Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Seia2e - 1003 10.3 Solving Equations Quadratic in Form
Загружено:
Thalia SandersОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Seia2e - 1003 10.3 Solving Equations Quadratic in Form
Загружено:
Thalia SandersАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter 10
Quadratic
Equations and
Functions
Section 3
Solving Equations
Quadratic in Form
Sullivan, III & Struve, Elementary and Intermediate Algebra 10.3 - 2 Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Section 10.3 Objectives
1 Solve Equations That Are Quadratic in Form
Sullivan, III & Struve, Elementary and Intermediate Algebra 10.3 - 3 Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Equations Quadratic in Form
If a substitution u transforms an equation into one of the form
au
2
+ bu + c = 0
then the original equation is called an equation quadratic in form.
Solving Equations Quadratic in Form
Step 1: Determine the appropriate substitution and write the
equation in the form au
2
+ bu + c = 0.
Step 2: Solve the equation au
2
+ bu + c = 0.
Step 3: Solve for the variable in the original equation using the
value of u found in Step 2.
Step 4: Check. Verify your solutions.
Sullivan, III & Struve, Elementary and Intermediate Algebra 10.3 - 4 Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Equations Quadratic in Form
Example: Solve: x
4
11x
2
+ 18 = 0
u
2
11u + 18 = 0 Replace x
4
with u
2
and x
2
with u.
(u 9)(u 2) = 0 Factor.
Set each equation equal to zero.
u = 9 Solve for u.
u 9 = 0 or u 2 = 0
u = 2
x
2
= 9 Replace u with x
2
. x
2
= 2
Solve for x. = 3 x
= 2 x
Continued.
Sullivan, III & Struve, Elementary and Intermediate Algebra 10.3 - 5 Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Equations Quadratic in Form
Example continued:
= 3 x
= 2 x
x
4
11x
2
+ 18 = 0 Check:
(3)
4
11(3)
2
+ 18 = 0
= 3 x
= 2 x
81 11(9) + 18 = 0
81 99 + 18 = 0
0 = 0
( 3)
4
11( 3)
2
+ 18 = 0
81 11(9) + 18 = 0
81 99 + 18 = 0
0 = 0
2
( )
4
11 2
( )
2
+18 = 0
4 11(2) +18 = 0
4 22 18 0 + =
0 0 =
2
( )
4
11 2
( )
2
+18 = 0
4 11(2) 18 0 + =
4 22 18 0 + =
0 0 =
Sullivan, III & Struve, Elementary and Intermediate Algebra 10.3 - 6 Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Equations Quadratic in Form
Example: Solve: 2x
1/2
x
1/4
1 = 0
2u
2
u 1 = 0 Replace x
1/2
with u
2
and x
1/4
with u.
(2u + 1)(u 1) = 0 Factor.
Set each equation equal to zero.
Solve for u.
2u + 1 = 0 or u 1 = 0
Replace u with x
1/4
.
Solve for x.
1
=
2
u =1 u
1/4
1
=
2
x
1/4
=1 x
x
1/ 4
( )
4
=
1
2
|
\
|
.
|
4
x
1/ 4
( )
4
=1
4
1
=
16
x =1 x
Continued.
Sullivan, III & Struve, Elementary and Intermediate Algebra 10.3 - 7 Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Equations Quadratic in Form
Example continued:
1
=
16
x =1 x
Check:
1/2 1/4
2 1= 0 x x
2
1
16
|
\
|
.
|
1/ 2
1
16
|
\
|
.
|
1/ 4
1= 0
2
1
4
|
\
|
.
|
1
2
1= 0
1 1
1 = 0
2 2
1 0 =
1/2 1/4
2 1= 0 x x
( ) ( )
1/2 1/4
1 2 = 1 1 0
( )
2 1 1 1 = 0
0 = 0
The solution set is {1}.
2 1 1= 0
is an
extraneous root.
