Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Teaching Listening and Speaking 2
Загружено:
Chim MiИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Teaching Listening and Speaking 2
Загружено:
Chim MiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
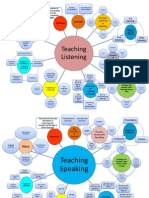
TEACHING LISTENING AND SPEAKING
Yza Cacayan Flora Michelle Hojas
The Teaching of Listening
Listening as Comprehension
Based
on the assumption that the main function of listening in second language learning is to facilitate understanding of spoken discourse
Listening as Acquisition
Considers
how listening can provide input that triggers the further development of secondlanguage proficiency.
Listening as comprehension Understanding spoken discourse:
Bottom-up processing Comprehension is viewed as the process of decoding
Input is scanned for familiar words Recognize the time reference of an utterance Distinguish between positive and negative statements Identify key words that occurred in a spoken text
Top-down processing Use of background knowledge in understanding the meaning of a message
Sample class activities:
Previous knowledge about the topic of discourse situational/contextual knowledge schemata or scripts
Sample activities: Students generate
A list of things they know about a topic Set of questions
Combining bottom-up and topdown listening in a lesson:
Pre-listening phase- activities involving
activating prior knowledge making predictions reviewing key vocabulary
While-listening phase- focuses on comprehension that require
Selective listening Gist listening Sequencing, etc. Involves a response to comprehension May require students to give opinions about a topic
Post-listening phase
Contains activities that link bottom-up and top-down processing
Listening Strategies
Cognitive Strategies
Comprehension
Metacognitive Strategies
Assessing
processes Storing and memory processes Using and retrieval processes
the
situation
Monitoring Self-evaluating Self-testing
Listening as Acquisition
Classroom Strategies
Noticing Involve
activities
returning the to the listening text that served as the basis for comprehension activities and using them as basis for language awareness
Restructuring Oral/written
activities
tasks that involve productive use of selected items from the listening text
The Teaching of Speaking
Nature of Spoken discourse
Conversational routines
Styles of speaking
Functions of speaking
Talk
as interaction Talk as transaction Talk as performance
Talk as interaction
Main Features
has a primarily social function Reflects role of relationships May be formal or casual
Teaching talk as interaction
Best taught by providing examples embedded in naturalistic dialogs Students are asked to
Skills involved
Opening and closing conversations Choosing topics Making small-talk Recounting personal incidents and experiences Reacting to others
Give feedback
Make follow-up questions
Talk as transaction
Main Features
Has a primarily information focus (message) frequent questions, repetitions, and comprehension checks
Teaching talk as transaction
Group activities Information-gap activities Role-plays Class activities include
Skills Involved
Explaining a need or intention Describing something Asking questions Asking for clarification
Ranking Values clarification Brainstorming
Talk as performance
Main Features
A focus on both message and audience Importance on both form and accuracy
Teaching talk as performance
Skills involved
Providing examples or models of speeches, oral presentations, stories, etc. through
Presenting information in an appropriate sequence Maintaining audience engagement Using correct pronunciation and grammar Using appropriate opening and closing
video, audio recordings written examples
Evaluating Performance on speaking activities:
