EverandTheory of Elastisity, Stability and Dynamics of Structures Common ProblemsОценок пока нет
- MMC Paper Materials and Design PDFДокумент7 страницMMC Paper Materials and Design PDFvelavansuОценок пока нет
- A Study On Mechanical and Machinability Characteristics of Hybrid Metal Matrix CompositeДокумент4 страницыA Study On Mechanical and Machinability Characteristics of Hybrid Metal Matrix CompositearundixituОценок пока нет
- Preparation of Hybrid Aluminium Metal Matrix Composites by Using Stir Process PDFДокумент9 страницPreparation of Hybrid Aluminium Metal Matrix Composites by Using Stir Process PDFvelavansuОценок пока нет
- A Study On Mechanical and Machinability Characteristics of Hybrid Metal Matrix CompositeДокумент4 страницыA Study On Mechanical and Machinability Characteristics of Hybrid Metal Matrix CompositearundixituОценок пока нет
- Paper 3Документ12 страницPaper 3velavansuОценок пока нет
- Wetting Agent For Boran Carbide - Al 6061 PDFДокумент13 страницWetting Agent For Boran Carbide - Al 6061 PDFvelavansuОценок пока нет
- 2Документ9 страниц2velavansuОценок пока нет
- PrefДокумент2 страницыPrefvelavansuОценок пока нет
- MT II Course Hand OutДокумент3 страницыMT II Course Hand OutvelavansuОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Constituents for Composites ManufacturingДокумент2 страницыFundamentals of Constituents for Composites ManufacturingvelavansuОценок пока нет
- Paper 7Документ14 страницPaper 7velavansuОценок пока нет
- Me2026 Ucmp Unit 1Документ32 страницыMe2026 Ucmp Unit 1velavansuОценок пока нет
- Index Terms LinksДокумент16 страницIndex Terms LinksvelavansuОценок пока нет
- Principles of The Manufacturing of Composite Materials: Suong V. HoaДокумент2 страницыPrinciples of The Manufacturing of Composite Materials: Suong V. HoavelavansuОценок пока нет
- About The Author: R Uong AN OAДокумент1 страницаAbout The Author: R Uong AN OAvelavansuОценок пока нет
- Directional Control ValvesДокумент15 страницDirectional Control ValveskuksiОценок пока нет
- Milling NotesДокумент16 страницMilling Notesvelavansu100% (1)
- Microsoft Word Ucm 2marks WordДокумент19 страницMicrosoft Word Ucm 2marks WordvelavansuОценок пока нет
- Mt1 Unit 5 NotesДокумент11 страницMt1 Unit 5 NotesvelavansuОценок пока нет
- ME 2201 MT 1 Short AnswersДокумент40 страницME 2201 MT 1 Short AnswersgurunathramОценок пока нет
- AHP 16 MarksДокумент4 страницыAHP 16 MarksvelavansuОценок пока нет
- Question Bank For Test 1 2013Документ5 страницQuestion Bank For Test 1 2013velavansuОценок пока нет
- Classification of Welding ProcessesДокумент25 страницClassification of Welding ProcessesvelavansuОценок пока нет
- MT Ii 2 Marks PDFДокумент19 страницMT Ii 2 Marks PDFParamasivam Veerappan100% (1)
- CylindersДокумент0 страницCylindersDhileepan KumarasamyОценок пока нет
- Entreship Notes 2013-2014Документ6 страницEntreship Notes 2013-2014velavansuОценок пока нет
- Mt1 Unit 4 NotesДокумент11 страницMt1 Unit 4 Notesvelavansu100% (1)
- Non Traditional Machines 1092Документ2 страницыNon Traditional Machines 1092velavansuОценок пока нет
- Mt1 Unit 1 NotesДокумент13 страницMt1 Unit 1 NotesvelavansuОценок пока нет
- Engineering Graphics June 2011Документ3 страницыEngineering Graphics June 2011velavansuОценок пока нет
- Rapid ECG Interpretation Skills ChallengeДокумент91 страницаRapid ECG Interpretation Skills ChallengeMiguel LizarragaОценок пока нет
- Ted Hughes's Crow - An Alternative Theological ParadigmДокумент16 страницTed Hughes's Crow - An Alternative Theological Paradigmsa46851Оценок пока нет
- JE Creation Using F0911MBFДокумент10 страницJE Creation Using F0911MBFShekar RoyalОценок пока нет