1
=
16
x
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Statistical Formulas (Business Stats)Документ4 страницыStatistical Formulas (Business Stats)Peter BentОценок пока нет
- 1.2 Matrices Notes PresentationДокумент5 страниц1.2 Matrices Notes PresentationArif ZainОценок пока нет
- Jackson Cert Opp Brief WesternSkyFinancial v. D.jacksonДокумент42 страницыJackson Cert Opp Brief WesternSkyFinancial v. D.jacksonThalia SandersОценок пока нет
- James Et Al v. Freder Cty Pub Sch. 441 F.supp.2d 755Документ8 страницJames Et Al v. Freder Cty Pub Sch. 441 F.supp.2d 755Thalia SandersОценок пока нет
- 1-Complaint6 Ceridian HCM Vs Chumash IndiansДокумент6 страниц1-Complaint6 Ceridian HCM Vs Chumash IndiansThalia SandersОценок пока нет
- Jackson Cert Opp Brief WesternSkyFinancial v. D.jacksonДокумент42 страницыJackson Cert Opp Brief WesternSkyFinancial v. D.jacksonThalia SandersОценок пока нет
- Goldberg v. Miller 371 Md. 591, 810 A.2d 947Документ15 страницGoldberg v. Miller 371 Md. 591, 810 A.2d 947Thalia SandersОценок пока нет
- Sta-Rite v. Peterson 876 So.2d 571Документ2 страницыSta-Rite v. Peterson 876 So.2d 571Thalia SandersОценок пока нет
- Mapp v. Ohio 367 U.S. 643, 81 S.Ct. 1684Документ26 страницMapp v. Ohio 367 U.S. 643, 81 S.Ct. 1684Thalia SandersОценок пока нет
- Western Sky Cert Stage ReplyДокумент22 страницыWestern Sky Cert Stage ReplyThalia SandersОценок пока нет
- Gideon v. Wainwwright 372 U.S. 335, 83 S.ct. 792Документ10 страницGideon v. Wainwwright 372 U.S. 335, 83 S.ct. 792Thalia SandersОценок пока нет
- Rafferty v. PGC 423 F.supp. 1045Документ21 страницаRafferty v. PGC 423 F.supp. 1045Thalia SandersОценок пока нет
- Washington v. Texas 388 U.S. 14-87 S.ct. 1920Документ8 страницWashington v. Texas 388 U.S. 14-87 S.ct. 1920Thalia SandersОценок пока нет
- Marvin Vs Marvin 18cal.3d660Документ19 страницMarvin Vs Marvin 18cal.3d660Thalia SandersОценок пока нет
- Edward v. SouthcarolinaДокумент11 страницEdward v. SouthcarolinaThalia SandersОценок пока нет
- Bell at Corp v. Twombly 550 U.S. 544, 127 S.ct. 1955Документ36 страницBell at Corp v. Twombly 550 U.S. 544, 127 S.ct. 1955Thalia SandersОценок пока нет
- Ibarra v. US 120 F.3d 472Документ6 страницIbarra v. US 120 F.3d 472Thalia SandersОценок пока нет
- Goldberg v. Miller 371 Md. 591, 810 A.2d 947Документ15 страницGoldberg v. Miller 371 Md. 591, 810 A.2d 947Thalia SandersОценок пока нет
- LaShawn A. v. Gray Progress Report November 21 2011Документ199 страницLaShawn A. v. Gray Progress Report November 21 2011Thalia SandersОценок пока нет
- Ashcroft v. Iqubal 129 S.ct. 1937Документ25 страницAshcroft v. Iqubal 129 S.ct. 1937Thalia SandersОценок пока нет
- Wiwa v. Royal Dutch Petroleum Co., DistДокумент16 страницWiwa v. Royal Dutch Petroleum Co., DistThalia SandersОценок пока нет
- 1989-6-20 DC Lashawn ComplaintДокумент48 страниц1989-6-20 DC Lashawn ComplaintThalia SandersОценок пока нет
- New York Life Ins. Co. v. Brown, 84 F .3d 137 141Документ18 страницNew York Life Ins. Co. v. Brown, 84 F .3d 137 141Thalia SandersОценок пока нет
- Plaintiffs ResponsetoMotiontoIntervene11 VannДокумент14 страницPlaintiffs ResponsetoMotiontoIntervene11 VannThalia SandersОценок пока нет
- Palsgraf v. Long Island Railroad 222 App. Div. 166Документ4 страницыPalsgraf v. Long Island Railroad 222 App. Div. 166Thalia SandersОценок пока нет
- Wiwa v. Royal Dutch Petroleum Co., 626 F. Supp. 2d 377 - DistДокумент9 страницWiwa v. Royal Dutch Petroleum Co., 626 F. Supp. 2d 377 - DistThalia SandersОценок пока нет
- Mar 24 2014Документ9 страницMar 24 2014Thalia SandersОценок пока нет
- African Island NationsДокумент5 страницAfrican Island NationsThalia SandersОценок пока нет
- Mar 25 2014 Int'l Bus Mngmt.Документ7 страницMar 25 2014 Int'l Bus Mngmt.Thalia SandersОценок пока нет