Determine the expected level of performance on a speaking task Criteria that will be used to assess student performance
depends on which kind of talk we are talking about and the kind of classroom activity we are using
Reference: Jack C. Richards (Cambridge University
Вам также может понравиться
- Teaching Language Skills TeflДокумент54 страницыTeaching Language Skills TeflYuniie Siwonest100% (3)
- Teaching Listening SkillsДокумент19 страницTeaching Listening Skillsnaumanahmad867129Оценок пока нет
- Teaching Listening SkillsДокумент21 страницаTeaching Listening SkillsVansh RatheeОценок пока нет
- Receptive Skills PPPДокумент25 страницReceptive Skills PPPZakia SiddiquiОценок пока нет
- Teaching Oral Communication Skills PDFДокумент8 страницTeaching Oral Communication Skills PDFYsamar Sanchez100% (1)
- Speak English Fluently Using The 3000 Most Common Words in EnglishДокумент2 страницыSpeak English Fluently Using The 3000 Most Common Words in Englishcoxb45509Оценок пока нет
- Teaching Oral SkillsДокумент16 страницTeaching Oral SkillsRhea Mae Torres100% (1)
- Masterclass Memory KitG - P@FB PDFДокумент49 страницMasterclass Memory KitG - P@FB PDFRavi KumarОценок пока нет
- Instructional Strategies List July 2015Документ10 страницInstructional Strategies List July 2015faquinitoОценок пока нет
- Teaching MacroskillsДокумент15 страницTeaching MacroskillsFCI Isabela SHSОценок пока нет
- TEACHING LISTENING AND SPEAKING TECHNIQUESДокумент9 страницTEACHING LISTENING AND SPEAKING TECHNIQUESElfera Adriana100% (1)
- English Didactics IIДокумент34 страницыEnglish Didactics IICésar OR100% (2)
- Important Lesson Planning For The Teacher and The Learners: InteractiveДокумент19 страницImportant Lesson Planning For The Teacher and The Learners: InteractivejosephkondoОценок пока нет
- ArtikelДокумент14 страницArtikellindaОценок пока нет
- Teaching Listening SkillsДокумент21 страницаTeaching Listening SkillsManal EzzОценок пока нет
- Linguaskill Agent Detail TRFДокумент2 страницыLinguaskill Agent Detail TRFBrunna FrançaОценок пока нет
- Goals and Techniques for Teaching ListeningДокумент23 страницыGoals and Techniques for Teaching ListeningArmen Neziri100% (1)
- Fifty Ways to Teach Reading: Fifty Ways to Teach: Tips for ESL/EFL TeachersОт EverandFifty Ways to Teach Reading: Fifty Ways to Teach: Tips for ESL/EFL TeachersРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (3)
- Teaching Grammar in ContextДокумент18 страницTeaching Grammar in ContextJelena Bobkina100% (4)
- Using L1 in Teaching Vocabulary To Low English Proficiency LevelДокумент8 страницUsing L1 in Teaching Vocabulary To Low English Proficiency LevelVinícius DiasОценок пока нет
- Speakingsubskills LackmanДокумент28 страницSpeakingsubskills LackmanJV Toledo100% (1)
- Grammar BackgroundДокумент10 страницGrammar Backgroundpandreop100% (1)
- Teaching ListeningДокумент16 страницTeaching ListeningRotariu Mihaela-Luciana100% (2)
- Knud IllerisДокумент12 страницKnud IllerisAzelAnn MirandaОценок пока нет
- Assessing Listening Skills: Types and MethodsДокумент15 страницAssessing Listening Skills: Types and MethodsAisyah MusfirahОценок пока нет
- Develop pupils' listening and reading skillsДокумент7 страницDevelop pupils' listening and reading skillsMohd Zulkhairi AbdullahОценок пока нет
- Post ListeningДокумент17 страницPost ListeningNanthini SubramaniamОценок пока нет
- Teaching Language Listening SkillsДокумент13 страницTeaching Language Listening SkillsAmirhosein MazloumiОценок пока нет
- ListeningДокумент12 страницListeningMohammad HossainОценок пока нет
- Listening and SpeakingДокумент10 страницListening and SpeakingSherannie AbaloОценок пока нет
- Teaching Listening: There Are Two Cognitive Conversion Processes in CommunicationДокумент12 страницTeaching Listening: There Are Two Cognitive Conversion Processes in Communicationapple pieОценок пока нет