- Compliance Risks and Controls: Speaker: Dott. Fabio AccardiДокумент14 страницCompliance Risks and Controls: Speaker: Dott. Fabio AccardiJefferson WidodoОценок пока нет
- Supply Chain Management of VodafoneДокумент8 страницSupply Chain Management of VodafoneAnamika MisraОценок пока нет
- Aditi Pant Internship ReportДокумент14 страницAditi Pant Internship ReportDR.B.REVATHYОценок пока нет
- Uvas CaractДокумент10 страницUvas CaractgondeluОценок пока нет
- The Three Key Linkages: Improving The Connections Between Marketing and SalesДокумент5 страницThe Three Key Linkages: Improving The Connections Between Marketing and SalesRuxandra PopaОценок пока нет
- Electronic Throttle ControlДокумент67 страницElectronic Throttle Controlmkisa70100% (1)
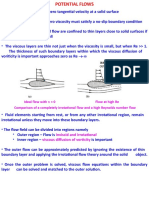
- An IDEAL FLOW Has A Non-Zero Tangential Velocity at A Solid SurfaceДокумент46 страницAn IDEAL FLOW Has A Non-Zero Tangential Velocity at A Solid SurfaceJayant SisodiaОценок пока нет
- DRUG LISTДокумент45 страницDRUG LISTAmitKumarОценок пока нет
- LinkedIn Learning - Workplace Learning Report 2021 EN 1Документ65 страницLinkedIn Learning - Workplace Learning Report 2021 EN 1Ronald FriasОценок пока нет
- Adjective: the girl is beautifulДокумент15 страницAdjective: the girl is beautifulIn'am TraboulsiОценок пока нет
- The Diffusion of Microfinance: An Extended Analysis & Replication ofДокумент33 страницыThe Diffusion of Microfinance: An Extended Analysis & Replication ofNaman GovilОценок пока нет
- Springhill Suites by Marriott / Houston Brookhollow Remit To:2750 N.Loop West, Houston TX 77092 713.290.9242Документ1 страницаSpringhill Suites by Marriott / Houston Brookhollow Remit To:2750 N.Loop West, Houston TX 77092 713.290.9242Josué SalazarОценок пока нет
- 1989 Volvo 740 Instruments and ControlsДокумент107 страниц1989 Volvo 740 Instruments and Controlsskyliner538Оценок пока нет
- Protección Fuego MetalДокумент16 страницProtección Fuego MetalTracy Mora ChОценок пока нет
- Lehman BrothersДокумент10 страницLehman BrothersJaikishin RuprajОценок пока нет
- ListДокумент4 страницыListgeralda pierrelusОценок пока нет
- 2016-08-03 Iot Global Forecast Analysis 2015-2025Документ65 страниц2016-08-03 Iot Global Forecast Analysis 2015-2025Hoang ThanhhОценок пока нет
- Valhalla Repair ManualДокумент8 страницValhalla Repair ManualKirby AllenОценок пока нет
- Gulfco 1049 MaxДокумент5 страницGulfco 1049 MaxOm Prakash RajОценок пока нет
- Method Statement Pressure TestingДокумент15 страницMethod Statement Pressure TestingAkmaldeen AhamedОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3-The Hospitality & Travel Marketing SystemДокумент14 страницChapter 3-The Hospitality & Travel Marketing SystemCharis AbadОценок пока нет
- Smartrac - Iolineug - r5Документ66 страницSmartrac - Iolineug - r5Darwin Elvis Giron HurtadoОценок пока нет
- aCTION PLAN IN HEALTHДокумент13 страницaCTION PLAN IN HEALTHCATHERINE FAJARDOОценок пока нет
- Entrepreneurial Intentions of Cavite Business StudentsДокумент12 страницEntrepreneurial Intentions of Cavite Business StudentsKevin Pereña GuinsisanaОценок пока нет
- Keb Combivis 6 enДокумент232 страницыKeb Combivis 6 enhaithamОценок пока нет
- Move Over G7, It's Time For A New and Improved G11: Long ShadowДокумент16 страницMove Over G7, It's Time For A New and Improved G11: Long ShadowVidhi SharmaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 20: Sleep Garzon Maaks: Burns' Pediatric Primary Care, 7th EditionДокумент4 страницыChapter 20: Sleep Garzon Maaks: Burns' Pediatric Primary Care, 7th EditionHelen UgochukwuОценок пока нет