- Coolidge v. New Hampshire - 403 U.S. 443 (1971)Документ49 страницCoolidge v. New Hampshire - 403 U.S. 443 (1971)Thalia SandersОценок пока нет
- Mar 26 2014 Int' Bus MGMTДокумент8 страницMar 26 2014 Int' Bus MGMTThalia SandersОценок пока нет
- Washington Post EXPRESS - 12032010Документ40 страницWashington Post EXPRESS - 12032010Thalia SandersОценок пока нет
- Non-Potential Forces LagrangianДокумент9 страницNon-Potential Forces LagrangianumerilyasОценок пока нет
- Math Chapter 7 & 8 Review Worksheet SolutionsДокумент2 страницыMath Chapter 7 & 8 Review Worksheet SolutionsSkyezine Via Kit FoxОценок пока нет
- SLC - OPT Math - FunctionsДокумент0 страницSLC - OPT Math - Functionswww.bhawesh.com.np100% (1)
- DifferentiAbility of Several VariablesДокумент11 страницDifferentiAbility of Several VariablesnitishkhebbarОценок пока нет
- Additional Mathematics SPM 2008 - : ProgressionsДокумент7 страницAdditional Mathematics SPM 2008 - : ProgressionsVivianne YongОценок пока нет
- RVS NUMERICAL METHODS LESSON PLAN FOR ENGINEERINGДокумент3 страницыRVS NUMERICAL METHODS LESSON PLAN FOR ENGINEERINGSaravanan AtthiappanОценок пока нет
- Ps 1 SolutionsДокумент4 страницыPs 1 SolutionsAdip ChyОценок пока нет
- Slides 05 03 Derivations AnnotatedДокумент22 страницыSlides 05 03 Derivations AnnotatedVa Ru NОценок пока нет
- Model Question Paper: SP 206 Wavelet Transforms: Theory and ApplicationsДокумент2 страницыModel Question Paper: SP 206 Wavelet Transforms: Theory and Applicationssafu_117100% (1)
- Mathematical Methods in EngineeringДокумент2 страницыMathematical Methods in EngineeringJagermeistОценок пока нет
- SMK Seri Kampar (Question)Документ2 страницыSMK Seri Kampar (Question)chimlaiyernОценок пока нет
- Example of Gaussian EliminationДокумент4 страницыExample of Gaussian Eliminationloserboi101Оценок пока нет
- Basic Numeracy SimplificationДокумент6 страницBasic Numeracy SimplificationIAS EXAM PORTALОценок пока нет
- Statistical Measures of DataДокумент11 страницStatistical Measures of DataMary Roxanne AngelesОценок пока нет
- Half Rate Effects of SQIДокумент29 страницHalf Rate Effects of SQIRashed SobujОценок пока нет
- Earned Value - One Page SummaryДокумент1 страницаEarned Value - One Page Summarymy.nafi.pmp5283Оценок пока нет
- R7410301 Operations ResearchДокумент2 страницыR7410301 Operations ResearchsivabharathamurthyОценок пока нет
- Signals and Systems Model - 1Документ2 страницыSignals and Systems Model - 1sharanyameen2704Оценок пока нет
- Sakurai&Napolite CH 5 - 5.12 Solutions 18apr12Документ4 страницыSakurai&Napolite CH 5 - 5.12 Solutions 18apr12radwanhasan100% (1)
- Suggested Answer Scheme MAT 565/480 (Advanced Differential Equation) JANUARY 2012Документ4 страницыSuggested Answer Scheme MAT 565/480 (Advanced Differential Equation) JANUARY 2012Fakhrur RaziОценок пока нет
- MAT-203: Calculating the Leibniz Rule for IntegrationДокумент2 страницыMAT-203: Calculating the Leibniz Rule for IntegrationJavier ToledoОценок пока нет
- Assignment 7Документ2 страницыAssignment 7pathasreedharОценок пока нет
- Laplace Transform of Partial DerivativesДокумент6 страницLaplace Transform of Partial DerivativesShashi KanthОценок пока нет
- Simple VLOOKUP Examples: Learn More About VLOOKUP & Other Lookup Functions. Get My BookДокумент3 страницыSimple VLOOKUP Examples: Learn More About VLOOKUP & Other Lookup Functions. Get My BookMohammad KamruzzamanОценок пока нет
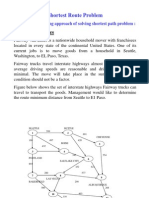
- Shortest Route ProblemДокумент7 страницShortest Route ProblemkaushalmightyОценок пока нет
- CS 2032 - Data Warehousing and Data Mining PDFДокумент3 страницыCS 2032 - Data Warehousing and Data Mining PDFvelkarthi92Оценок пока нет
- Convex Analysis and Optimization - SyllabusДокумент3 страницыConvex Analysis and Optimization - SyllabusCoursePinОценок пока нет