- Abilities ChartДокумент4 страницыAbilities Chartapi-224695265Оценок пока нет
- 1 How Are Receptive and Productive Skills Related?Документ2 страницы1 How Are Receptive and Productive Skills Related?LI JIAN XIОценок пока нет
- KTDG 2Документ11 страницKTDG 2Phương Thảo Trần NguyễnОценок пока нет
- Literacy Across Curriculum Teaches Key SkillsДокумент13 страницLiteracy Across Curriculum Teaches Key SkillsAdu Charles OseiОценок пока нет
- Lecture Guide in Teaching English in The Elementary Grades 1 2Документ13 страницLecture Guide in Teaching English in The Elementary Grades 1 2Jessica FranciscoОценок пока нет
- ELT Methodology: Teaching SpeakingДокумент34 страницыELT Methodology: Teaching Speakingkavya.noriОценок пока нет
- Teaching Listening SkillsДокумент20 страницTeaching Listening SkillsChristine Anne ClementeОценок пока нет
- International House-Jeddah Language CenterДокумент21 страницаInternational House-Jeddah Language CenterlallumonОценок пока нет
- Celta TerminologyДокумент6 страницCelta TerminologyWonder81Оценок пока нет
- Speaking HandoutДокумент5 страницSpeaking Handoutapi-183214315Оценок пока нет
- What Are Some Strategies To Assist in Reading Development?Документ9 страницWhat Are Some Strategies To Assist in Reading Development?Zandrine Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- Post - Listening ActivitiesДокумент3 страницыPost - Listening ActivitiesMohammad HossainОценок пока нет
- Listening and Speaking - Jack RichardsДокумент29 страницListening and Speaking - Jack RichardsRuby Agustin100% (1)
- Article Presentation by Carinne Karlick ESL 501Документ19 страницArticle Presentation by Carinne Karlick ESL 501raju19785186Оценок пока нет
- Strategies in Teaching ListeningДокумент23 страницыStrategies in Teaching ListeningZiazel AsiloОценок пока нет
- Speaking Activities W4Документ2 страницыSpeaking Activities W4Farah SyahirahОценок пока нет
- DR Mary Drossou Rcel Research Associate and Coordinator of The "Tefl Practicum" and The "Practice Teaching in Tefl"Документ54 страницыDR Mary Drossou Rcel Research Associate and Coordinator of The "Tefl Practicum" and The "Practice Teaching in Tefl"Isabel SalazarОценок пока нет
- Lecture 8. Teaching ListeningДокумент6 страницLecture 8. Teaching ListeningАйсулу БахытжолОценок пока нет
- Purposes of Teaching Listening and Speaking SkillsДокумент1 страницаPurposes of Teaching Listening and Speaking SkillsAlvin Isaac ChanОценок пока нет
- 61 113 PDFДокумент3 страницы61 113 PDFSharifah Al-JamalullailОценок пока нет
- Glossary 2Документ5 страницGlossary 2DajanaОценок пока нет
- Why I Get Students To Do PresentationsДокумент3 страницыWhy I Get Students To Do PresentationsRaghd EsamОценок пока нет
- What Is Listening Skill?Документ5 страницWhat Is Listening Skill?Elsa VargasОценок пока нет
- Teaching Listening MaterialДокумент5 страницTeaching Listening MaterialRizky CoyОценок пока нет
- Speaking Skill AinaДокумент1 страницаSpeaking Skill AinaNur Atikah IbrahimОценок пока нет
- Motivation - Listening and SpeakingДокумент12 страницMotivation - Listening and SpeakingDAni's SMileОценок пока нет
- SSW 10Документ3 страницыSSW 10Ayana BadyrovaОценок пока нет
- Teaching ListeningДокумент18 страницTeaching ListeningBarbara KerstensОценок пока нет
- Lweb 311 ReviewerДокумент20 страницLweb 311 ReviewerCaitlin DCОценок пока нет
- Strategies in Teaching Listening 1 3Документ53 страницыStrategies in Teaching Listening 1 3Lucas XiiОценок пока нет
- At The Beginning Stages of Language Study, Listening ThatДокумент14 страницAt The Beginning Stages of Language Study, Listening ThatJanine BenoliraoОценок пока нет
- Teaching SkillsДокумент21 страницаTeaching SkillsAMIR HAMIDОценок пока нет
- TESOLДокумент25 страницTESOLshahzadОценок пока нет
- The Language Skills-I 5659Документ25 страницThe Language Skills-I 5659mubarak201160% (5)
- Developing Macro Skills in Acompetence Based CurriculumДокумент47 страницDeveloping Macro Skills in Acompetence Based CurriculumSantiago Jr KadusaleОценок пока нет
- Unit1. English Language ArtsДокумент22 страницыUnit1. English Language ArtsBrenda MishimaОценок пока нет
- Unit Plan 8voДокумент15 страницUnit Plan 8voJulio LeonОценок пока нет
- 2015 Principal Test Application FormДокумент1 страница2015 Principal Test Application FormChim MiОценок пока нет
- Telling Time by The HourДокумент1 страницаTelling Time by The HourChim MiОценок пока нет
- Countable and Uncountable NounsДокумент1 страницаCountable and Uncountable NounsChim MiОценок пока нет
- Countable and Uncountable NounsДокумент1 страницаCountable and Uncountable NounsChim MiОценок пока нет
- Some Fundamental Problems in The Study of TransferДокумент54 страницыSome Fundamental Problems in The Study of TransferTu NguyenОценок пока нет
- Grammar in Discrimination, ImitationДокумент14 страницGrammar in Discrimination, ImitationJames Gildardo CuasmayànОценок пока нет
- Language Curriculum Design - (2. Environment Analysis)Документ2 страницыLanguage Curriculum Design - (2. Environment Analysis)Sumbal ChohanОценок пока нет
- This Material Is For Students' After-Class Use. If You're Using, Please Go To: Cloud Disk Authorized ResourcesДокумент25 страницThis Material Is For Students' After-Class Use. If You're Using, Please Go To: Cloud Disk Authorized Resourcesgrace roma khanОценок пока нет
- Tesol Module 1Документ13 страницTesol Module 1Ayesha AR100% (1)
- The Syllabus Design of English For SecretaryДокумент0 страницThe Syllabus Design of English For SecretaryDhiptya RatriОценок пока нет
- Universal Grammar and Second Language LearningДокумент6 страницUniversal Grammar and Second Language LearningMuhammad HoldhonОценок пока нет
- Bicks' Overall ReportДокумент38 страницBicks' Overall Reportuttam khatriОценок пока нет
- DiffusionismДокумент26 страницDiffusionismRusty LantacaОценок пока нет
- HBET1303Документ216 страницHBET1303Tce ShikinОценок пока нет
- Key Concepts of Language Education in Light of Sociocultural TheoryДокумент19 страницKey Concepts of Language Education in Light of Sociocultural TheoryAdi NovskyОценок пока нет
- ECCE 2013 Sample Test KeyДокумент1 страницаECCE 2013 Sample Test KeyÁngela RomeroОценок пока нет
- My Elt Exercises Unit 1 To Unit 12Документ24 страницыMy Elt Exercises Unit 1 To Unit 12vargastamudiojuanjose758Оценок пока нет
- Theories in SLA (MCQS) - PDF - Second Language Acquisition - Second LanguageДокумент52 страницыTheories in SLA (MCQS) - PDF - Second Language Acquisition - Second LanguageMahdОценок пока нет
- 1 The Antecedents of Language DevelopmentДокумент43 страницы1 The Antecedents of Language DevelopmentLara100% (2)
- AEF2e - Correlations To Standards and TestsДокумент1 страницаAEF2e - Correlations To Standards and Testsanaceci100% (1)
- The Nature of Listening SkillsДокумент12 страницThe Nature of Listening SkillsIlham IsmailОценок пока нет
- Virtual Orientation and Demonstration On Early Grade Assessment (EGRA) Administration and PHIL-IRI English AssessmentДокумент64 страницыVirtual Orientation and Demonstration On Early Grade Assessment (EGRA) Administration and PHIL-IRI English Assessmentmaricelle sazonОценок пока нет
- Miller - Language Use, Identity, and Social Interaction - Migrant Students in AustraliaДокумент33 страницыMiller - Language Use, Identity, and Social Interaction - Migrant Students in Australiatwa900Оценок пока нет
- Stoppard's plays demonstrate corpus linguistics approach to language learningДокумент22 страницыStoppard's plays demonstrate corpus linguistics approach to language learningRobert H. RempeОценок пока нет